safety valve relief valve Safety Certifications
Safety and relief valves are critical components in various industrial systems, designed to prevent overpressure conditions and ensure operational safety. These valves are subject to stringent safety certifications to ensure their reliability and effectiveness.
1. ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers): The ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) Section I and VIII establishes the requirements for the design, manufacture, testing, and certification of safety valves and relief valves. The “UV” stamp under Section VIII certifies pressure relief valves used in unfired pressure vessels, while the “V” stamp under Section I is for valves used in power boilers.
2. API (American Petroleum Institute): API Standard 526 details the requirements for flanged steel pressure relief valves, and API 527 outlines the seat tightness of pressure relief valves. These standards ensure valves used in petrochemical and refinery applications meet industry requirements.
3. PED (Pressure Equipment Directive): The PED (2014/68/EU) is a European directive that applies to the design and manufacture of pressure equipment. Safety valves sold within the European Economic Area (EEA) must comply with this directive to ensure they can withstand the specified pressure and temperature ranges.
4. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO 4126 is the international standard for safety devices for protection against excessive pressure. It covers various types of safety devices, including safety valves, and establishes guidelines for their design, testing, and certification.
5. National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors: The National Board certifies organizations that manufacture, assemble, and repair safety valves. The “NB” mark signifies compliance with established safety standards and ensures uniformity in safety valve performance.
Adhering to these certifications guarantees that safety and relief valves function correctly, avoiding catastrophic failures and ensuring the continued safe operation of industrial systems. Compliance with these standards also facilitates global acceptance and interoperability of safety and relief valves in various applications.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “safety valve relief valve”
Certainly! Here are the key technical parameters to consider for safety relief valves:
1. Set Pressure (PS): The pressure at which the valve opens to relieve excess pressure.
2. Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP): The peak internal pressure that the system can safely tolerate.
3. Relief Capacity: The volume of fluid or gas the valve can discharge over a specified period, typically measured in lbs/hr, SCFM, or Nm³/hr.
4. Blowdown/Reseat Pressure: The pressure point where the valve will close after having opened, usually a percentage below the set pressure.
5. Operating Temperature Range: The temperature limits within which the valve performs reliably, essential for material compatibility and function.
6. Orifice Area: The effective opening size through which the media flows during relief, impacting flow capacity.
7. Back Pressure: The pressure in the discharge line at the valve outlet, affecting valve performance and set pressure.
8. Overpressure: The safety factor above set pressure, often a percentage, ensuring the valve can handle transient spikes.
9. Material Specifications: Construction materials for the body, internals, and seals, crucial for compatibility with the media and environmental conditions.
10. Pressure/Temperature Ratings: Compliance with standards such as ASME, API, or ISO, defining limits for safe operation.
11. Response Time: How quickly the valve reacts to overpressure, critical for fast-acting systems or highly hazardous materials.
12. Lift: The extent to which the valve opens, which affects flow capacity and pressure drop across the valve.
13. Vibration and Shock Resistance: Ability of the valve to maintain integrity and performance under mechanical stress.
14. Connections: Types and sizes of inlet and outlet connections, crucial for system integration and flow dynamics.
15. Certification and Compliance: Adherence to regulatory standards and certifications like PED, CE, or ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
These parameters ensure the safety relief valve performs optimally under varying operating conditions while minimizing risks.
List Product features of “safety valve relief valve”
Sure! Below are the key product features of a safety valve relief valve:
1. Pressure Regulation: Automatically releases pressure to prevent system overpressure conditions.
2. Set Pressure Accuracy: Precisely calibrated to open at a predetermined pressure level to ensure system safety.
3. High Flow Capacity: Capable of handling high flow rates to quickly relieve excess pressure.
4. Material Durability: Constructed from robust materials such as stainless steel, brass, or bronze, ensuring long-lasting performance.
5. Temperature Range: Designed to operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures, suitable for various industrial applications.
6. Overpressure Protection: Provides essential protection for equipment, pipelines, and pressure vessels by preventing overpressure incidents.
7. Leak Tightness: Engineered to ensure leak-free performance under normal operating conditions.
8. Low Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance, with easy inspection and servicing features.
9. Adjustable Set Pressure: Some models offer adjustable set pressure ranges for versatility and adaptability to different system requirements.
10. Certification and Standards Compliance: Manufactured in compliance with international safety and quality standards like ASME, API, and ISO.
11. Fast Response Time: Quick reaction to overpressure conditions, offering immediate relief to protect system integrity.
12. Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to corrosion, extending the valve’s lifespan in harsh environments.
13. Installation Flexibility: Available in various mounting options and sizes to fit diverse installation needs.
14. Noise Reduction: Some designs incorporate features to minimize operational noise during pressure relief.
15. Back Pressure Tolerance: Capable of performing reliably even under varying back pressure conditions.
16. Safety Shutoff Mechanism: Some models include a safety shutoff feature to completely halt flow if necessary.
17. Visual Indicators: Optional visual indicators to show valve status, ensuring easier monitoring and maintenance.
These features collectively ensure that a safety valve relief valve provides reliable, efficient, and safe pressure management in various applications.
List Various Types of “safety valve relief valve”
Certainly! Safety valves and relief valves are crucial components in many industrial systems to ensure safety by preventing overpressure conditions. Here’s an overview of various types of these valves:
1. Spring-Loaded Safety Valves:
– Direct Acting Safety Valves: Utilize a spring to apply force. The valve opens when the internal pressure exceeds the spring force.
– Balanced Bellows Safety Valves: Incorporate a bellows to counteract the backpressure and provide more accurate performance.
2. Pilot-Operated Relief Valves:
– These use a smaller pilot valve to control a larger main valve. They are suitable for applications requiring precise control over set pressure.
3. Thermal Relief Valves:
– Designed to release pressure caused by temperature increases. Often used in liquid systems where thermal expansion can lead to overpressure.
4. Conventional Relief Valves:
– Simply use a spring and seat design, suitable for lower backpressure conditions.
5. Balanced Relief Valves:
– Tailored to handle higher backpressure by balancing the pressure on both sides of the valve, minimizing the effect on set pressure.
6. Safety Relief Valves:
– Combination of safety and relief valve characteristics. Can be used in both liquid and gas systems.
7. Vacuum Relief Valves:
– Protect systems from excessively low pressure by allowing air to enter the system when a vacuum condition occurs.
8. Power-Actuated Safety Relief Valves:
– Operated externally via pneumatic, hydraulic, or electrical activation. Useful for remote or automated control.
9. Low-Pressure Safety Valves:
– Designed to protect systems operating at relatively low pressures, such as storage tanks or large vessels.
10. High-Set Pressure Valves:
– Engineered for applications involving very high pressure, often seen in specialized industrial processes.
Each type of safety or relief valve is engineered to meet specific operational requirements in terms of pressure, temperature, and application environment. Selecting the appropriate valve type is essential to ensure the safety and efficiency of the system.
List Application of “safety valve relief valve”
Safety valves and relief valves are critical components in various industrial and commercial applications to prevent over-pressurization and ensure safe operation. Here are some key applications:
1. Boilers and Pressure Vessels: Safety valves prevent over-pressurization in boilers, ensuring the safe release of excess steam or gas to avoid explosions.
2. Chemical and Petrochemical Plants: They protect reactors, storage tanks, and pipelines from excessive pressure that could lead to hazardous situations, leaks, or ruptures.
3. Oil and Gas Industry: Relief valves are used in upstream, midstream, and downstream processes to safeguard against pressure spikes in pipelines and processing equipment.
4. Power Generation: In thermal, nuclear, and renewable energy plants, safety valves ensure the protection of turbines, condensers, and other critical equipment from overpressure conditions.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry: Valves help maintain pressure within reactors and storage vessels, ensuring safe production and storage of pharmaceuticals.
6. Food and Beverage Industry: Safety valves are critical in maintaining safe pressures in cooking, fermentation, and pasteurization processes.
7. Cryogenic Applications: Relief valves are essential in equipment handling liquefied gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and LNG, preventing overpressure conditions due to rapid thermal changes.
8. Compressed Air Systems: In industrial and commercial applications, they ensure the safe operation of compressors by preventing excessive build-up of air pressure.
9. HVAC Systems: Relief valves ensure safety and efficiency in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems by regulating high-pressure conditions.
10. Fire Protection Systems: In fire sprinkler and suppression systems, safety valves release excess pressure, ensuring system integrity and operation during emergencies.
11. Marine Industry: They protect shipboard systems, including boilers and engines, from pressure-induced hazards.
In all these applications, safety and relief valves are designed to automatically release substances (liquid or gas) when the system pressure exceeds a preset limit, thus maintaining operational integrity and ensuring safety.
List Buyer Types of “safety valve relief valve”
Certainly! Buyers of safety valves and relief valves span various industries and applications. Here are the primary types:
1. Industrial Manufacturers: Companies involved in manufacturing processes often require safety and relief valves to ensure the safe operation of equipment such as boilers, pressure vessels, and pipelines. These buyers prioritize reliability and compliance with industrial standards.
2. Oil and Gas Sector: This industry needs robust safety valves due to the high pressures and hazardous materials involved in drilling, refining, and transporting oil and gas. Safety is paramount, and these buyers look for valves that can withstand extreme conditions.
3. Chemical Plants: Safety valves are critical in chemical manufacturing to prevent overpressure scenarios that can lead to dangerous releases of chemicals. Buyers in this sector seek highly durable and corrosion-resistant valves.
4. Power Generation Facilities: Power plants, including nuclear, coal, and natural gas facilities, utilize safety valves to protect turbines, boilers, and other critical infrastructure. Reliability and precision are crucial for these buyers.
5. Water Treatment Facilities: These facilities use safety valves in various applications, including maintaining proper pressures in filtration and distribution systems. Buyers here focus on durability and resistance to water and chemicals.
6. Pharmaceutical Manufacturers: In this sector, safety valves are essential for maintaining precise pressure controls in production equipment. Buyers often need valves that are compliant with stringent hygiene standards.
7. Food and Beverage Industry: This industry requires safety valves for processing equipment to ensure safe operation and avoid contamination. Buyers need valves made from food-grade materials.
8. Aerospace and Defense: These sectors use safety valves in equipment and vehicles that encounter high pressures and extreme conditions. Valves must meet rigorous standards for reliability and performance.
9. HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems use safety valves to ensure safe operation. Buyers typically look for valves that are reliable and easy to maintain.
10. Marine Industry: Ships and offshore platforms use safety valves for controlling pressures in various systems. These buyers need valves that can resist corrosion and endure harsh marine environments.
In summary, buyers of safety valves and relief valves are found across industries where pressure control and safety are critical. Their specific requirements may vary, but reliability, durability, and compliance with industry standards are universally important.
List “safety valve relief valve” Project Types for Different Industries
Safety valves and relief valves are crucial components across various industries to ensure system safety and prevent overpressure conditions. Here are the main project types for different industries:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Pipeline Systems: Safety valves in pipelines prevent overpressure due to blockages or pump failure.
– Refineries: Relief valves protect against overpressure during distillation, cracking, and reforming processes.
– Offshore Platforms: Specialized valves protect against harsh marine conditions and pressure surges.
2. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry:
– Chemical Reactors: Relief valves mitigate risks of pressure buildup due to uncontrolled reactions.
– Storage Tanks: Safety valves protect tanks from overpressure during filling or temperature changes.
– Process Equipment: Valves safeguard heat exchangers, compressors, and other equipment against pressure surges.
3. Power Generation Industry:
– Boilers: Safety valves are essential to avoid overpressure in steam boilers.
– Turbines: Relief valves protect steam and gas turbines from overpressure.
– Nuclear Plants: Specialized safety valves are critical to prevent reactor vessel overpressure.
4. Water Treatment and Distribution:
– Municipal Water Systems: Relief valves prevent pipelines and storage tanks from overpressure.
– Desalination Plants: Safety valves are used in high-pressure reverse osmosis systems.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry:
– Bioreactors: Relief valves prevent overpressure during fermentation and other bioprocesses.
– Storage and Transport: Safety valves protect pressurized storage containers and transport vessels.
6. Aerospace and Defense:
– Aircraft Systems: Relief valves are crucial in aircraft hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
– Rocket Propulsion: High-performance relief valves manage pressure in propulsion systems.
7. Manufacturing Industry:
– HVAC Systems: Safety valves ensure safe operation in industrial heating and cooling systems.
– Hydraulic Systems: Relief valves prevent overpressure in hydraulic machinery and equipment.
8. Food and Beverage Industry:
– Production Lines: Safety valves are used in pasteurization, fermentation, and bottling processes.
– Storage Vessels: Relief valves protect against pressure changes in storage tanks for liquids and gases.
Each industry requires specific types of safety and relief valves designed to handle unique environmental conditions, pressure ranges, and regulatory standards.
safety valve relief valve Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Safety valves and relief valves are crucial components in various industrial systems, ensuring the safe operation of pressure vessels and pipelines by preventing overpressure conditions. Accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options enhance the functionality, reliability, and lifespan of these valves.
Accessories:
1. Test Gags: Used to temporarily prevent the valve from opening during system tests.
2. Lifting Levers: Allow manual operation of the valve to ensure it is functioning correctly.
3. Silencers: Minimize noise during valve discharge.
4. Pressure Gauges: Indicate real-time pressure levels.
5. Heating Jackets: Prevent freezing in cold environments.
6. Discharge Piping: Safely directs the released medium away from personnel and equipment.
Upgrades:
1. Material Enhancements: Upgrading to corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel for longer lifespan.
2. Seal Improvements: Enhanced sealing materials such as PTFE for better performance in extreme temperatures and pressures.
3. Spring Upgrades: Higher-grade springs for more accurate pressure control.
4. Advanced Coatings: Protective coatings to resist wear and tear, especially in harsh environments.
5. Digital Monitoring: Integration with digital control systems for real-time monitoring and remote operation.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Size Customization: Valves can be manufactured to specific sizes to fit unique system requirements.
2. Special Pressure Ratings: Custom pressure ratings to accommodate specific industrial needs.
3. Unique Configurations: Tailored designs for specialized applications, including unique inlet and outlet sizes.
4. Industry-Specific Standards: Compliance with industry standards like ASME, API, or ISO for safety and quality assurance.
5. Localized Manufacturing: Custom valves produced to meet regional standards and requirements, ensuring local compliances are met.
By leveraging these accessories, upgrades, and customization options, industries can significantly enhance the performance, safety, and longevity of their safety and relief valves, ensuring seamless and safe operations.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “safety valve relief valve”
Quality Control for Safety Relief Valves
1. Material Inspection:
– Ensure materials meet specifications.
– Perform traceability checks and material certificates verification.
2. Dimensional Verification:
– Utilize precise measuring tools to confirm dimensions.
– Ensure adherence to design tolerances.
3. Mechanical Testing:
– Conduct tensile, impact, and hardness tests.
– Validate material strength and durability.
4. Pressure Testing:
– Hydrostatic and pneumatic tests to ensure leak-proof seals.
– Verify valve performance under pressure.
5. Functional Testing:
– Inspect opening and closing pressures.
– Confirm consistent and reliable operation.
6. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
– Use radiography, ultrasonic, or dye penetrant tests.
– Identify internal and external flaws.
7. Documentation and Certification:
– Maintain detailed quality control records.
– Provide certificates of compliance and test reports.
Manufacturing Process for Safety Relief Valves
1. Design and Engineering:
– Develop detailed valve designs using CAD software.
– Conduct simulations and stress analysis.
2. Material Procurement:
– Source high-quality metals and components.
– Ensure compliance with standards (e.g., ASTM, ASME).
3. Casting/Forging:
– Create valve bodies through casting or forging.
– Machine rough parts to required shapes and sizes.
4. Machining:
– Utilize CNC machines for precision cutting and shaping.
– Perform drilling, threading, and turning.
5. Assembly:
– Carefully assemble internal components like springs and diaphragms.
– Ensure exact alignment and fitting of parts.
6. Welding and Heat Treatment:
– Execute welding for certain components if needed.
– Perform heat treatments to enhance material properties.
7. Surface Treatment:
– Apply coatings or painting to prevent corrosion.
– Conduct surface finishing for smooth operations.
8. Final Testing and Inspection:
– Perform thorough functional and pressure tests.
– Conduct final quality inspections.
9. Marking and Documentation:
– Engrave identification and certification marks.
– Compile detailed documentation for traceability.
10. Packaging and Shipping:
– Pack valves ensuring protection during transit.
– Dispatch according to customer requirements.
How to use “safety valve relief valve”
A safety valve, often referred to as a relief valve, is a crucial device in various industrial systems designed to protect against excessive pressure build-up. Below is a simple guide on its use:
Installation
1. Selection: Choose the appropriate valve type and size based on system specifications, including maximum pressure and temperature.
2. Placement: Install the valve at a point where pressure build-up could be hazardous. This is usually at the top of the pressure vessel or pipeline.
3. Orientation: Ensure the valve is mounted vertically to function correctly.
Setting
1. Pressure Setting: Adjust the valve’s set pressure to match the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of the system. This is typically done by turning an adjustment screw.
2. Seal Check: Ensure the valve’s seal is intact to prevent leaks.
Operation
1. Regular Testing: Periodically test the valve to ensure it opens at the set pressure. This can usually be done manually or with a test lever.
2. Monitoring: Continuously monitor the system’s pressure to ensure it doesn’t exceed the valve’s set point.
Maintenance
1. Inspection: Regularly inspect the valve for signs of wear, corrosion, or blockage.
2. Cleaning: Clean the valve as necessary to prevent debris from affecting its operation.
3. Replacement: Replace the valve or its components as required to maintain safety and efficiency.
Safety Considerations
1. Proper Venting: Ensure that the outlet of the valve is properly vented to a safe location to avoid hazardous discharge.
2. Isolation: Isolate the system, if possible, before performing any maintenance to prevent accidental discharge.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively use a safety valve to protect your industrial system from dangerous pressure levels. Regular maintenance and checks are essential to ensure its proper functioning and longevity.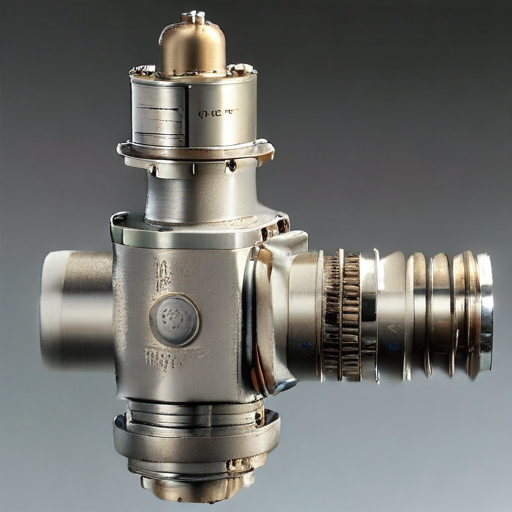
“safety valve relief valve” Comparative Analysis
Safety valves and relief valves are essential components in pressure management systems, yet they serve distinct purposes:
Function:
– Safety Valve: Primarily used to protect equipment and operators from overpressure scenarios. It automatically releases pressure once a preset limit is reached, ensuring safe operational conditions.
– Relief Valve: Often used in liquid systems to maintain optimal process pressure. They gradually release fluid to regulate ongoing pressure, ensuring system stability.
Applications:
– Safety Valve: Common in steam systems, boilers, and compressed gas setups. Critical in sectors where any overpressure can be catastrophic, like petrochemical plants and power generation.
– Relief Valve: Typically found in liquid systems such as hydraulic machinery and fluid processing plants, where pressure fluctuations are more gradual.
Operation Mechanism:
– Safety Valve: Rapid opening with a pop action at set pressure thresholds. Designed for immediate pressure release to prevent system failure.
– Relief Valve: Opens proportionally to the pressure increase. Slow and controlled fluid discharge to maintain steady pressure levels.
Set Pressure Adjustment:
– Safety Valve: Usually has a fixed, non-adjustable set point to ensure immediate response during emergencies.
– Relief Valve: Generally adjustable to allow fine-tuning for consistent operational efficiency.
Discharge:
– Safety Valve: Discharges excess pressure directly into the atmosphere or designated containment systems.
– Relief Valve: Channels the relieved fluid back into the system or a storage tank for reuse or controlled disposal.
Cost and Maintenance:
– Safety Valve: Often higher initial cost due to their critical role and certification requirements. However, maintenance is generally straightforward.
– Relief Valve: Typically less expensive but might require more frequent adjustments and maintenance to ensure precise pressure control.
In conclusion, while both safety valves and relief valves manage pressure, their specific functions, applications, and operational mechanics distinguish them, making each suitable for particular contexts within industrial pressure regulation.
“safety valve relief valve” Warranty and Support
Our Safety Valve Relief Valves come with a comprehensive warranty and support policy designed to provide peace of mind and ensure optimal performance.
Warranty
Each valve is backed by a two-year limited warranty from the date of purchase, covering defects in materials and workmanship under normal usage conditions. This warranty does not cover damage caused by misuse, improper installation, or unauthorized modifications.
In the event of a malfunction, we offer a hassle-free return and replacement process. To initiate a claim, please keep your proof of purchase and contact our customer service team. We strive to process claims promptly to minimize downtime for your operations.
Support
To ensure your valves function optimally, we provide extensive support resources:
– Technical Assistance: Our team of experienced engineers is available to offer troubleshooting and installation guidance. Feel free to reach out via phone or email for expert advice.
– Documentation: Our website hosts a comprehensive library of manuals, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides to assist in setup and maintenance.
– Training Programs: We offer both online and in-person training sessions to help you and your team understand the proper handling and maintenance of our valves.
– Maintenance Services: We also provide optional maintenance packages, which include regular inspections and servicing by certified technicians to extend the lifespan of your valves.
Contact Us
For any warranty claims or support inquiries, please contact our Customer Service:
– Phone: 1-800-VALVE-01
– Email: support@valvepro.com
– Website: www.valvepro.com/support
We are committed to ensuring the longevity and reliability of our products, helping you maintain the safety and efficiency of your system. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
List “safety valve relief valve” FAQ
FAQ: Safety Valve Relief Valve
1. What is a safety valve relief valve?
– A safety valve relief valve is a device designed to release excess pressure from a system to prevent equipment damage or catastrophic failure. It automatically opens when pressure exceeds a preset limit.
2. Where are safety valve relief valves commonly used?
– They are used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and HVAC systems, to ensure safe operation of boilers, pressure vessels, and pipelines.
3. What’s the difference between a safety valve and a relief valve?
– A safety valve typically refers to devices used in steam systems, rapidly releasing pressure to prevent explosions. A relief valve is often used in liquid systems, gradually releasing pressure to maintain system stability.
4. How do safety valve relief valves work?
– They operate using a spring-loaded mechanism. When system pressure exceeds the valve setpoint, it forces the valve open, allowing media to escape and reducing pressure. Once normal conditions are restored, the valve closes automatically.
5. How is the set pressure of a safety valve determined?
– The set pressure is determined based on the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of the system. Setting it too high or too low can lead to ineffective protection or unnecessary operation.
6. Is regular maintenance required for safety valve relief valves?
– Yes, regular maintenance, including periodic inspection, testing, and calibration, is essential to ensure they function properly and provide reliable protection.
7. Can safety valves be manually operated?
– While primarily automatic, some safety valves feature manual overrides for testing or emergency scenarios. However, manual operation should only be performed by qualified personnel.
8. What are common signs of a malfunctioning safety valve?
– Common signs include frequent or continuous discharge, leakage, unusual noise, or failure to open at set pressure. Immediate inspection and maintenance are advised if these issues are observed.
9. How should a safety valve relief valve be sized?
– Proper sizing involves considering factors like the maximum flow rate, temperature, operating pressure, and the type of media within the system. Incorrect sizing can compromise safety.
10. Are there standards regulating safety valve relief valve designs?
– Yes, standards like ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and API (American Petroleum Institute) provide guidelines ensuring uniformity, reliability, and safety of these critical devices.
Proper use and understanding of safety valve relief valves are crucial for maintaining system integrity and ensuring operational safety.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about safety valve relief valve for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about safety and relief valves for buyers sourcing from China:
1. What is the difference between a safety valve and a relief valve?
Safety valves are designed to open and release pressure to prevent equipment failure. Relief valves steadily release pressure to maintain a set level. Both are essential for system safety but operate differently.
2. Are Chinese-manufactured valves compliant with international standards?
Many suppliers in China produce valves according to international standards like ASME, API, and CE. It’s crucial to verify certifications and compliance documentation.
3. How do I ensure the quality of valves sourced from China?
Conduct thorough due diligence: check supplier certifications, request production samples, and consider third-party inspections. Visiting the manufacturer can also provide assurance.
4. What materials are commonly used in the construction of these valves?
Typical materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and various alloys. Ensure material specifications meet your project’s requirements.
5. What is the usual lead time for valve orders from China?
Lead times vary based on order size and complexity, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Custom orders might take longer.
6. Can I obtain custom-designed valves from Chinese suppliers?
Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer custom designs. Provide detailed specifications and work closely with the supplier to ensure your needs are met.
7. What is the warranty policy for valves from Chinese suppliers?
Warranty periods vary but generally range from 1 to 2 years. Ensure the warranty terms and conditions are clearly stated in the contract.
8. How are shipping and logistics managed?
Manufacturers often handle shipping logistics. Confirm Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) with your supplier and factor in additional time for customs clearance.
9. What payment methods are accepted by Chinese valve suppliers?
Common payment methods include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes PayPal for smaller orders. Agree on payment terms in advance.
10. How do I handle after-sales service and technical support?
Discuss after-sales services with the supplier before finalizing the purchase. Some manufacturers offer local service agents or remote technical support.
These FAQs provide a fundamental understanding for buyers sourcing valves from China, helping ensure a smooth and reliable procurement process.





