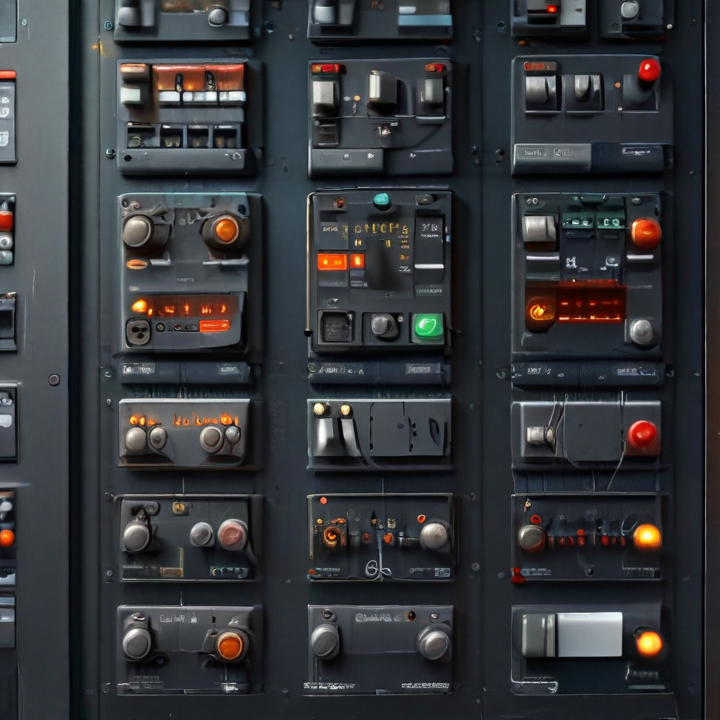
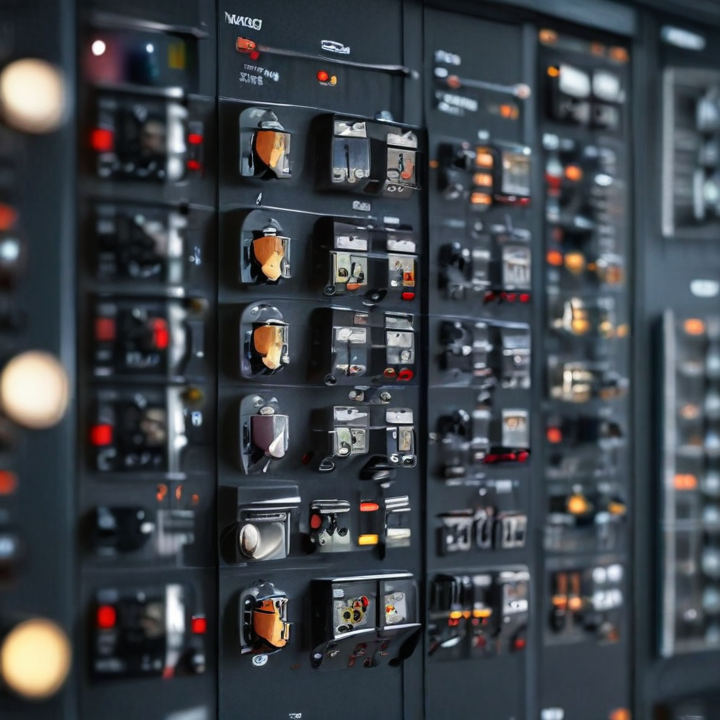
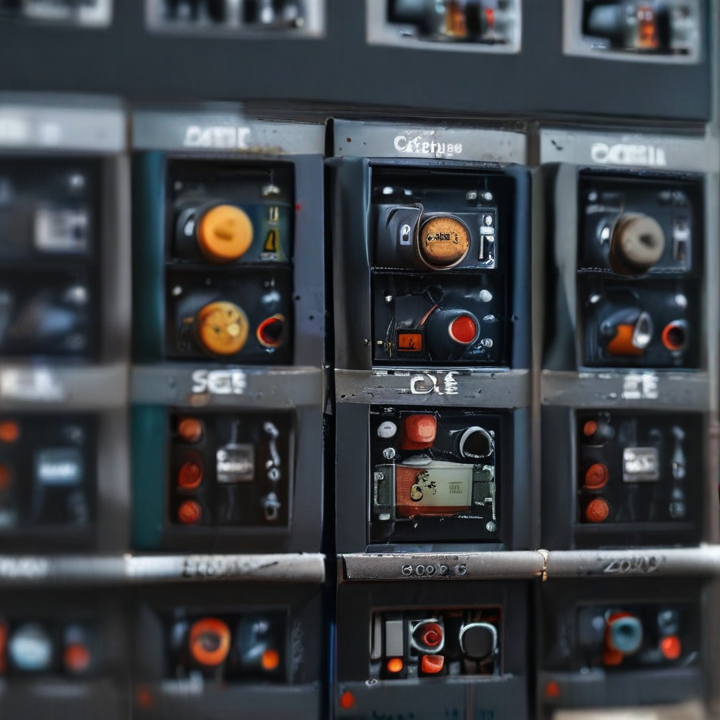
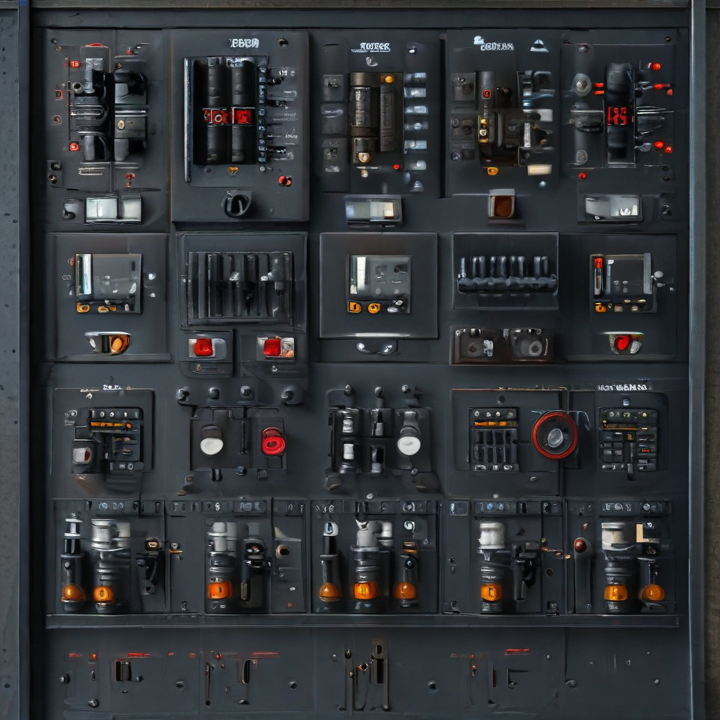
control panels electrical Safety Certifications
Electrical control panels are integral to managing and distributing electrical power in various settings, from industrial to commercial applications. Ensuring the safety and compliance of these panels is crucial to preventing accidents and ensuring reliable operation. Here are key safety certifications to be aware of:
1. UL 508A:
– United States: UL 508A is a widely recognized standard provided by Underwriters Laboratories (UL). It ensures that industrial control panels are constructed with proper materials and adhere to stringent safety protocols to prevent electrical fires and shock hazards.
2. CSA C22.2 No. 286:
– Canada: The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) certification, particularly CSA C22.2 No. 286, ensures that control panels meet Canadian electrical safety standards, similar to the UL standards in the U.S.
3. CE Marking:
– European Union: CE Marking is mandatory for control panels sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). It indicates conformity with the European Union’s Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive, ensuring safety and performance standards.
4. IEC 61439:
– International: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 61439 standard covers the safety and performance requirements for low-voltage switchgear and control gear assemblies. It provides a framework for electrical panels used globally.
5. NFPA 79:
– Worldwide: The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 79 standard focuses on the electrical standards for industrial machinery worldwide. Compliance ensures panels are designed to mitigate fire and electrical hazards in an industrial setting.
6. TÜV Certification:
– Germany and International: TÜV Rheinland and TÜV SÜD provide certification services that assess the safety and quality of control panels. Achieving TÜV certification ensures adherence to rigorous German and international safety standards.
7. NEMA Standards:
– North America: Compliance with the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) standards ensures panels are built to withstand particular environmental conditions, offering added assurance of safety and reliability.
Compliance with these certifications verifies that control panels are designed and manufactured to prevent electrical hazards, ensuring both user safety and operational reliability. Always choose panels with relevant certifications for your specific region and application to uphold the highest safety standards.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “control panels electrical”
Control panels in electrical systems are integral for managing and automating various industrial processes. In the design and evaluation of these panels, several technical parameters must be considered to ensure safety, performance, and compliance with standards. Below are key reference technical parameters for electrical control panels:
1. Voltage Rating: Specifies the maximum operating voltage the panel can handle, typically categorized into low voltage (up to 1kV), medium voltage (1kV to 35kV), and high voltage (above 35kV).
2. Current Rating: Indicates the maximum current the panel can carry without overheating. It includes the main busbar and individual circuit ratings, often measured in Amperes (A).
3. Ingress Protection (IP) Rating: Determines the panel’s resistance to dust and water ingress, crucial for environmental suitability. Common ratings include IP54, IP65, and IP66.
4. Short-Circuit Withstand Capacity: Defines the maximum current the panel can withstand during a short circuit without damage. This rating is essential for ensuring the panel can handle fault conditions safely.
5. Thermal Management: Includes parameters like the heat dissipation capacity and the need for cooling mechanisms (fans, vents, or air conditioning) to prevent overheating.
6. Enclosure Material: Specifies the material (metal, plastic, stainless steel) and its compliance with standards (e.g., NEMA, IEC) for durability and safety under different conditions.
7. Component Certification: Ensures that all components (circuit breakers, relays, contactors) comply with relevant standards (UL, CSA, CE) for quality and reliability.
8. Panel Dimensions: Includes height, width, and depth specifications to fit available space and ensure ease of maintenance and installation.
9. Grounding and Bonding: Ensures the panel is properly grounded and bonded to prevent electrical shocks and enhance safety.
10. Control Circuit Voltage: Differentiates between control voltage levels (usually 24VDC, 48VDC, 120VAC) for compatibility with control devices.
11. Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Details on the user interface elements like displays, buttons, and controls for user accessibility.
12. Communication Protocols: Specifies supported communication standards (such as Modbus, Ethernet, Profibus) for integration into broader control systems.
These parameters must be meticulously evaluated to design a functional and safe electrical control panel tailored to specific industrial needs.
List Product features of “control panels electrical”
1. Durable Construction: Designed to withstand harsh environments, these panels are typically made from high-quality materials like stainless steel or powder-coated metal.
2. Safety Compliance: Built to meet industry standards such as UL, CE, and IEC, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
3. Customization Options: Various sizes, configurations, and components can be customized to match specific application requirements.
4. Advanced Control Systems: Integrated with PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) for sophisticated control and monitoring capabilities.
5. Wiring and Cable Management: Features organized and labeled wiring systems to reduce errors and simplify maintenance.
6. IP and NEMA Ratings: Available in multiple IP (Ingress Protection) and NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) ratings to provide protection against dust, water, and other environmental factors.
7. Thermal Management: Equipped with fans, ventilation systems, or air conditioning units to manage internal temperatures and prevent overheating.
8. Energy Efficiency: Designed to operate efficiently, often incorporating energy-saving components like variable frequency drives (VFDs) and energy-efficient transformers.
9. Easy Installation: Pre-wired and pre-tested, allowing for quick and straightforward installation.
10. Expansion Capability: Modular design allows for future upgrades and expansion without significant overhauls.
11. Diagnostic Features: Built-in diagnostic tools and indicators assist in troubleshooting and ensuring optimal performance.
12. Remote Monitoring: Advanced models offer remote access and monitoring capabilities, providing real-time data and control from remote locations.
13. Security Features: Lockable enclosures and secure access points help safeguard internal components against unauthorized access.
14. User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive control interfaces with touchscreens or tactile buttons for easy navigation and operation.
15. Compatibility: Compatible with a wide range of sensors, actuators, and other peripheral devices, ensuring flexibility in various applications.
16. Robust Power Management: Designed to handle high power loads, with safety features like circuit breakers and surge protectors.
These features collectively make electrical control panels essential for managing and automating industrial processes, enhancing both safety and efficiency.
List Various Types of “control panels electrical”
Certainly! Here is a concise overview of various types of control panels used in electrical systems:
1. Motor Control Centers (MCCs): Designed to control multiple motors from a central location. These panels include motor starters, overload relays, and circuit breakers.
2. PLC Control Panels: Utilize Programmable Logic Controllers to automate industrial processes. They integrate various control and monitoring operations through software-based logic.
3. VFD Control Panels: Use Variable Frequency Drives to control motor speed and torque, enhancing efficiency in motor operation. Ideal for applications requiring variable motor speeds.
4. Relay Logic Panels: Traditional control systems using electromechanical relays for straightforward control logic. Suited for smaller, less complex systems.
5. Distribution Panels: Distribute electrical power from a single source to multiple circuits. These panels include circuit breakers, bus bars, and fuses to ensure safety and manage power distribution.
6. Pneumatic Control Panels: Use compressed air to control equipment and processes, commonly found in industrial settings where mechanical actions are controlled pneumatically.
7. SCADA Control Panels: Integrate Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems to monitor and control industrial processes remotely. Vital for large-scale operations like water treatment plants or electrical grids.
8. Lighting Control Panels: Manage lighting systems in commercial and industrial buildings. They offer automated control based on timers, sensors, or programmable schedules.
9. Fire Pump Control Panels: Specifically designed to control the operation of fire pump systems. Essential for ensuring reliable fire protection in buildings.
10. Process Control Panels: Used in industries like chemical manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals to maintain and regulate production processes.
11. ATS Control Panels: Automatic Transfer Switch panels ensure reliable power transfer from primary to backup sources during power outages. Essential for critical applications like hospitals and data centers.
Each type of control panel serves a specific purpose, tailored to the varying needs of industrial, commercial, and residential applications.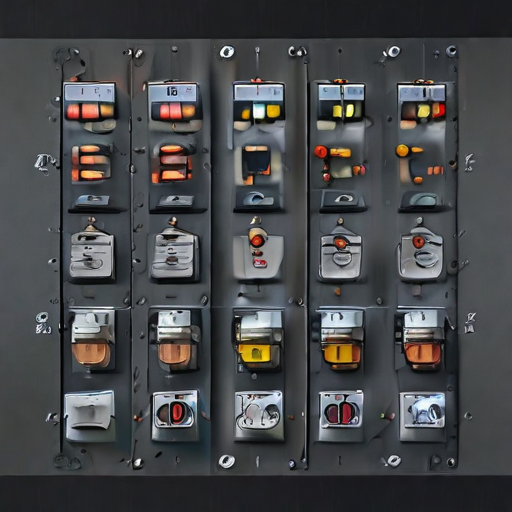
List Application of “control panels electrical”
Control panels in electrical systems are crucial for managing and automating various processes. Here, I will list some key applications within 300 words:
1. Industrial Automation: Control panels are foundational in manufacturing environments. They regulate machinery, automate production lines, and ensure safety protocols. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) within these panels control equipment ranging from conveyor belts to robotic arms.
2. Building Management Systems (BMS): These panels manage electrical, lighting, HVAC, and security systems within commercial and residential buildings. They optimize energy usage and maintain indoor comfort and security.
3. Renewable Energy Systems: In solar and wind energy systems, control panels manage the conversion of energy, monitor performance, and store data. They ensure the consistent and efficient operation of power inverters and battery storage systems.
4. Water and Wastewater Treatment: Control panels automate the operation of pumps, filters, and other treatment processes. They monitor critical parameters such as flow rates and water quality to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
5. Utility Distribution Networks: These panels are used in power distribution networks to control substations and manage the distribution of electricity. They help in fault detection, load balancing, and remote operation of circuit breakers.
6. Transportation Systems: Control panels are integral in the management of railways, traffic signals, and airport lighting systems. They ensure the safe and efficient movement of vehicles and pedestrians.
7. Agricultural Automation: In modern farming, control panels are used for irrigation systems, greenhouse climate control, and livestock feeding mechanisms. They improve productivity and precision in farming operations.
8. Marine and Offshore Applications: Ships and offshore oil rigs utilize control panels to manage navigation systems, engine rooms, and safety mechanisms. They ensure reliable and safe maritime operations.
9. Telecommunication Infrastructure: Control panels manage power systems for telecommunication towers and data centers. They ensure uninterrupted power supply and system integrity.
These varied applications highlight the versatility and essential role of electrical control panels in modern technological and industrial ecosystems.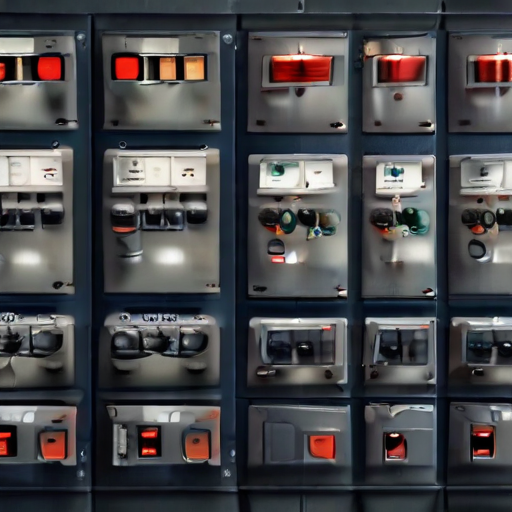
List Buyer Types of “control panels electrical”
Sure, control panels for electrical systems are essential components across various industries and applications. Understanding the different buyer types can help suppliers tailor their offerings more effectively. Here are the primary buyer types of control panel electrical:
1. Industrial Manufacturers:
– Industrial sectors, like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery, require control panels for managing machinery and production lines. These buyers seek robust, reliable, and customized solutions that ensure safety and efficiency.
2. Construction Companies:
– Construction firms need control panels for new buildings and infrastructure projects. These buyers look for panels that are compliant with safety regulations, easy to install, and maintain.
3. Commercial Building Managers:
– Office buildings, malls, and hospitals require control panels to manage electrical systems like lighting, HVAC, and security. They prioritize panels that offer seamless integration, remote monitoring, and energy efficiency.
4. OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers):
– These companies need control panels for their equipment and machinery. They seek highly specialized and customized control panels that meet specific technical requirements and standards.
5. Utility Companies:
– Providers of electricity and water utilities use control panels to manage distribution networks and substations. Their focus is on reliability, durability, and ease of maintenance.
6. Energy Sector:
– Renewable energy plants, like solar and wind farms, as well as traditional power plants, need advanced control panels for energy generation and distribution. They demand high-performance, sustainable, and scalable solutions.
7. Marine and Offshore:
– Ships and offshore platforms need control panels for various operations, including navigation, communication, and machinery control. These buyers require panels that are resistant to harsh environments and meet maritime standards.
8. Agriculture Sector:
– Modern farms use control panels for irrigation systems, livestock management, and farm machinery. They need solutions that are durable, easy to use, and can withstand outdoor conditions.
9. Service and Maintenance Providers:
– Companies offering maintenance and repair services for electrical systems often buy control panels to replace or upgrade existing setups. They prioritize availability, compatibility, and ease of replacement.
By understanding the specific needs and priorities of these buyer types, suppliers can develop targeted marketing strategies and product offerings.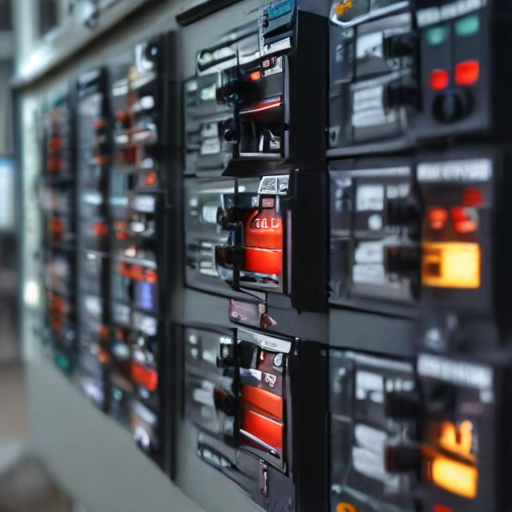
List “control panels electrical” Project Types for Different Industries
Certainly! Control panels are integral in managing electrical systems across various industries, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability. Here are the project types for different industries:
1. Manufacturing:
– Production Line Automation: Facilitates the seamless operation of assembly lines and machinery.
– Process Control Panels: Manages parameters like temperature, pressure, and flow rates for manufacturing processes.
2. Oil and Gas:
– SCADA Systems: Monitors and controls drilling operations and well-site activities.
– Safety and Shutdown Panels: Ensures safe operation and emergency shutdown of critical infrastructure.
3. Water and Wastewater:
– Pump Control Panels: Manages the operation of pumps in water treatment facilities.
– Filtration System Panels: Controls filtration processes to maintain water quality.
4. Energy and Power:
– Substation Control Panels: Oversees the distribution and regulation of electrical power.
– Renewable Energy Panels: Manages solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources.
5. Building Automation:
– HVAC Control Panels: Regulates heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
– Lighting Control Panels: Manages lighting systems for energy efficiency and convenience.
6. Transportation:
– Railway Signal Panels: Ensures safe railway operations through signal control.
– Traffic Management Panels: Controls traffic lights and signage to optimize flow and safety.
7. Food and Beverage:
– Batch Control Panels: Manages the mixing and production of food and beverage products.
– Packaging Control Panels: Oversees the packaging process for consistency and safety.
8. Pharmaceutical:
– Cleanroom Environment Panels: Maintains specific environmental conditions.
– Process Validation Panels: Ensures compliance with regulatory standards through precise control.
9. Mining:
– Ventilation Control Panels: Manages airflow in mines to ensure safety.
– Material Handling Panels: Controls conveyors and material transport systems.
By tailoring control panels to the specific needs of each industry, these projects enhance operational performance and ensure regulatory compliance.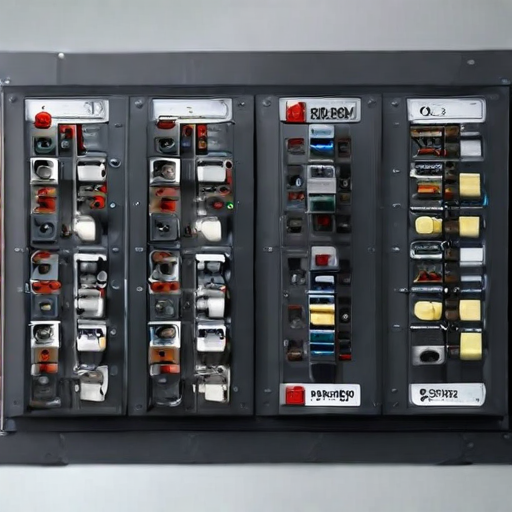
control panels electrical Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Control panels are essential in managing and automating various electrical systems, offering centralized control and monitoring. With the rapid advancement in technology, upgrading and customizing electrical accessories for control panels has become increasingly important to enhance functionality and efficiency.
Upgrades include:
1. Advanced Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): Modern HMIs with touchscreen displays and intuitive user interfaces make monitoring and control more accessible and efficient.
2. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Upgrading to state-of-the-art PLCs enables better automation, faster processing speeds, and improved reliability.
3. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Integrating VFDs allows precise control of motor speeds, energy savings, and extended equipment life.
4. Enhanced Communication Protocols: Incorporating Ethernet, Modbus, or PROFIBUS ensures robust and efficient communication between devices, facilitating remote monitoring and control.
5. Energy Management Systems: Upgrading includes installing energy meters and management software to monitor and optimize power usage.
Custom Manufacturing Options include:
1. Panel Size and Enclosures: Customizable sizes and materials for enclosures, such as NEMA-rated for different environmental conditions, ensure fitment and protection.
2. Component Layout: Tailoring the internal layout of components for optimal space utilization and easy access for maintenance.
3. Cable Management: Custom cable routing and labeling for organized and safe electrical connections.
4. Integration of Specialized Components: Incorporating specific sensors, relays, or circuit breakers tailored to unique operational requirements.
5. Aesthetic Customizations: Color-coding, LED indicators, and bespoke labeling for improved visibility and operation.
Upgrading and customizing your control panels not only enhances the performance and reliability of your electrical systems but also ensures compliance with safety standards and operational needs. Investing in modern accessories and personalized solutions can significantly streamline processes and boost overall efficiency.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “control panels electrical”
Quality Control and Manufacturing Process of Electrical Control Panels
Manufacturing Process:
1. Design and Engineering: Initial phase involves detailed design and engineering, including schematic diagrams, component selection, and layout designs using CAD software.
2. Material Procurement: Sourcing high-quality components such as circuit breakers, relays, PLCs (programmable logic controllers), terminal blocks, and wiring according to the design specifications.
3. Panel Fabrication: Building the enclosure involves cutting, bending, and welding metal sheets to form the structure. This is often followed by painting or coating to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal.
4. Component Mounting: Assembling involves mounting switches, relays, PLCs, and other components onto DIN rails or backplanes within the panel according to the design.
5. Wiring and Connections: This step involves wiring components according to the electrical schematic, ensuring proper connections and routing to maintain a clean and organized layout.
6. Testing and Programming: The assembled panel undergoes rigorous testing. This includes functionality checks, continuity tests, and insulation resistance testing. PLCs and other programmable devices are configured and tested to ensure correct operation.
7. Quality Inspection: Final inspection verifies that the assembled panel meets all design criteria, safety standards, and regulatory requirements.
8. Packaging and Shipping: The completed panel is securely packaged to prevent damage during transit and then shipped to the client.
Quality Control:
1. Vendor Quality Assurance: Ensure all purchased components meet specified quality and industry standards.
2. In-Process Inspections: Implement checks during critical stages of assembly to identify and rectify potential issues early.
3. Compliance Testing: Perform electrical tests (e.g., Hi-pot, continuity, and functional tests) to verify performance against specifications and safety standards like UL or IEC.
4. End-of-Line Testing: Comprehensive testing of the finished panel, including operational verification under simulated conditions to ensure it meets customer requirements.
5. Documentation and Traceability: Maintain detailed records of component batches, assembly procedures, and test results to ensure traceability and support future quality audits.
6. Continuous Improvement: Regular feedback and analysis to refine processes and address any recurring issues, ensuring continuous quality enhancement.
By adhering to these rigorous manufacturing and quality control processes, manufacturers ensure that electrical control panels are reliable, safe, and meet customer specifications.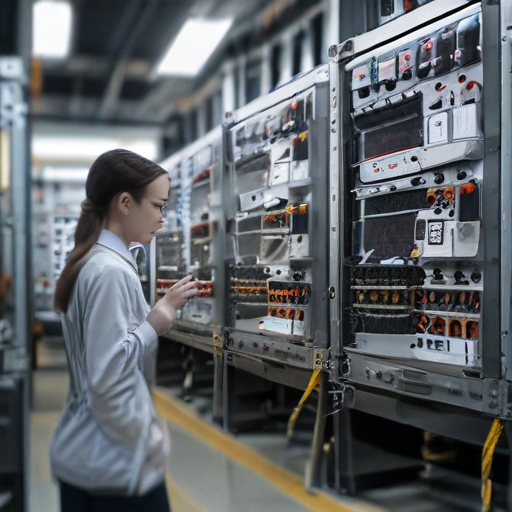
How to use “control panels electrical”
Using electrical control panels effectively involves understanding their components and functionality. Here’s a concise guide to help you:
1. Identify Components: Familiarize yourself with the main components of the control panel, which may include circuit breakers, fuses, relays, power supplies, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
2. Safety First: Ensure the power supply is disconnected before you start any work. Always follow safety protocols and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
3. Understand the Schematic: Review the electrical schematic diagram that accompanies the control panel. This will provide insight into the wiring and connections of various components.
4. Connect Power Supply: Verify the input voltage requirements. Connect the power supply to the input terminals as per the schematic diagram.
5. Verify Grounding: Ensure the control panel is properly grounded to prevent electrical hazards and ensure the correct operation of circuit protection devices.
6. Check Connections: Inspect and tighten all terminal connections to avoid loose wires, which can cause malfunctions or shorts.
7. Install Input Devices: Connect sensors, switches, and other input devices to the designated terminals on the PLC or control modules.
8. Configure Outputs: Attach output actuators, such as motors, solenoids, or lighting systems, to the appropriate output terminals.
9. Program the PLC (if applicable): Upload or configure the necessary control logic using appropriate software tools. Ensure the program matches the intended operation sequence of your machinery or system.
10. Testing and Calibration: Once all connections and programming are completed, reconnect the power. Test each input and output component to confirm proper operation. Make necessary adjustments or calibrations to achieve desired performance.
11. Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the control panel. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or any potential faults. Clean the panel periodically to ensure dust or debris does not affect its operation.
By following these steps, you can safely and effectively use electrical control panels in various applications.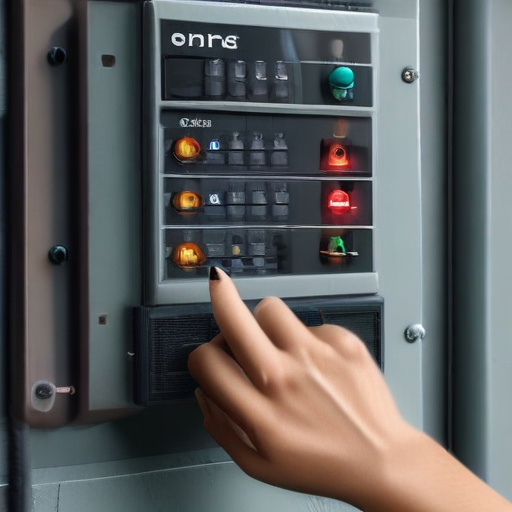
“control panels electrical” Comparative Analysis
When analyzing electrical control panels, it’s crucial to consider various aspects such as design, functionality, safety standards, and application fields. Here’s a comparative analysis focusing on these key areas:
1. Design and Configuration:
– Standard Control Panels:
– Pre-engineered and ready for general applications.
– Cost-effective and quicker to deploy.
– Customized Control Panels:
– Tailored to specific requirements, ideal for unique industrial processes.
– Higher initial cost and longer development time, but optimized for efficiency.
2. Components and Integration:
– Basic Panels:
– Contain essential components like circuit breakers, relays, and switches.
– Suitable for simple systems with straightforward control needs.
– Advanced Panels:
– Include PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces), and various sensors for automation.
– Enhanced for complex operations requiring precise control and monitoring.
3. Safety and Compliance:
– Standard Compliance:
– Panels must adhere to regional and international standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) in the U.S., IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) globally, and CE marking in Europe.
– Advanced Safety Features:
– High-end panels may include additional safety mechanisms such as redundant power supplies, emergency stop functions, and fault diagnostics.
4. Applications and Use Cases:
– Industrial Panels:
– Used in manufacturing, process control, and heavy machinery.
– Often customized to manage high loads and harsh environmental conditions.
– Commercial Panels:
– Deployed in buildings, HVAC systems, and lighting controls.
– Typically standardized for broad usage and ease of integration.
5. Future Trends:
– Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
– Enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect against digital threats.
– Increased use of sustainable and energy-efficient designs.
In summary, when choosing an electrical control panel, it’s crucial to balance cost, customization, complexity, and compliance with safety standards. Understanding the specific needs of the application will guide whether a standard or customized solution is appropriate.
“control panels electrical” Warranty and Support
Our control panels are built to the highest standards of quality and reliability, ensuring they deliver optimal performance throughout their lifespan. To reinforce our commitment to excellence, we offer a comprehensive warranty and support package for our electrical control panels.
Warranty Coverage:
We provide a standard warranty that covers defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one year from the date of purchase. During this time, any issues arising from these defects will be addressed promptly at no cost to you. Extended warranty options are available upon request, providing additional peace of mind for those seeking long-term protection.
Warranty Exclusions:
Please note that our warranty does not cover damage caused by improper installation, unauthorized modifications, misuse, or any external factors beyond our control. Routine wear and tear, as well as consumable components, are also excluded from the warranty.
Technical Support:
Our dedicated technical support team is available to assist you with any questions or issues you may encounter. Support is available via phone, email, or through our online support portal, ensuring that help is always within reach. Our experts can provide guidance on installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance to keep your control panels operating efficiently.
Maintenance Services:
To ensure the longevity and reliability of your control panels, we offer a range of maintenance services. These include routine inspections, preventive maintenance, and calibration services. Our trained technicians can identify potential issues before they become serious problems, helping to minimize downtime and extend the life of your equipment.
Software and Firmware Updates:
We regularly release software and firmware updates to enhance the functionality and security of our control panels. Our support team will notify you of available updates and provide instructions for their installation, ensuring your equipment remains up-to-date with the latest features and improvements.
In summary, our warranty and support services are designed to provide you with complete confidence in our electrical control panels, ensuring they perform reliably and efficiently throughout their lifespan. For more information, please contact our customer service team.
List “control panels electrical” FAQ
Control Panels Electrical FAQ
1. What is an electrical control panel?
An electrical control panel is an assembly of electrical components that manage, direct, and regulate the operation of electrical equipment or machinery. It typically includes circuit breakers, relays, switches, and control devices.
2. What are the main components of an electrical control panel?
The main components include circuit breakers, fuses, relays, contactors, switches, transformers, timers, and control devices like programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs).
3. What are the different types of electrical control panels?
Common types include power distribution panels, motor control centers (MCCs), automation panels, relay panels, and lighting control panels.
4. How do I choose the right electrical control panel?
Consider the application requirements, power ratings, environmental conditions, space constraints, and compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
5. What standards and regulations apply to electrical control panels?
Standards like UL 508A in the US, IEC 61439 internationally, and other regional standards ensure safety and reliability in design, manufacturing, and operation.
6. How do I maintain an electrical control panel?
Regular inspections, cleaning, torque verification on connections, thermal imaging to detect hotspots, and firmware updates for smart components are crucial for maintenance.
7. Can control panels be customized?
Yes, control panels can be tailored to specific requirements, including custom layouts, component selection, and environmental protection features like NEMA or IP ratings.
8. What is the difference between a PLC and an HMI?
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is used for automated control of machinery, while an HMI (Human-Machine Interface) provides a user interface for monitoring and interacting with the control system.
9. What is the role of a circuit breaker in a control panel?
Circuit breakers protect the electrical circuit by interrupting the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit, thereby preventing damage.
10. Why is grounding important in control panels?
Proper grounding prevents electric shock, protects against transient voltages, and improves the reliability of the electrical system.
Note: Always consult with a certified electrician or engineer for specific advice tailored to your electrical control panel needs.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about control panels electrical for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about sourcing electrical control panels from China, along with concise answers:
1. What are the advantages of buying electrical control panels from China?
– Answer: Lower production costs, extensive industrial base, and a wide range of suppliers offering customizable options are key advantages.
2. How do I verify the quality of electrical control panels from Chinese suppliers?
– Answer: Verify certifications like ISO, CE, or UL, request sample products, inspect factory facilities, and use third-party audit services.
3. What certifications should I look for in electrical control panels?
– Answer: Look for international certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, CE for European markets, and UL for North American markets.
4. How do I ensure the supplier understands my technical requirements?
– Answer: Provide detailed technical specifications, ideally in both English and Chinese, and engage in direct communication to clarify any uncertainties.
5. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing and delivery?
– Answer: Lead times can vary but typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on complexity and order volume. Always confirm with the supplier.
6. How are quality control and testing handled?
– Answer: Suppliers should perform stringent quality control checks and testing, including functionality tests, before shipment. Consider third-party inspections for added assurance.
7. What are the common payment terms for buying from China?
– Answer: Common payment terms include Letter of Credit (L/C), Telegraphic Transfer (T/T), and sometimes, a small deposit upfront with the balance paid upon delivery.
8. How do I handle shipping and logistics?
– Answer: Work with experienced freight forwarders, confirm Incoterms (such as FOB or CIF), and ensure comprehensive shipping insurance to manage risks.
9. Can I get custom-designed control panels?
– Answer: Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization based on client specifications. Provide detailed design requirements to facilitate this process.
10. What should I do if I encounter issues with the product after delivery?
– Answer: Establish clear warranty terms and support agreements before purchase. Communicate issues promptly with the supplier and consider local technical support agreements if necessary.
By addressing these common concerns, buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing electrical control panels from China.





