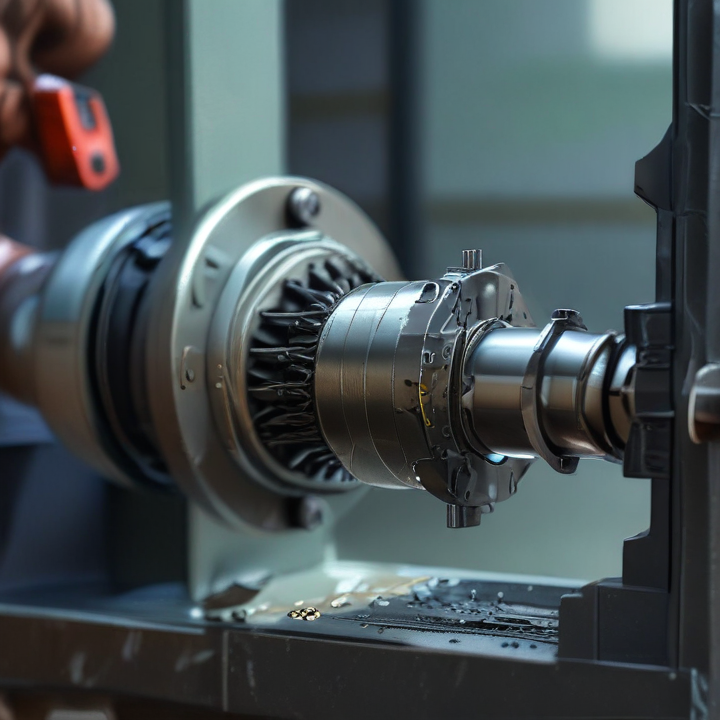
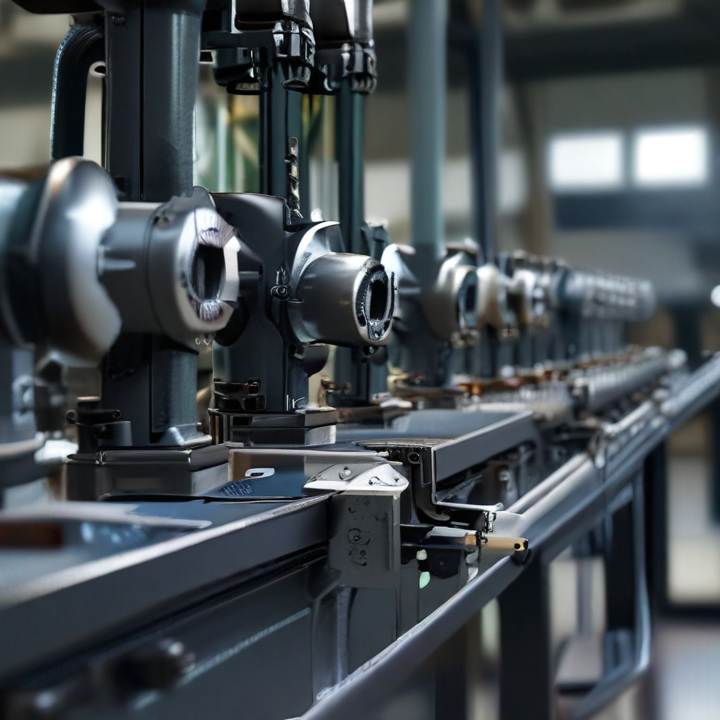
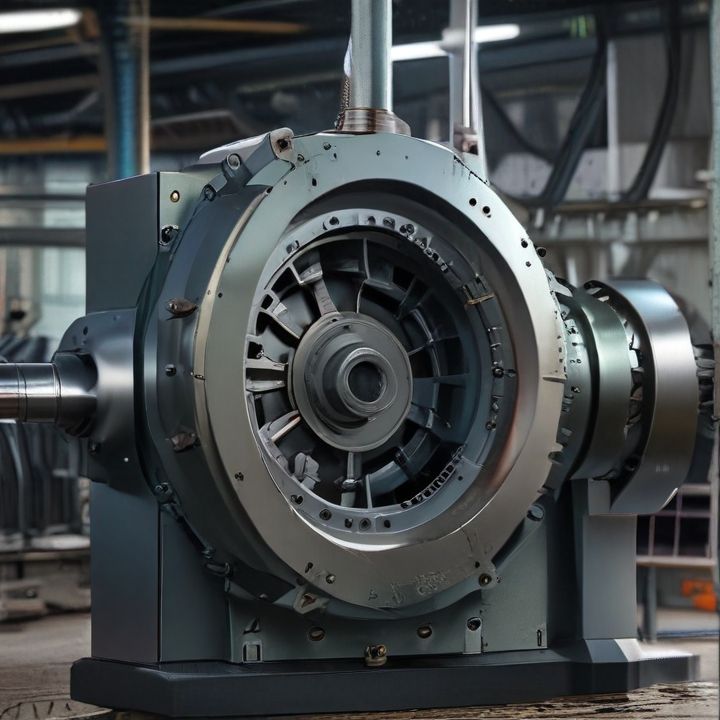
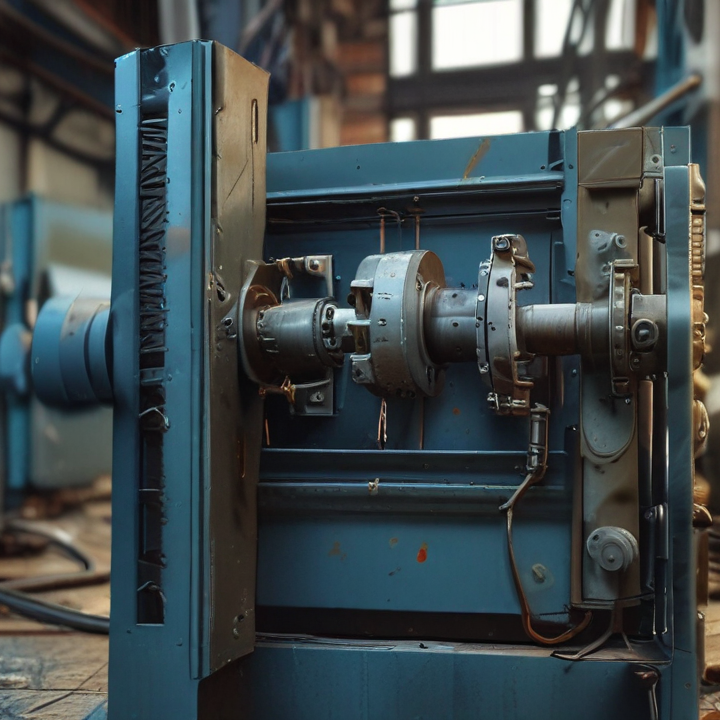
bolts making machine Safety Certifications
When considering safety certifications for a bolts making machine, it’s essential to ensure compliance with both international and local safety standards to protect workers and maintain operational efficiency. Key safety certifications to look for include:
1. CE Marking (Conformité Européenne):
– Indicates compliance with the EU’s health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– Mandatory for machines sold or used in the European Economic Area (EEA).
2. ISO 12100:
– International standard addressing basic principles of machinery safety.
– Provides guidelines for the design, risk assessment, and risk reduction of machines.
3. ISO 13849-1 and ISO 13849-2:
– Standards for the safety-related parts of control systems.
– Emphasizes the qualification of safety mechanisms and risk reduction measures.
4. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration):
– Pertains mainly to the United States.
– Covers regulations to maintain workplace safety including machinery operation.
5. ANSI B11 Standards:
– Focuses on safety requirements for the construction, care, and use of metalworking machines in the USA.
– Ensures the machine is equipped with necessary guarding, emergency stops, and other safety features.
6. CSA (Canadian Standards Association):
– Standard for Canada ensuring adherence to the safety requirements for electrical, hydraulic, and mechanical systems.
7. UL (Underwriters Laboratories):
– OSHA-recognized certification for machinery to ensure components meet the required safety standards.
8. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances):
– Ensures that the machine does not contain certain hazardous substances, promoting safer work environments.
Ensuring a bolts making machine meets these certifications not only complies with regulatory requirements but also enhances the safety of operations, reduces liability risks, and promotes long-term operational efficiency. Always verify that the machine is tested and certified by accredited bodies to align with the appropriate standards.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “bolts making machine”
Sure! Below are the reference technical parameters of a typical bolts making machine:
1. Machine Capacity:
– Bolt Diameter Range: Typically ranges from 2mm to 42mm.
– Bolt Length Range: Up to 300mm or more, depending on the machine.
2. Production Speed:
– Output Rate: Measured in bolts per minute (BPM), ranges from 30 to 400 BPM based on model and complexity.
3. Power Supply:
– Voltage: Usually 220V-480V, 3-phase.
– Power Consumption: Varies from 5 kW to 50 kW depending on the machine’s size and capabilities.
4. Motor Specifications:
– Motor Type: Generally uses AC induction motors.
– Motor Power: Can range from 5 HP to 100 HP.
5. Machine Dimensions:
– Length, Width, Height: Typically between 2-8 meters in length, 1-3 meters in width, and 1.5-3 meters in height.
6. Weight:
– Machine Weight: Ranges from 2 tons to 15 tons.
7. Control System:
– Typically equipped with PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human-Machine Interface) systems for precision and automation.
8. Forming Stations:
– Number of Stations: Ranges from 1 to 6 forming stations, facilitating multi-stage forming processes.
9. Die Specifications:
– Die Material: Generally high-speed steel or carbide.
– Die Life: Varies based on material and operation, ranging from thousands to millions of cycles.
10. Lubrication System:
– Usually includes automated lubrication to reduce wear and maintenance requirements.
11. Cooling System:
– Mostly equipped with air or water cooling systems to maintain operational temperatures.
12. Safety Features:
– Incorporates emergency stop buttons, safety guards, and interlock systems.
13. Raw Material Compatibility:
– Materials: Capable of working with steel, stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and their alloys.
By understanding these parameters, users can better match a bolts making machine to their production needs and materials to ensure efficiency and quality.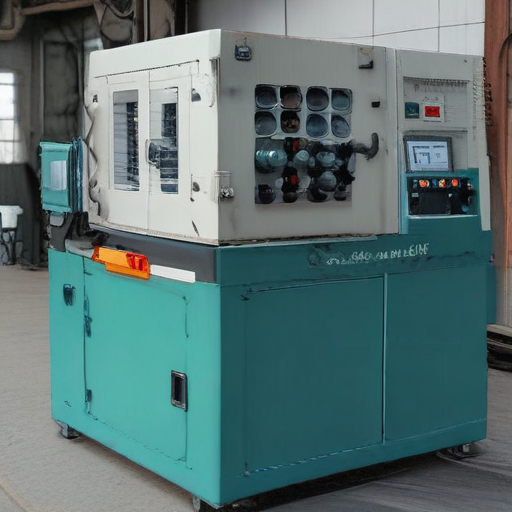
List Product features of “bolts making machine”
Sure, here are the key product features of a bolts making machine, presented concisely:
1. High Precision Manufacturing: Ensures consistent bolt dimensions and tight tolerances.
2. Automated Operation: Minimizes manual labor with fully automated processes, from feeding to finishing.
3. Durable Construction: Made with robust materials for long-term, heavy-duty use.
4. Versatile Bolt Sizes: Capable of producing bolts of various sizes and thread types.
5. High-Speed Production: Facilitates rapid bolt manufacturing, increasing overall productivity.
6. Energy Efficient: Designed to consume minimal power while maintaining high performance.
7. User-Friendly Interface: Easy-to-use control panel for monitoring and adjusting settings.
8. Safety Features: Equipped with emergency stops and safety guards to protect operators.
9. Low Maintenance: Built with reliable components that require minimal maintenance.
10. Advanced Lubrication System: Reduces wear and tear, extending machine lifespan.
11. Quality Control Integration: Allows for real-time monitoring of quality standards.
12. Noise Reduction: Engineered to operate quietly, enhancing workplace comfort.
13. Remote Monitoring: Includes options for remote diagnostics and troubleshooting.
14. Modular Design: Enables easy upgrades and component replacements.
15. Compact Footprint: Optimized design for efficient space utilization.
16. Compatibility: Compatible with various materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel.
17. Eco-Friendly: Incorporates eco-friendly components reducing environmental impact.
18. Rapid Changeover: Facilitates quick changes in bolt specifications with minimal downtime.
19. Custom Programming: Allows customization for specific production requirements.
20. Precision Tooling: Comes with high-quality dies and cutting tools for superior output.
These features collectively ensure the bolts making machine is effective, efficient, and reliable for industrial applications.
List Various Types of “bolts making machine”
Sure, here is a list of various types of bolts making machines:
1. Cold Heading Machines: These machines shape bolts by forcing metal into a die at room temperature, creating the head and initial shape. They are highly efficient and used for mass production.
2. Hot Forging Machines: These use heat to make the metal pliable before shaping it into bolts. They are typically used for larger bolts and specialized applications.
3. Thread Rolling Machines: After the bolt is initially formed, these machines roll threads onto the bolt shaft, creating strong and precise threads through a non-cutting process.
4. Thread Cutting Machines: Unlike thread rolling, these machines cut the threads into the bolt. This method is often used for smaller production runs or specialized bolts.
5. Bolt Part Forming Machines: These machines can perform multiple functions such as heading, threading, and pointing, providing a comprehensive solution for bolt manufacturing.
6. Multi-station Bolt Making Machines: These have multiple dies and stations, allowing for various forming and shaping operations to be completed in a single production cycle, significantly increasing efficiency.
7. High-speed Bolt Making Machines: Designed for maximum production efficiency, these machines can produce thousands of bolts per hour and are often used in large-scale manufacturing environments.
8. Bolt Making CNC Machines: These use computer numerical control (CNC) to ensure high precision in bolt production, allowing for the manufacture of complex and custom bolts.
9. Hydraulic Bolt Making Machines: Utilizing hydraulic pressure, these machines provide powerful and consistent force, suitable for shaping high-strength bolts.
10. Automatic Bolt Making Machines: These highly automated machines can perform multiple stages of bolt production with minimal human intervention, increasing productivity and reducing labor costs.
Each type of machine offers unique benefits and capabilities, making them suitable for specific applications and production requirements in the bolt manufacturing industry.
List Application of “bolts making machine”
A bolts-making machine is an essential piece of equipment in various sectors, providing numerous applications by automating the bolt manufacturing process. Below are some primary applications:
Industrial Manufacturing
1. Automotive Industry: Essential for producing bolts used in vehicle assembly, including engine, chassis, and body components.
2. Aerospace Industry: Vital for manufacturing high-strength bolts used in aircraft construction and maintenance.
3. Electronics: Produces small precision bolts used in assembling electronic devices and appliances.
Construction
4. Building Infrastructure: Produces bolts used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
5. HVAC Systems: Used to create bolts for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning installations.
Mechanical and Electrical Engineering
6. Machinery Assembly: Necessary for creating bolts used in various machinery and equipment.
7. Electrical Assemblies: Produces specific bolts used in electrical panel installations and transformer assemblies.
Fasteners Supply
8. Hardware Stores: Supplies bolts in bulk for retail, catering to DIY enthusiasts and small contractors.
9. Specialized Bolt Suppliers: Produces custom bolts for specialized industries, such as marine or oil and gas sectors.
Agricultural Equipment
10. Farm Machinery: Bolts produced for use in assembling and maintaining agricultural equipment.
Railways
11. Railway Construction and Maintenance: Produces high-durability bolts for railway tracks and train components.
Marine Applications
12. Shipbuilding: Necessary for producing corrosion-resistant bolts used in ship construction and maintenance.
Renewable Energy
13. Wind Turbines and Solar Panels: Produces bolts for assembling and installing wind turbines and solar panel structures.
These applications highlight the versatility and critical role that bolts-making machines play across various industries, facilitating both everyday products and essential infrastructure.
List Buyer Types of “bolts making machine”
Certainly! Here are the primary buyer types for a “bolts making machine”:
1. Manufacturing Companies: These are businesses involved in large-scale production of bolts and fasteners for various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. They typically require high-capacity machines to meet large volume demands.
2. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Smaller manufacturing units or workshops needing to produce bolts on a smaller scale. They look for cost-effective machines that offer good performance at lower volumes.
3. Automotive Industry Suppliers: Companies supplying components to automotive manufacturers. They need machines that can produce bolts with high precision and consistency to meet industry standards.
4. Construction Firms: These buyers often need custom bolts for specific construction projects and may opt for their own machines to produce bolts on-demand, ensuring timely project completion.
5. Aerospace and Defense Contractors: These buyers require highly specialized bolts made to stringent specifications, necessitating machines capable of producing high-precision bolts for critical applications.
6. Maintenance and Repair Operations (MROs): Organizations that provide maintenance and repair services for industrial equipment. They might invest in bolt-making machines to manufacture custom bolts specific to repair needs.
7. Industrial Distributors and Suppliers: Companies that supply a wide range of bolts and fasteners to other industries. They may use bolt-making machines to diversify their product offerings and ensure a steady supply.
8. Agricultural Equipment Manufacturers: Given that agricultural machinery often requires robust and durable bolts, these manufacturers might purchase bolt-making machines to fulfill their specific needs.
9. Metal Fabrication Shops: These are workshops specializing in metal components. Owning a bolt-making machine allows them to create custom bolts for various projects, enhancing their service offering.
10. Research and Development Laboratories: Facilities focused on developing new materials and fastening technologies may need bolt-making machines to prototype and test new designs.
These buyer types range from large corporations to specialized firms, all requiring bolts to maintain, construct, or innovate within their respective fields.
List “bolts making machine” Project Types for Different Industries
Creating a bolt-making machine that caters to different industries involves varying specifications, tailored features, and unique design considerations. Below are key project types for distinct industries:
1. Automotive Industry:
– High-Strength Bolts Machines: Manufacture bolts with high tensile strength.
– Precision Fasteners Machines: Ensure exact specifications for critical automotive components.
2. Construction Industry:
– Heavy-Duty Bolt Machines: Produce large, durable bolts for structural applications.
– Corrosion-Resistant Bolt Machines: For environments exposed to moisture and chemicals.
3. Aerospace Industry:
– Lightweight Alloy Bolt Machines: Manufacture bolts with materials like titanium and aluminum.
– High-Precision Micro Bolt Machines: For small, intricate components needing high precision.
4. Electronics Industry:
– Miniature Bolt Machines: Create tiny bolts for securing electronic components.
– Specialized Coating Bolt Machines: Apply coatings that prevent electromagnetic interference.
5. Marine Industry:
– Saltwater-Resistant Bolt Machines: Produce bolts with high corrosion resistance for marine environments.
– Heavy-Duty Marine Bolt Machines: For large vessels and sub-sea structures.
6. Medical Industry:
– Sterilizable Bolt Machines: Manufacture bolts that can withstand sterilization processes.
– Bio-compatible Bolt Machines: Ensure bolts are safe for use in medical devices.
7. Energy Industry:
– High-Temperature Bolt Machines: Produce bolts able to endure extreme temperatures, ideal for power plants.
– Heavy-Duty Fastener Machines: For renewable energy structures like wind turbines.
8. Railway Industry:
– Vibration-Resistant Bolt Machines: Bolts that can withstand constant vibration and shock.
– Heavy Load Bearing Bolt Machines: Ensure bolts can carry significant weight and force.
Each project type involves specific material selection, precision engineering, and tailoring manufacturing processes to meet the respective industry standards and requirements.
bolts making machine Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Upgrading and customizing a bolts making machine can significantly enhance its efficiency, precision, and product quality. Here are some recommended accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options:
1. Automated Feeding Systems:
– Vibratory Bowl Feeders: Automate bolt feeding, reducing manual intervention and increasing throughput.
– Hopper Systems: Ensure continuous material supply, minimizing downtime.
2. Control Systems:
– PLC Integration: Enhance machine control, allowing for programmable operations, better diagnostics, and improved automation.
– Touchscreen HMIs: Facilitate easier and more intuitive user interaction.
3. Tooling and Dies:
– High-Precision Dies: Improve the accuracy of bolt dimensions and threading.
– Quick-Change Tooling: Reduce setup times and enhance flexibility for different bolt sizes and types.
4. Lubrication Systems:
– Automatic Lubrication Units: Maintain optimal lubrication of moving parts, reducing wear and extending machine life.
– Mist Lubrication: Provide consistent and controlled lubrication for high-speed operations.
5. Sensors and Quality Control:
– Laser Measuring Systems: Ensure bolts meet precise dimensional requirements.
– Camera Inspection Systems: Automatically detect defects and ensure high quality.
6. Heat Treatment Integration:
– In-Line Heat Treatment Units: Integrate heat treatment to harden bolts as part of the manufacturing process.
– Temperature Control Systems: Monitor and adjust heat treatment processes for optimal results.
7. Customization Options:
– Custom Sized Machines: Tailored to specific space constraints and production needs.
– Specialized Bolt Production: Customize the machine to produce specialty bolts, such as those with unique threading or head designs.
By leveraging these accessories, upgrades, and customization options, manufacturers can boost productivity, ensure consistent quality, and adapt to various production requirements.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “bolts making machine”
Quality Control in Bolt Manufacturing
1. Raw Material Inspection: Verify the quality and chemical composition of the raw steel or alloy.
2. Dimensional Checks: Measure length, diameter, and thread conformations using precision instruments.
3. Hardness Testing: Ensure the bolts meet specified hardness using Rockwell or Brinell hardness tests.
4. Tensile Testing: Test for tensile strength and yield point to confirm mechanical properties.
5. Surface Finish Inspection: Evaluate surface quality to detect cracks or flaws via visual inspections or dye penetrant tests.
6. Thread Quality: Check thread precision using thread gauges to ensure they meet the required standards.
7. Plating and Coating: Verify coating thickness and adhesion through tests like salt spray and peel tests.
8. Sampling and Batch Testing: Implement statistical process control (SPC) to monitor and maintain quality.
Manufacturing Process of Bolts Making Machine
1. Design and Engineering:
– Specification Development: Define machine specifications based on the types and sizes of bolts to be produced.
– CAD Modelling: Create detailed designs using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software.
2. Raw Material Selection:
– Material Choice: Choose high-grade steel or alloys for durability of the machine components.
3. Component Manufacturing:
– Machining: Fabricate machine parts such as dies, mandrels, and frames.
– Heat Treatment: Harden crucial components to extend wear life.
– Grinding and Polishing: Ensure components are finished to precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
4. Assembly:
– Subassembly: Assemble individual components such as feeding mechanisms, cutting tools, and threading dies.
– Full Assembly: Integrate subassemblies into the main machine frame.
5. Calibration and Testing:
– Initial Calibration: Set the machine to produce bolts within specified tolerances.
– Trial Runs: Perform test runs to fine-tune settings and verify functionality.
– Quality Testing: Ensure the machine operates efficiently and produces bolts that meet predefined standards.
6. Final Inspection and Packaging:
– Inspection: Conduct comprehensive final inspections to affirm all components function correctly.
– Packaging: Pack the machine securely for shipment and delivery.
By maintaining stringent quality control and following a meticulous manufacturing process, bolt-making machines can consistently produce high-quality bolts for various applications.
How to use “bolts making machine”
Using a bolts making machine involves several key steps to ensure efficiency and safety. Here’s a concise guide:
1. Preparation:
– Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the machine’s operation manual.
– Safety Gear: Wear appropriate safety gear including gloves, goggles, and ear protection.
– Raw Material: Load the correct type and size of metal rods into the machine’s feeder system.
2. Machine Setup:
– Tooling Setup: Install the appropriate dies and cutting tools based on the desired bolt size and specification.
– Adjust Settings: Set the machine parameters like cutting speed, feeding speed, and thread dimensions according to your bolt specifications.
– Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts are properly lubricated to minimize friction and wear.
3. Operation:
– Start Machine: Power on the machine and allow it to go through initial calibration if required.
– Feeding Material: The machine will automatically feed the metal rods into the cutting area where they will be shaped into bolts.
– Forming Bolts: The rods will be cut to length, headed (if necessary), and threaded according to the set parameters.
– Monitoring: Constantly monitor the operation for any anomalies or issues. Adjust settings if necessary.
4. Quality Control:
– Inspection: Regularly inspect produced bolts to ensure they meet quality standards and specifications.
– Adjustment: Make any needed adjustments to the machine settings if bolts do not meet the desired quality.
5. Shutdown:
– Turn Off: Power down the machine following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
– Clean: Clean the machine and remove any metal shavings or debris.
– Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance checks as recommended.
By following these steps, you can efficiently and safely operate a bolts making machine, ensuring high-quality production.
“bolts making machine” Comparative Analysis
When conducting a comparative analysis of bolts making machines, several essential factors must be considered: productivity, precision, automation level, cost, and maintenance requirements. Here’s a succinct comparison:
1. Productivity: High-speed forging machines outperform their counterparts, capable of producing up to 500 bolts per minute. Cold heading machines, while slightly slower, offer a production rate of approximately 300 bolts per minute. Thread rolling machines, although crucial for threading bolts, have a lower output, averaging around 200 bolts per minute.
2. Precision: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) bolt making machines deliver exceptional precision, handling complex shapes and tight tolerances with ease due to their programmable nature. Cold heading and thread rolling machines are also precise but may require adjustments for varying bolt specifications.
3. Automation Level: The latest high-speed forging and CNC machines come equipped with advanced automation, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency. Basic cold heading machines are less automated, relying more on skilled labor. Integration of robotics and IoT (Internet of Things) in modern machines further enhances automation, allowing for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
4. Cost: High-speed forging machines and CNC machines typically entail a higher initial investment, ranging from $100,000 to $500,000 depending on capabilities and size. Cold heading machines, being less complex, range from $50,000 to $200,000. Basic thread rolling machines are the most cost-effective, priced between $20,000 and $100,000.
5. Maintenance Requirements: CNC machines, while highly automated, demand regular software updates and occasional technical servicing. High-speed forging machines, given their high output and operating speeds, require regular mechanical maintenance to sustain performance. Cold heading and thread rolling machines are relatively easier to maintain but necessitate periodic check-ups to ensure consistent quality.
In summary, the choice of bolts making machine hinges on the specific needs of production volume, precision, and budget. High-speed forging machines are ideal for large-scale production, CNC machines for precision tasks, and cold heading machines for balanced performance and cost-effectiveness.
“bolts making machine” Warranty and Support
When investing in a bolts-making machine, it is essential to consider the warranty and support services provided by the manufacturer. Typically, reputable manufacturers offer a warranty period ranging from one to three years. This warranty covers defects in materials and workmanship under normal usage conditions. Specific details, such as which parts are covered or excluded, should be clarified before purchase to avoid any unexpected costs.
Support services are equally crucial. Comprehensive customer support should include:
1. Installation Support: Often, manufacturers provide assistance during the machine installation phase to ensure proper setup and functioning.
2. Training: Operators may need training to properly use and maintain the machine, which can be offered on-site or online.
3. Technical Support: Access to a knowledgeable technical support team via phone, email, or live chat is vital for troubleshooting and resolving issues promptly.
4. Spare Parts Availability: The manufacturer should guarantee the availability of spare parts during and beyond the warranty period to minimize downtime in case of parts failure.
5. Regular Maintenance Plans: Some manufacturers offer maintenance plans that include routine inspections and servicing to enhance the machine’s longevity.
6. Software Updates: If the machine includes software components, regular updates should be provided to improve performance and address any identified vulnerabilities.
Before making your purchase, it’s advisable to read customer reviews and possibly contact current users of the machinery to gauge their satisfaction with the warranty and support services. This ensures that your investment is safeguarded and that any operational issues can be swiftly managed, ultimately leading to a more efficient and productive experience.
List “bolts making machine” FAQ
Bolts Making Machine FAQ
1. What is a bolts making machine?
– A bolts making machine is specialized equipment used to manufacture bolts of various sizes and types. The process typically involves cutting, heading, threading, and sometimes heat treating to produce durable and precise bolts.
2. What types of bolts can be produced?
– These machines can produce hex bolts, carriage bolts, anchor bolts, flange bolts, and more, depending on the machine’s capabilities and configuration.
3. What materials can be processed?
– Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum. The material choice depends on the intended application of the bolts.
4. How does the bolts making process work?
– The process generally involves several stages: wire cutting, cold forging or heading to shape the bolt head, threading (either rolling or cutting), and sometimes heat treatment and surface finishing.
5. What are the machine’s capacity and speed?
– Capacity and speed vary by machine model. High-speed machines can produce hundreds of bolts per minute, while smaller, more versatile machines may have lower output but can handle a wider range of sizes.
6. What are the power requirements?
– Power requirements differ based on the machine’s size and type but typically range from several kilowatts (kW) to tens of kW. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications.
7. Do I need special training to operate these machines?
– Yes, operating a bolt-making machine requires specialized training to ensure safety and efficiency. Many manufacturers provide training programs or manuals.
8. How much does a bolts making machine cost?
– Prices can vary widely based on the machine’s size, capacity, features, and brand. Entry-level machines may cost a few thousand dollars, while high-end, high-capacity machines can be well into the six-figure range.
9. What are the maintenance requirements?
– Regular maintenance includes lubrication, checking and replacing worn parts, and ensuring all mechanical and electrical components are in good working order. Routine inspections are essential for optimal performance and longevity.
10. Can the machine be customized?
– Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific production needs or integrate with existing equipment.
Understanding these key points can help in selecting the right bolts making machine for your manufacturing needs.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about bolts making machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions about sourcing bolt-making machines from China, along with concise answers:
1. What types of bolt-making machines are available?
– China offers various types such as cold heading machines, thread rolling machines, and bolt-forming machines. Each type caters to different sizes and specifications of bolts.
2. How do Chinese bolt-making machines compare in quality?
– Chinese manufacturers often use modern technology and standards. Leading companies offer machines that comply with international certifications like ISO and CE, ensuring competitive quality.
3. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing and delivery?
– Lead times vary but generally range from 30 to 60 days. Custom orders may take longer. Always confirm with the manufacturer.
4. Can I get a custom-designed machine according to my specific needs?
– Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization services to meet specific requirements such as size, thread type, and material compatibility.
5. What is the average cost range for these machines?
– Prices can vary based on machine type and specifications. Basic models may start around $10,000 while more advanced or larger models can exceed $100,000.
6. How does the after-sales service work?
– Reputable suppliers typically offer warranties, spare parts, and technical support. Many provide remote assistance and on-site services if necessary.
7. What payment terms are acceptable?
– Common terms include T/T (Bank Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes Western Union. A down payment (usually 30%) with the balance paid before shipping is typical.
8. How do I verify the reliability of a Chinese supplier?
– Check for certifications, read reviews, ask for references, and consider using third-party inspection services like SGS or TÜV. Visiting the factory is also beneficial.
9. What shipping options are available?
– Suppliers typically offer FOB (Free on Board) but can also arrange CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) or EXW (Ex Works). Air and sea freight are common methods.
10. Are there language barriers during transactions?
– Most major suppliers have English-speaking staff. Clear communication is usually feasible via email, phone, and video conferencing.
This succinct guide should assist buyers in sourcing bolt-making machines from China effectively.





