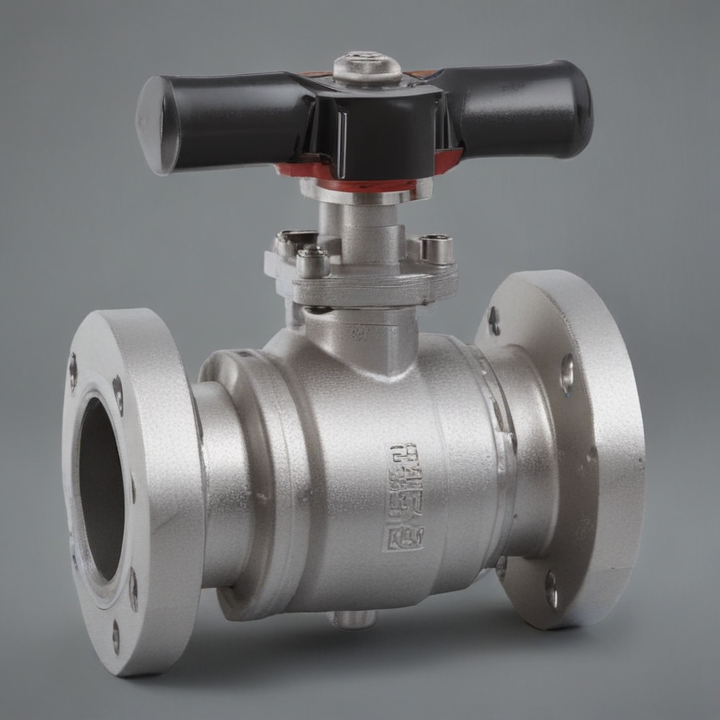
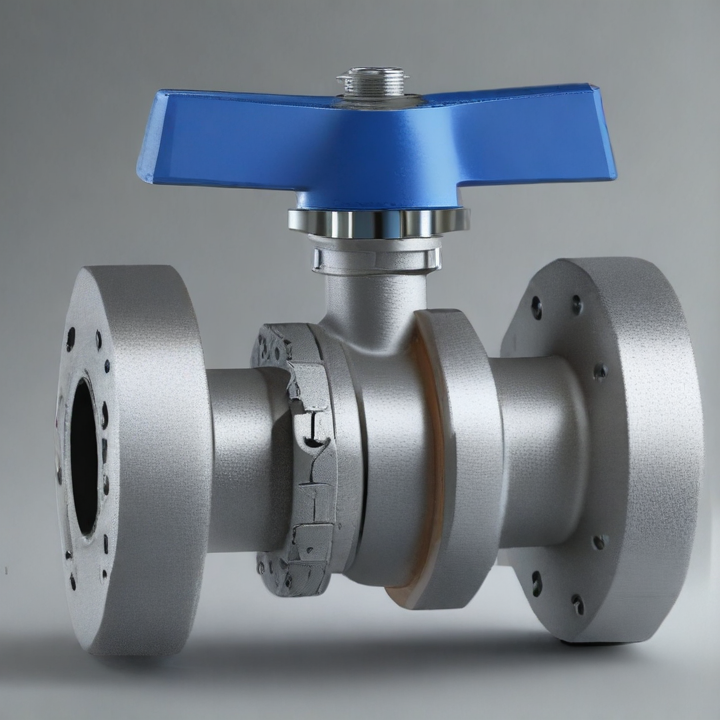
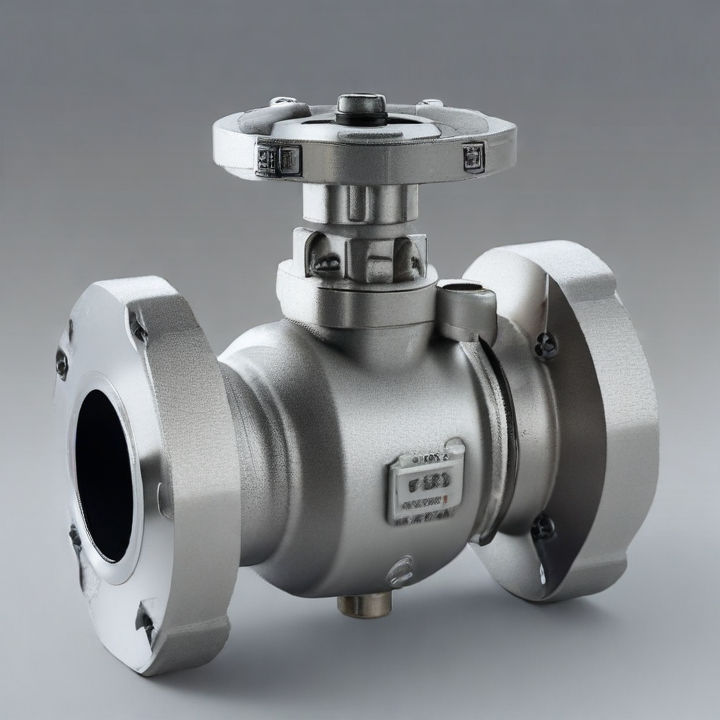
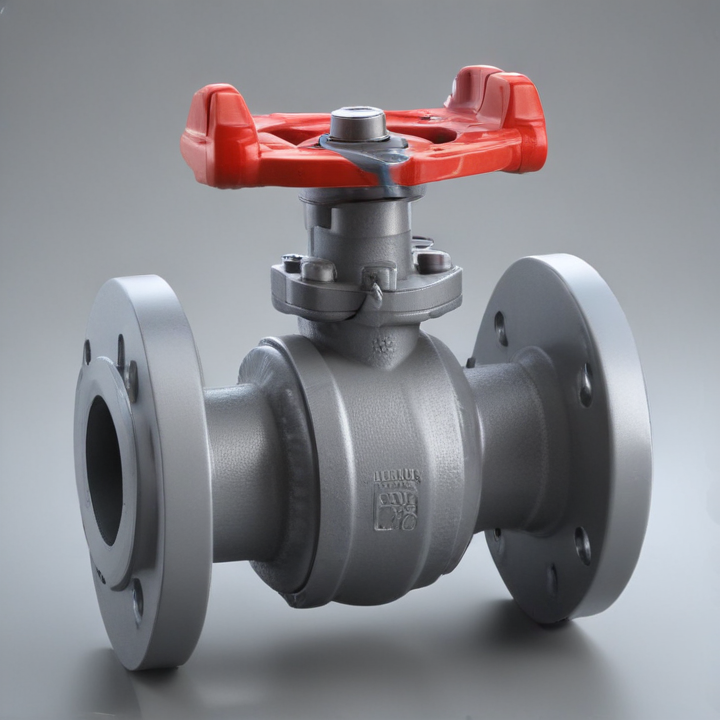
flanged ball valve Safety Certifications
Flanged ball valves are critical components in various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient control of fluid flow. Their safety and performance are governed by several key certifications and standards to guarantee their reliability and suitability for specific applications. Here are some essential safety certifications for flanged ball valves:
1. ISO 9001: This standard ensures that the valve manufacturer maintains a quality management system that meets international requirements for consistency and improvement of products and services. It is a fundamental certification for manufacturers.
2. API 6D: The American Petroleum Institute (API) specifies the design, manufacturing, testing, and documentation requirements for pipeline valves, including ball valves. API 6D certification is crucial for valves used in the oil and gas industry.
3. ASME B16.34: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provides standards for the design, materials, manufacturing, and testing of valves. ASME B16.34 certification ensures that flanged ball valves can withstand the specified pressures and temperatures.
4. CE Marking: This certification indicates that the valve complies with the European Union’s safety, health, and environmental requirements. It is mandatory for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA).
5. PED (Pressure Equipment Directive): The PED certification is a European directive that ensures the valve can handle the specified pressure conditions. It is required for all pressure equipment sold in the EU.
6. ATEX: This certification is necessary for valves used in potentially explosive environments. ATEX ensures that the valve is designed to prevent ignition in hazardous areas.
7. SIL (Safety Integrity Level): SIL certification indicates the valve’s reliability in safety instrumented systems, particularly in critical safety applications where failure could lead to significant hazards.
These certifications collectively ensure that flanged ball valves are safe, reliable, and compliant with international standards, providing confidence to users in various industries.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “flanged ball valve”
A flanged ball valve is a type of valve with flanges on both ends that provide a means for bolting the valve to a pipe system. Below are the key technical parameters for a flanged ball valve:
1. Size Range:
– Typically from ½ inch to 24 inches (DN15 to DN600).
2. Pressure Ratings:
– ANSI Class 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500.
– PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN64, PN100 (for European standards).
3. Temperature Range:
– Depending on materials, typically from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F).
4. Materials:
– Body: Carbon steel (e.g., ASTM A216 WCB), stainless steel (e.g., ASTM A351 CF8/CF8M), cast iron, ductile iron.
– Ball: Stainless steel, carbon steel, chrome-plated brass.
– Seat: PTFE, RPTFE, PEEK, metal-seated options for high temperatures.
5. End Connections:
– Flanges conform to ASME B16.5, EN1092-1 standards.
– Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), and Ring Type Joint (RTJ).
6. Operation:
– Manual (lever or gear-operated), pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuators.
7. Design Standards:
– API 6D, ASME B16.34, ISO 17292.
8. Face-to-Face Dimensions:
– ANSI B16.10, ISO 5752.
9. Fire Safe Design:
– Compliance with API 607, API 6FA.
10. Testing Standards:
– API 598, ISO 5208.
11. Flow Characteristics:
– Full port (full bore) or reduced port (reduced bore).
12. Leakage Class:
– Typically Class VI per ANSI/FCI 70-2 for soft-seated valves, Class V for metal-seated valves.
13. Certification:
– ATEX, CE, SIL (Safety Integrity Level), NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 for sour gas applications.
These parameters provide essential information for selecting and specifying flanged ball valves for various industrial applications, ensuring compatibility with the system requirements and compliance with relevant standards.
List Product features of “flanged ball valve”
A flanged ball valve is a critical component in various industrial applications, designed to regulate the flow of fluids. Here are its key features:
1. Flanged Connections: These valves feature flanges on either end, allowing for secure, bolted connections to the piping system. This design facilitates easy installation, removal, and maintenance.
2. Ball Mechanism: The core of the valve is a spherical ball with a central hole (bore). When the ball is rotated 90 degrees, the flow is either allowed or blocked, providing quick and reliable shutoff.
3. Full Port Design: Many flanged ball valves are designed with a full port, meaning the bore is the same diameter as the pipeline, ensuring minimal pressure drop and allowing for unrestricted flow.
4. Materials: They are typically constructed from robust materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or PVC, making them suitable for a wide range of temperatures and pressures and providing resistance to corrosion and wear.
5. Sealing Mechanism: High-quality seats and seals made from materials like PTFE (Teflon) or other elastomers ensure a tight shutoff and prevent leakage, even in high-pressure applications.
6. Actuation Options: Flanged ball valves can be manually operated with a handle or lever. They can also be automated using pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuators for remote control and automation in complex systems.
7. Versatility: These valves are suitable for various applications, including water, oil, gas, chemicals, and steam. Their design allows them to handle diverse flow conditions and media types.
8. Pressure and Temperature Ratings: They are designed to operate under a wide range of pressures and temperatures, ensuring flexibility and reliability in demanding environments.
9. Maintenance and Durability: The design facilitates easy maintenance, with features like blow-out proof stems and anti-static devices enhancing safety and longevity. The valves are built for durability, ensuring long service life with minimal maintenance requirements.
These features make flanged ball valves a versatile, reliable, and essential component in many industrial systems.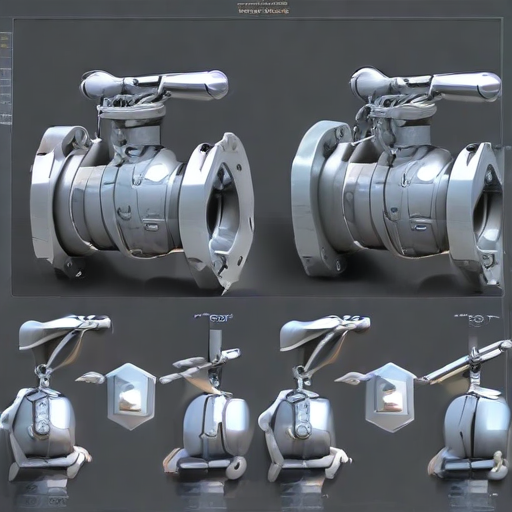
List Various Types of “flanged ball valve”
Flanged ball valves are essential in various industrial applications due to their reliability and ease of operation. Here are some key types:
1. Floating Ball Valve:
– The ball is suspended in the fluid, and pressure from the flow pushes it against the downstream seat, creating a seal. This type is suitable for low to medium pressure applications.
2. Trunnion Mounted Ball Valve:
– The ball is supported by trunnions (shafts) at the top and bottom, which reduces the torque required to operate the valve. Ideal for high-pressure and large diameter applications.
3. Top Entry Ball Valve:
– The valve allows for the removal of internal parts from the top without removing the valve from the pipeline. This design simplifies maintenance and repair.
4. Fully Welded Ball Valve:
– The body of the valve is welded, ensuring no risk of leakage from body joints. This type is used in buried pipelines or other critical applications.
5. Three-Way Ball Valve:
– This valve type has three ports and can be used for mixing or diverting flow. It is available in “L” or “T” configurations for different flow patterns.
6. Cryogenic Ball Valve:
– Designed for extremely low temperatures, these valves are used in applications involving liquefied gases. They feature extended bonnets to protect the stem seals from cold temperatures.
7. V-Port Ball Valve:
– The ball has a “V” shaped notch that allows for better flow control and throttling capabilities. Suitable for applications requiring precise flow control.
8. Double Block and Bleed Ball Valve:
– This valve type provides two sealing surfaces and allows for bleeding of the cavity between the seats. It is used for applications where isolation is critical for safety and maintenance.
Each type of flanged ball valve offers unique advantages and is chosen based on specific application requirements, pressure ratings, and environmental conditions.
List Application of “flanged ball valve”
A flanged ball valve is a versatile and widely used type of valve in various industries due to its robust design and efficient operation. Here are some key applications:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Pipeline Systems: Used to control the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products in pipelines.
– Offshore Platforms: Essential for isolating and regulating fluid flow in harsh offshore environments.
2. Chemical and Petrochemical Plants:
– Process Lines: Ideal for handling aggressive chemicals and corrosive fluids due to their durable construction.
– Safety Systems: Utilized in emergency shutdown systems to quickly isolate sections of a plant.
3. Water and Wastewater Treatment:
– Flow Control: Used in municipal and industrial water treatment facilities for regulating water flow.
– Sludge Handling: Effective in handling thick, abrasive sludge in wastewater systems.
4. Power Generation:
– Cooling Systems: Employed in cooling water circuits in power plants.
– Steam Distribution: Suitable for controlling high-temperature steam flow in thermal power plants.
5. Pharmaceutical and Food Processing:
– Sanitary Applications: Used in processes requiring high levels of hygiene and cleanliness, thanks to their ability to provide tight shut-off.
– Fluid Transfer: Critical for managing the flow of liquids and gases in various production stages.
6. HVAC Systems:
– Heating and Cooling: Used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to control the flow of heating or cooling fluids.
– Building Automation: Integrated into automated systems for efficient building climate control.
7. Marine Applications:
– Ballast Systems: Used in ballast water systems on ships to manage water flow and balance the vessel.
– Firefighting Systems: Integrated into onboard firefighting systems for reliable fluid control.
8. Mining and Mineral Processing:
– Slurry Handling: Suitable for handling abrasive slurries in mining operations.
– Separation Processes: Used in various mineral separation processes due to their durability and tight sealing capabilities.
Flanged ball valves are favored in these applications for their reliability, ease of operation, and maintenance, as well as their ability to provide tight shut-off in both high and low-pressure conditions.
List Buyer Types of “flanged ball valve”
Buyers of flanged ball valves generally fall into several key categories, each with specific requirements and applications. These categories include:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Upstream: Exploration and production companies use flanged ball valves for drilling and extraction operations due to their ability to handle high pressures and corrosive environments.
– Midstream: Pipeline operators use these valves for transportation and storage facilities, needing reliable flow control and isolation.
– Downstream: Refineries and petrochemical plants require robust valves for processing, distribution, and refining activities.
2. Chemical Industry:
– Manufacturers: Companies involved in the production of chemicals use flanged ball valves for handling aggressive and hazardous fluids, ensuring safety and efficiency in their processes.
3. Water and Wastewater Treatment:
– Municipal and Industrial Facilities: These facilities use flanged ball valves for controlling and isolating flow in treatment plants, managing large volumes of water and effluents with reliability and ease of maintenance.
4. Power Generation:
– Thermal and Nuclear Plants: These plants require flanged ball valves for high-pressure steam and cooling water systems, where durability and high performance are critical.
– Renewable Energy: Facilities like geothermal plants also use these valves for their high-temperature fluid handling capabilities.
5. Pharmaceutical and Food & Beverage Industries:
– Manufacturing Plants: These industries need flanged ball valves that meet strict hygiene and safety standards, ensuring contamination-free processing and consistent quality.
6. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning):
– Commercial and Industrial Buildings: These systems use flanged ball valves for efficient control and regulation of heating and cooling fluids.
7. Marine and Shipbuilding:
– Shipyards and Fleets: These buyers require durable flanged ball valves for various on-board systems, including fuel, water, and wastewater management.
Each buyer type has unique needs, such as pressure ratings, material compatibility, and regulatory compliance, driving their selection of flanged ball valves.
List “flanged ball valve” Project Types for Different Industries
Flanged Ball Valve Project Types for Different Industries
1. Oil and Gas Industry
– Pipeline Systems: Used for isolating and regulating flow in pipelines transporting crude oil and natural gas.
– Refinery Applications: Employed in various processing units to control the flow of hydrocarbons.
2. Chemical Industry
– Process Flow Control: Essential for managing the flow of aggressive chemicals and solvents in chemical processing plants.
– Safety Systems: Implemented in emergency shut-off systems to ensure safety and prevent hazardous leaks.
3. Water and Wastewater Treatment
– Water Distribution Networks: Utilized in potable water supply systems to control water flow.
– Wastewater Management: Applied in sewage treatment plants for handling wastewater streams and sludge.
4. Power Generation
– Cooling Systems: Used in the cooling water circuits of power plants to regulate water flow.
– Steam Distribution: Essential for controlling steam flow in thermal power plants.
5. Food and Beverage Industry
– Sanitary Processing: Implemented in processing lines to ensure the hygienic handling of liquids.
– CIP Systems: Used in Clean-in-Place systems to manage the flow of cleaning solutions.
6. Pharmaceutical Industry
– Sterile Processing: Applied in the production of sterile products to control fluid flow without contamination.
– Chemical Feed Systems: Used to manage the flow of chemical reagents in drug manufacturing processes.
7. HVAC Systems
– Heating Systems: Used to control the flow of hot water or steam in heating systems.
– Cooling Systems: Essential for regulating the flow in chilled water systems.
8. Marine Industry
– Ballast Water Systems: Applied in controlling ballast water for stability of ships.
– Fuel Management: Used in marine engines to manage fuel flow efficiently.
9. Mining and Metals
– Slurry Transport: Employed in the transport of mineral slurries in mining operations.
– Process Water: Used in managing the flow of process water in metal processing.
10. Pulp and Paper Industry
– Pulp Processing: Applied in the control of chemicals and pulp stock in paper mills.
– Water Treatment: Essential in managing the flow of water in the pulp and paper manufacturing process.
These varied applications highlight the versatility and critical importance of flanged ball valves across different industrial sectors.
flanged ball valve Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Flanged Ball Valve Accessories, Upgrades, and Custom Manufacturing Options
Flanged ball valves are vital components in fluid control systems, known for their durability, efficiency, and tight sealing capabilities. To enhance their performance and extend their functionality, various accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available.
#### Accessories
1. Actuators: Electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators automate valve operations, improving precision and control.
2. Positioners: Ensure the valve reaches the desired position accurately, essential for precise flow regulation.
3. Limit Switches: Provide feedback on valve position, enhancing system monitoring and control.
4. Locking Devices: Secure the valve in a specific position to prevent accidental operation.
5. Stem Extensions: Facilitate valve operation in hard-to-reach locations.
6. Handwheels: Offer manual operation for ease of use in non-automated systems.
7. Gear Operators: Allow for smooth manual operation, especially for larger valves.
#### Upgrades
1. High-Temperature Seals: Upgrade seals to withstand extreme temperatures, enhancing valve longevity and reliability.
2. Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Use of advanced materials like Hastelloy, Inconel, or titanium for increased resistance to corrosive environments.
3. Fire-Safe Designs: Implement fire-safe features to ensure valve integrity during fire incidents.
4. Cryogenic Extensions: Tailor valves for low-temperature applications with special extensions and seals.
5. Noise and Vibration Reduction: Integrate components that minimize noise and vibration for smoother operation.
#### Custom Manufacturing Options
1. Tailored Port Configurations: Customize port sizes and shapes to meet specific flow requirements.
2. Special Coatings: Apply coatings like PTFE or epoxy for enhanced chemical resistance.
3. Size Variations: Produce valves in non-standard sizes for unique applications.
4. Pressure Ratings: Customize valves to handle higher or lower pressure conditions than standard offerings.
5. Customized End Connections: Adapt end connections (e.g., threaded, welded) to fit specific piping systems.
These enhancements and custom options ensure that flanged ball valves can be optimized for diverse industrial applications, offering improved performance, reliability, and longevity tailored to specific operational needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “flanged ball valve”
Quality Control
1. Material Verification: Ensuring raw materials meet specified standards.
2. Dimensional Inspection: Checking dimensions against engineering drawings.
3. Pressure Testing: Subjecting the valve to various pressure levels to test for leaks.
4. Functional Testing: Verifying the valve operates correctly under simulated conditions.
5. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Using techniques like ultrasonic or radiographic testing to detect internal defects.
6. Surface Finish Inspection: Ensuring smoothness and lack of surface defects.
7. Coating and Corrosion Resistance: Testing protective coatings for durability and effectiveness.
8. Documentation Review: Verifying all quality checks and tests are documented properly.
9. Final Inspection: Comprehensive review before shipping to ensure all standards are met.
Manufacturing Process
1. Design and Engineering: Creating detailed designs and specifications.
2. Material Selection: Procuring high-quality materials based on design requirements.
3. Forging and Casting: Shaping raw materials into rough valve components.
4. Machining: Precision machining of components to achieve final dimensions.
5. Assembly: Assembling the valve components, including the ball, seats, stem, and flanges.
6. Welding: Welding parts together if necessary, followed by heat treatment to relieve stresses.
7. Surface Treatment: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
8. Pressure and Functional Testing: Testing assembled valves for leaks and operational efficiency.
9. Quality Control: Conducting various inspections and tests as outlined in the quality control section.
10. Packaging and Shipping: Ensuring valves are packaged securely for transportation.
This comprehensive approach to quality control and a detailed manufacturing process ensures the reliability and durability of flanged ball valves, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
How to use “flanged ball valve”
A flanged ball valve is used to control the flow of liquids and gases in a piping system. It features a ball with a hole through the center, which rotates to either allow or block the flow. Here’s a brief guide on how to use a flanged ball valve:
1. Installation:
– Positioning: Ensure the valve is installed in the correct orientation, with the flow direction indicated by an arrow on the valve body.
– Flange Connection: Align the flanges of the valve with the flanges of the pipe. Use appropriate gaskets between the flanges to ensure a tight seal.
– Bolting: Secure the valve by bolting the flanges together. Tighten the bolts in a crisscross pattern to evenly distribute pressure.
2. Operation:
– Opening the Valve: Rotate the handle or actuator 90 degrees to align the ball’s hole with the flow path, allowing fluid to pass through.
– Closing the Valve: Rotate the handle or actuator back 90 degrees to turn the ball so the hole is perpendicular to the flow path, stopping the fluid flow.
– Partial Flow Control: Position the handle between fully open and fully closed to regulate the flow rate, if precise flow control is required.
3. Maintenance:
– Regular Inspection: Check for leaks, wear, or damage periodically.
– Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to the ball and stem to ensure smooth operation.
– Cleaning: Clean the valve as needed to remove debris that might obstruct its function.
4. Safety:
– Pressure Check: Ensure the system is depressurized before maintenance or inspection.
– Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for installation and maintenance to avoid damaging the valve.
By following these steps, you can effectively use and maintain a flanged ball valve to control fluid flow in your piping system.
“flanged ball valve” Comparative Analysis
A flanged ball valve is a critical component in fluid handling systems, offering reliable shut-off and control of liquids and gases. This analysis compares different types of flanged ball valves based on key factors: material, design, application, and performance.
Material:
1. Stainless Steel: Highly resistant to corrosion, suitable for a wide range of temperatures and pressures, often used in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
2. Carbon Steel: Durable and cost-effective, suitable for high-pressure applications, but less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for low-pressure applications and aggressive chemicals, but limited to lower temperatures and pressures.
Design:
1. Two-Piece Design: Common for standard applications, easy to maintain, with two body parts bolted together, allowing for disassembly and cleaning.
2. Three-Piece Design: Provides better maintenance options, as the center section can be removed for servicing without disturbing the pipeline, suitable for frequent maintenance needs.
3. Floating Ball Design: The ball is not fixed, allowing it to move slightly to press against the seat for a tight seal, suitable for low to medium pressure.
4. Trunnion Mounted Ball Design: The ball is fixed, and additional mechanical anchoring provides a secure seal, suitable for high-pressure applications.
Application:
1. Industrial: Flanged ball valves in stainless steel or carbon steel are preferred for their durability and ability to handle high pressures and temperatures.
2. Commercial: PVC valves are often used due to their cost-effectiveness and resistance to corrosion from chemicals used in commercial cleaning and water treatment.
3. Residential: Simpler designs like two-piece valves in materials like PVC are common for household plumbing due to ease of use and installation.
Performance:
1. Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Stainless steel and carbon steel valves offer higher ratings compared to PVC.
2. Durability and Maintenance: Three-piece and trunnion mounted designs provide better options for maintenance and longer service life in demanding environments.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right flanged ball valve depends on the specific requirements of the application, including material compatibility, pressure and temperature conditions, and maintenance needs. Stainless steel valves offer superior performance in harsh environments, while PVC valves provide a cost-effective solution for less demanding applications.
“flanged ball valve” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Flanged Ball Valves
Warranty:
Flanged ball valves typically come with a manufacturer’s warranty, which usually covers defects in materials and workmanship. The standard warranty period ranges from 1 to 5 years, depending on the manufacturer and the valve’s specifications. During this period, if the valve fails due to a defect covered by the warranty, the manufacturer may offer to repair or replace the faulty valve at no cost to the customer. It’s important to review the specific warranty terms provided by the manufacturer, as these can vary widely.
Conditions for Warranty:
1. Proper Installation: The valve must be installed according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
2. Appropriate Use: The valve should be used within the specified pressure, temperature, and media limits.
3. Maintenance: Regular maintenance as per the manufacturer’s recommendations must be performed.
4. Non-Modification: The valve should not be modified or repaired by unauthorized personnel.
Support:
Manufacturers and suppliers often provide various levels of support for flanged ball valves, including:
1. Technical Support: Assistance with installation, operation, and troubleshooting through phone, email, or on-site visits.
2. Documentation: Comprehensive manuals, installation guides, and maintenance instructions.
3. Training: Training sessions for maintenance staff and operators to ensure proper handling and maintenance of the valve.
4. Spare Parts: Availability of genuine spare parts to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
5. After-Sales Service: Periodic maintenance checks, emergency repair services, and extended service agreements.
Claim Process:
To make a warranty claim, customers typically need to provide:
1. Proof of purchase.
2. Detailed description of the defect.
3. Maintenance records.
4. Photos or videos showing the defect.
Exclusions:
Warranty typically does not cover damage caused by:
1. Improper installation or use.
2. Accidental damage or misuse.
3. Wear and tear from normal operation.
Understanding the warranty and support services for flanged ball valves helps ensure their reliable operation and longevity, providing peace of mind to the user.
List “flanged ball valve” FAQ
Flanged Ball Valve FAQ
#### What is a flanged ball valve?
A flanged ball valve is a valve with flanged ends, designed to control the flow of liquids and gases. The ball inside the valve rotates to either allow or block flow.
#### What are the common applications of flanged ball valves?
Flanged ball valves are used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and power generation, for on/off control of fluid flow.
#### How do flanged ball valves work?
These valves use a rotating ball with a hole through its center. When the ball is aligned with the pipeline, fluid flows through. Turning the ball perpendicular to the pipeline stops the flow.
#### What materials are flanged ball valves made of?
Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys, chosen based on the fluid type and operating conditions.
#### What are the advantages of using a flanged ball valve?
– Durability: Resistant to high pressures and temperatures.
– Leak-proof: Excellent sealing capabilities.
– Easy operation: Quick to open and close.
#### How do you install a flanged ball valve?
Ensure the valve and pipeline flanges match. Use appropriate gaskets and bolt the flanges together, tightening to the specified torque.
#### What maintenance is required for flanged ball valves?
Regular inspection for leaks, lubrication of the stem, and ensuring the integrity of the seals and gaskets are essential.
#### Can flanged ball valves handle high-pressure applications?
Yes, they are suitable for high-pressure environments, provided they are rated for the specific pressure range.
#### Are flanged ball valves suitable for throttling applications?
Typically, they are not ideal for throttling. They are best for fully open or closed positions to avoid wear and damage.
#### What sizes are available for flanged ball valves?
They come in various sizes, typically ranging from 1/2 inch to 24 inches or larger, depending on the manufacturer and application requirements.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about flanged ball valve for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQ about Flanged Ball Valves for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What are flanged ball valves?
Flanged ball valves are valves that use a spherical ball to control the flow of liquids or gases. The flanged ends allow for secure and easy connection to piping systems.
2. Why source flanged ball valves from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a wide range of options, and high production capacities. Many manufacturers in China adhere to international quality standards.
3. What materials are used in flanged ball valves?
Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and PVC. The choice of material depends on the application and the fluids being handled.
4. How do I ensure the quality of flanged ball valves from China?
Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, request quality assurance documentation, and consider third-party inspections. Supplier audits can also be beneficial.
5. What are the common sizes for flanged ball valves?
Flanged ball valves are available in various sizes, typically ranging from 1/2 inch to 24 inches. Larger sizes may be available upon request.
6. What is the pressure rating for these valves?
Pressure ratings can vary but generally range from 150 PSI to 3000 PSI. Verify the pressure rating according to your system requirements.
7. What are the standard connections for flanged ball valves?
Flanged connections usually comply with standards like ANSI, DIN, JIS, and BS. Ensure compatibility with your existing piping system.
8. How long is the typical lead time for orders?
Lead times vary by supplier and order size but generally range from 2 to 8 weeks. Custom orders may take longer.
9. Are there customization options available?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for size, material, pressure rating, and additional features like actuators or special coatings.
10. What should I consider regarding shipping and logistics?
Consider the Incoterms (like FOB, CIF), shipping method (sea or air), and the supplier’s proximity to major ports. Ensure all documentation and packaging meet international shipping standards.
By addressing these FAQs, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing flanged ball valves from China, ensuring they get the right products at competitive prices.





