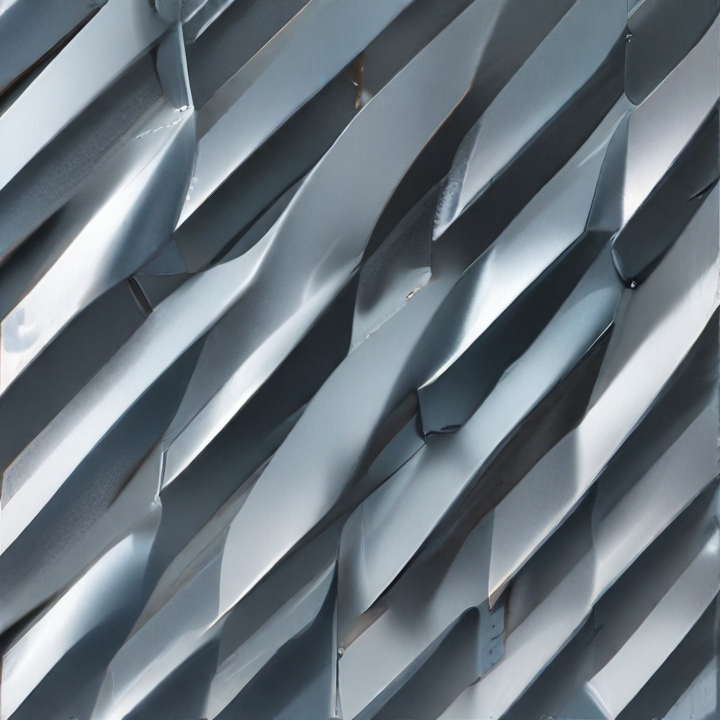
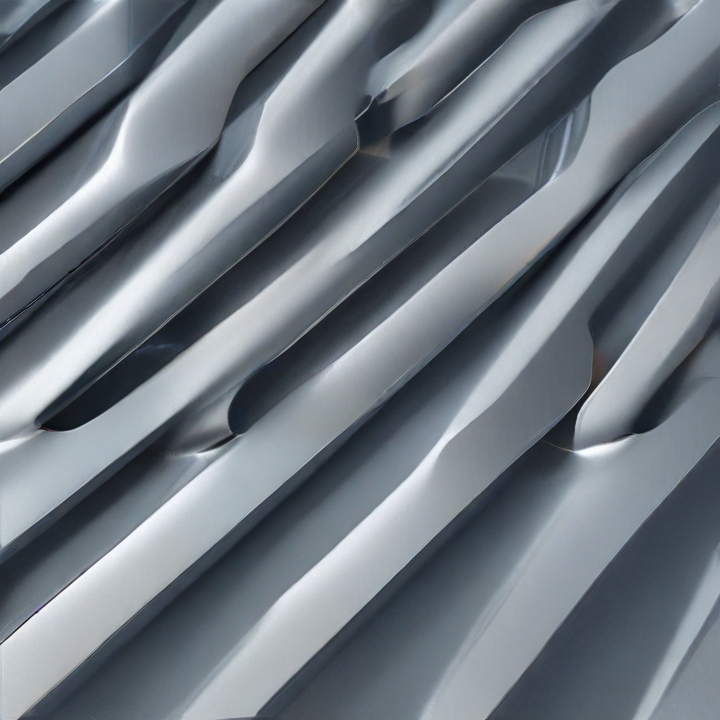
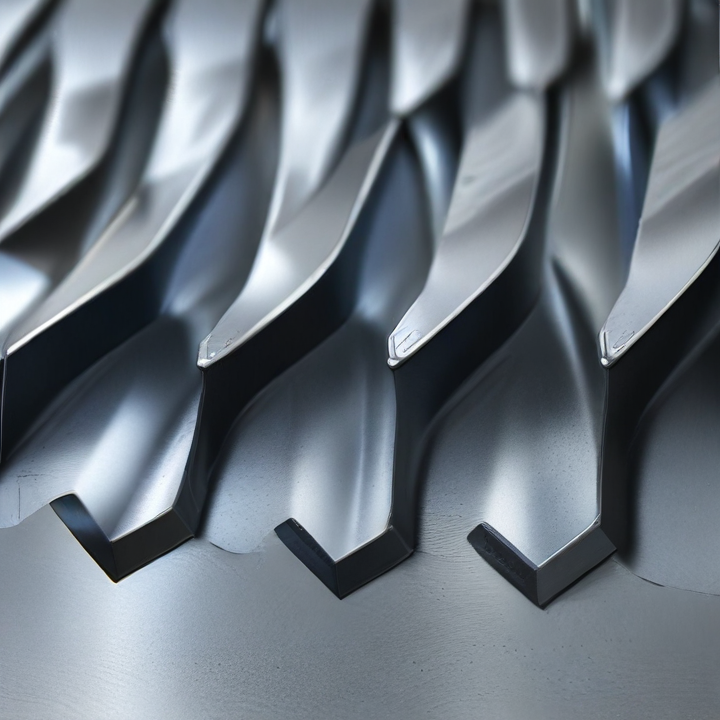
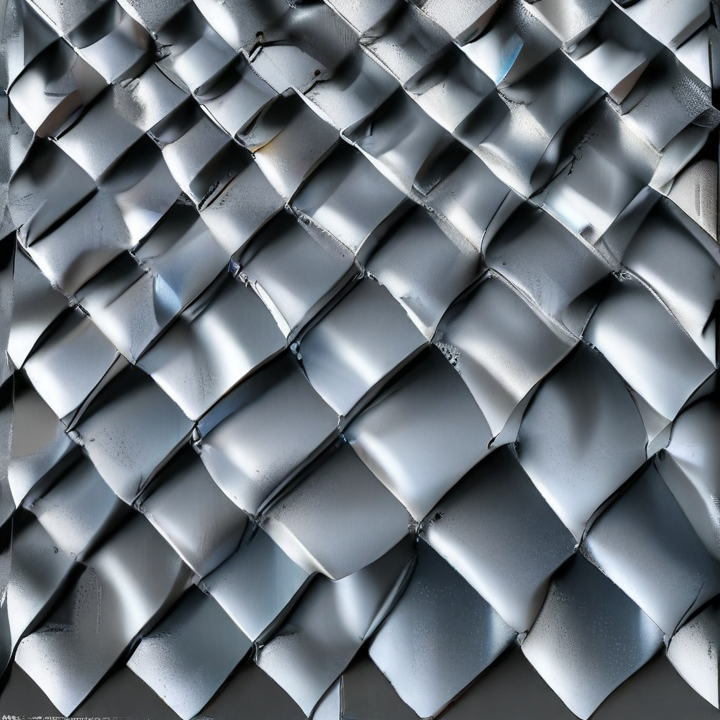
flat expanded steel Safety Certifications
Flat expanded steel is commonly used in construction, automotive, and industrial applications due to its strength and versatility. Ensuring its safety and reliability involves adhering to various certifications and standards. Here are some key safety certifications relevant to flat expanded steel:
1. ISO 9001: This is a quality management system standard that ensures the manufacturing process consistently produces products meeting customer and regulatory requirements. It doesn’t pertain exclusively to safety but ensures the overall quality and reliability of the steel.
2. ASTM Standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides numerous standards related to steel, including its manufacturing, testing, and performance. For expanded steel, relevant standards might include ASTM A36 for carbon structural steel or ASTM A1011 for hot-rolled steel sheets.
3. EN 10025: This is a European standard for hot rolled structural steel products. It specifies technical delivery conditions and covers various grades with different mechanical properties.
4. OSHA Compliance: In the U.S., the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets regulations to ensure safe working conditions, which can affect how expanded steel is handled and installed on job sites.
5. CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), the CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
6. ISO 14001: This is an environmental management standard that helps organizations minimize their environmental footprint. Compliance with this standard ensures that the manufacturing process of flat expanded steel is environmentally responsible.
These certifications and standards collectively ensure that flat expanded steel is reliable, safe for use, and produced in an environmentally sustainable manner. When selecting or using flat expanded steel, it’s crucial to verify compliance with these standards to meet safety, regulatory, and quality benchmarks.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “flat expanded steel”
Flat expanded steel is a versatile and durable material used in a variety of industrial applications. Here are the key technical parameters:
1. Material Composition:
– Typically made from low-carbon steel. Variations include stainless steel and aluminum for specific applications requiring corrosion resistance.
2. Strand and Bond Design:
– Strand Width: Typically ranges from 0.5 mm to 5 mm, affecting the load distribution and aesthetic look.
– Bond Width: Reflects the connection points between strands, influencing strength and rigidity.
3. Thickness:
– Varies from 0.5 mm to 6 mm depending on the required application strength and load-bearing capacity.
4. Opening Size and Shape:
– Common shapes are diamond, hexagonal, and square openings.
– SWD (Short Way of Diamond) and LWD (Long Way of Diamond) dimensions generally range from 2 mm to 200 mm, affecting airflow, light passage, and structural strength.
5. Weight:
– Measured in kg/m² or lbs/ft², depends on strand width, thickness, and overall dimensions.
– Influence installation processes and operational load calculations.
6. Surface Treatment:
– Can be untreated, galvanized, powder-coated, or anodized. Surface treatment enhances corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and durability.
7. Tensile Strength:
– Varies by material and treatment but typically ranges from 250 MPa to 900 MPa, affecting its suitability for different structural applications.
8. Manufacturing Tolerance:
– Typical tolerances include a few millimeters in strand width and opening dimensions, essential for ensuring compatibility in precise applications.
9. Standards Compliance:
– Compliance with ASTM, ISO, or EN standards, ensuring quality and performance consistency across applications.
These parameters ensure flat expanded steel meets the diverse needs in industries like construction, automotive, and architecture, providing a balance of strength, flexibility, and adaptability.
List Product features of “flat expanded steel”
Flat expanded steel is a versatile and widely used material known for a range of beneficial features. Here are the main product features:
1. Strength and Durability:
– Made from high-quality steel, it offers impressive strength and longevity, capable of withstanding significant loads and harsh environmental conditions.
2. Lightweight:
– Despite its strength, flat expanded steel is relatively lightweight due to its open pattern, making it easier to handle and install.
3. Versatile Applications:
– Its robust yet lightweight nature makes it suitable for a wide range of uses, including construction, infrastructure, fencing, shelving, and walkways.
4. Non-Slip Surface:
– The unique expanded pattern provides a textured surface that enhances traction, reducing the risk of slipping, making it suitable for flooring in industrial and commercial environments.
5. Air and Light Permeability:
– The open design allows for excellent air and light flow, which is ideal for applications where ventilation and visibility are crucial, such as fencing, security screens, and enclosures.
6. Cost-Effective:
– Being produced from a single sheet of steel without the need for assembling multiple parts, it is often more economical compared to other materials offering similar benefits.
7. Corrosion Resistance:
– When galvanized or coated, flat expanded steel exhibits enhanced resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor use and in corrosive environments.
8. Customizability:
– Available in various sizes, thicknesses, and patterns, it can be tailored to meet specific project requirements, ensuring flexibility in design and functionality.
9. Aesthetic Appeal:
– The modern, industrial look of expanded steel can add an aesthetic element to architectural projects, enhancing the visual appeal of structures.
10. Ease of Fabrication:
– It can be easily cut, shaped, and welded to accommodate various design requirements, facilitating straightforward customization and integration into different projects.
These features make flat expanded steel a preferred choice in numerous sectors, balancing performance, efficiency, and visual appeal.
List Various Types of “flat expanded steel”
Flat expanded steel is a versatile material used for various applications due to its strength, flexibility, and open structure. Here are some common types:
1. Standard Expanded Metal: Made from a single sheet of metal that is slit and stretched to create diamond-shaped openings. It is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and is used in applications like fencing, walkways, and grating.
2. Flattened Expanded Metal: This type is produced by passing standard expanded metal through a cold roll reducing mill, which flattens the strands and bonds. The result is a smoother and more uniform sheet, useful for applications requiring a finer, smoother surface, like in architectural designs and safety guards.
3. Heavy Expanded Metal: Characterized by thicker strands and larger openings, this type provides enhanced strength and durability. It is often used in demanding applications such as heavy-duty flooring, load-bearing platforms, and security barriers.
4. Micromesh Expanded Metal: Featuring smaller and more precise openings, micromesh is used in delicate applications that require fine filtration or close screening, such as in air or grease filters.
5. Grating: A sturdy form of expanded metal designed for use in walkways, platforms, and stairs. It offers excellent load-bearing capabilities and provides a non-slip surface.
6. Decorative Expanded Metal: This type focuses on aesthetics and is used in architectural applications. It can have a variety of shapes and patterns and is often used in facades, ceilings, and interior designs.
7. Expanded Metal Lath: Commonly used in the construction industry for plastering and stucco applications, it provides an excellent surface for these materials to adhere to.
Understanding these types helps in selecting the appropriate expanded steel for specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
List Application of “flat expanded steel”
Flat expanded steel is a versatile material used in various applications due to its unique properties of strength, durability, and flexibility. Here are some common applications:
1. Construction and Architecture: Used as grating, walkways, and catwalks for its non-slip properties. Often employed in ceilings, partitions, and facades for aesthetic appeal and structural support.
2. Industrial and Safety: Utilized in machine guards to protect operators while allowing visibility and airflow. Forms sturdy barriers, enclosures, and protective screens in manufacturing environments.
3. Infrastructure and Transport: Serves as reinforcement in concrete slabs, bridges, and tunnels. Applied in platforms, ramps, and stair treads for enhanced traction and load distribution.
4. Agricultural and Fencing: Used in fencing, cages, and enclosures for livestock and poultry. Effective for creating durable, secure barriers around fields and property.
5. Automotive and Aerospace: Implemented in filtration systems to filter air and liquids. Used in vehicle grilles, protective covers, and ventilation components for durability and performance.
6. Design and Furniture: Employed in modern furniture design, such as chairs, tables, and shelving, for its industrial look and sturdy construction. Used in decorative elements like room dividers, wall art, and lighting fixtures.
7. Energy and Utilities: Applied in solar panel mounts and wind turbine platforms for stability and efficiency. Used in the construction of electrical and telecommunications infrastructure for protective grounding and support.
List Buyer Types of “flat expanded steel”
Flat expanded steel is a versatile material used in various industries due to its strength, durability, and lightweight properties. Here are the primary buyer types:
1. Construction Industry:
– Architects and Engineers: Utilize flat expanded steel for structural applications, supporting frameworks, and aesthetic features.
– Contractors: Implement it in various construction projects for fencing, walkways, and grating due to its robustness and non-slip surface.
2. Manufacturing Sector:
– Automotive Manufacturers: Use flat expanded steel in vehicle parts for its combination of lightweight and strength characteristics.
– Aerospace Industry: Employ it in aircraft components, taking advantage of its high strength-to-weight ratio.
3. Agriculture:
– Farmers and Agribusinesses: Utilize this material for machinery guards, fencing, and trailers, valuing its durability and ease of maintenance.
4. Mining and Quarrying:
– Mining Companies: Use flat expanded steel for screening, ventilation, and protective barriers because of its ruggedness and adaptability.
5. Energy Sector:
– Oil and Gas Companies: Apply it in offshore platforms, refineries, and pipelines for its corrosion resistance and structural integrity.
– Renewable Energy Firms: Use it in wind turbine platforms and solar panel mounts.
6. Municipal and Public Works:
– Local Governments: Utilize it for road grates, public seating, and park benches, benefiting from its longevity and low maintenance needs.
7. Retail and Display:
– Store Fixture Manufacturers: Use flat expanded steel for shelving, fixtures, and displays due to its modern look and strength.
– Interior Designers: Apply it in innovative interior features and furniture designs.
8. Safety and Security:
– Security Companies: Implement flat expanded steel for protective barriers, cages, and enclosures for high-security applications.
These buyer types represent the diverse applications of flat expanded steel across multiple industries, highlighting its functionality and adaptability.
List “flat expanded steel” Project Types for Different Industries
Flat expanded steel, known for its strength, versatility, and lightweight properties, finds applications across various industries. Here’s a brief overview of its project types:
1. Construction Industry:
– Flooring: Used in industrial and commercial flooring for non-slip surfaces.
– Façades and Cladding: Offers aesthetic appeal and durability for building exteriors.
– Walkways and Catwalks: Provides safe, anti-slip surfaces in industrial settings.
2. Infrastructure:
– Bridges and Platforms: Utilized for reinforcement in bridge structures and public platforms.
– Drain Covers and Gratings: Common in sewer systems and drainage projects for durability and strength.
3. Automotive and Transportation:
– Grilles and Ventilation: Used in vehicle grilles and air ventilation systems for protection and airflow.
– Train Walkways: Ensures safety and durability in railway maintenance walkways.
4. Agriculture:
– Fencing: Serves as robust fencing material for agricultural fields and livestock enclosures.
– Machinery Guards: Protects machinery and operators in farm equipment.
5. Industrial:
– Machinery Safety Guards: Ensures worker safety by covering moving parts and machinery.
– Shelving and Storage: Used in heavy-duty industrial shelving and storage systems.
– Partitions and Enclosures: Creates durable partitions within factories and warehouses.
6. Energy:
– Offshore Platforms: Utilized in oil and gas platforms for walkways and safety barriers.
– Solar Panel Mounts: Provides support structures for solar panels.
7. Architecture and Design:
– Interior Design: Incorporated in furniture, decorative panels, and artistic installations.
– Urban Furniture: Used in benches, waste bins, and other urban installations.
These varied applications across industries showcase the adaptability and utility of flat expanded steel, making it an essential material in numerous project types.
flat expanded steel Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Flat expanded steel offers a versatile and robust material choice for various industrial and architectural applications. Here are some accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options available for this material:
Accessories:
1. Fasteners and Mounting Systems:
– Specialty bolts, nuts, and washers designed to secure flat expanded steel panels to different substrates.
– Mounting brackets and clips for easy installation and stability.
2. Protective Coatings:
– Anti-corrosion coatings like galvanization or powder coating to enhance durability, especially in harsh environments.
– Fire-resistant coatings to improve safety in flammable settings.
3. Trims and Edges:
– Decorative trims and edge protectors to give a polished finish to installations.
– Rubber or plastic edge trims for additional safety and durability.
Upgrades:
1. Surface Treatments:
– Anodizing or painting for a refined aesthetic appeal.
– Teflon or other non-stick coatings aimed at reducing material adherence in manufacturing or food processing applications.
2. Material Options:
– Utilize high-strength alloys for applications requiring extra durability and load-bearing capacity.
– Opt for stainless steel variants for increased resistance to rust and staining.
3. Mesh Patterns and Sizes:
– Customizable mesh openings to suit specific filtration or ventilation requirements.
– Variations in steel gauge to balance between strength and weight for specific uses.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Precision Cutting:
– Laser cutting for intricate designs and precise dimensions.
– Water jet cutting for complicated patterns without thermal distortion.
2. Forming and Shaping:
– Bending and folding services to fit unique architectural or structural needs.
– Rolling or curving options for cylindrical or curved installations.
3. Assembly and Fabrication:
– Custom welding and fabrication services to create bespoke assemblies.
– Integration with other materials like glass or wood for hybrid designs.
4. Design Consultation:
– Professional design services to help tailor the flat expanded steel to specific project requirements, ensuring optimal performance and aesthetic appeal.
Flat expanded steel’s adaptability makes it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, and these accessories, upgrades, and customization options ensure that it meets virtually any need.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “flat expanded steel”
Quality Control in Flat Expanded Steel Manufacturing:
1. Raw Material Inspection: Ensure high-quality steel is sourced. Check chemical composition and mechanical properties through spectral analysis and tensile testing.
2. Process Control: Monitor parameters such as temperature, speed, and alignment of equipment during expansion.
3. Dimensional Accuracy: Use calipers and micrometers to measure expanded steel dimensions, ensuring they meet design specifications.
4. Visual Inspection: Identify defects such as surface irregularities, cracks, or inconsistencies through visual checks.
5. Tensile and Hardness Testing: Confirm mechanical integrity by testing samples for tensile strength and hardness.
6. Coating and Finish Check: If applicable, inspect the quality of coatings for corrosion resistance and adherence.
7. Final Inspection: Conduct a thorough examination of the final product for defects, dimensional accuracy, and adherence to quality standards.
8. Documentation and Traceability: Maintain records of all inspections and tests for traceability and quality audits.
Manufacturing Process of Flat Expanded Steel:
1. Material Selection: Choose appropriate steel sheets based on required grade and thickness.
2. Cutting: Cut steel sheets to specified sizes using shearing or slitting machines.
3. Expanding Process:
– Slitting: Feed the steel sheet into an expanding machine equipped with slitting knives to cut the sheet in a staggered pattern.
– Expanding: Stretch the sheet laterally. This creates a diamond-shaped pattern, transforming the flat sheet into expanded steel while maintaining material strength.
4. Leveling: Pass the expanded mesh through leveling rollers to flatten and straighten it.
5. Deburring: Remove sharp edges and burrs generated during the expansion process using deburring tools or abrasive machines.
6. Heat Treatment (Optional): Apply heat treatment to achieve desired mechanical properties.
7. Cutting and Shaping: Trim the expanded steel to final dimensions and shapes as required by the design.
8. Surface Treatment (Optional): Apply surface treatments like galvanizing or painting for enhanced corrosion resistance.
9. Packaging: Properly pack the finished product to prevent damage during transportation.
This concise synthesis ensures the production of high-quality flat expanded steel, meeting stringent quality standards and industry specifications.
How to use “flat expanded steel”
Flat expanded steel is a versatile material used in construction, industrial, and decorative applications. Here’s a concise guide on how to utilize it effectively:
1. Selection and Preparation:
– Choose the appropriate type of expanded steel for your specific purpose, considering factors like thickness, strand width, and opening size.
– Measure the area where it will be used and cut the steel sheet to the required dimensions using metal shears or a mechanical saw.
2. Installation for Construction:
– Flooring: Lay the expanded steel over supporting beams or a subfloor. Secure it with screws, bolts, or welding. Ensure that the surface is level and free of sharp edges that could cause injuries.
– Walkways and Platforms: Anchor the expanded steel to steel frames or supports using heavy-duty fasteners. This provides a robust, non-slip surface ideal for industrial environments.
3. Decorative Applications:
– Facades and Panels: Use expanded steel for building facades to create a modern aesthetic. Attach the sheets to the building’s framework with screws or clips. Consider painting or powder-coating for a sleek finish.
– Interior Design: Use as a decorative element in furniture, partitions, or ceilings. It can be shaped to fit design needs and mounted using suitable hardware.
4. Safety Considerations:
– Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing when handling and cutting expanded steel.
– Ensure all edges are smoothened to prevent cuts and injuries.
5. Maintenance:
– Inspect regularly for signs of wear, rust, or damage, especially in outdoor or humid environments.
– Apply anti-corrosion treatments or paint to extend lifespan.
By following these steps, you can effectively use flat expanded steel in various applications, ensuring safety, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
“flat expanded steel” Comparative Analysis
Flat expanded steel is a versatile and widely used material in construction and industrial applications. It is created by cutting and stretching a sheet of steel, which produces a mesh-like pattern. This material is known for its strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Below is a comparative analysis:
1. Material Strength:
– Expanded Steel: This material offers high structural integrity due to its unique design. It distributes weight efficiently, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like catwalks, platforms, and walkways.
– Flat Steel: In its solid form, flat steel provides uniform strength across the surface. It is ideally used in applications where a smooth, unbroken surface is needed, such as in cladding or structural beams.
2. Weight and Flexibility:
– Expanded Steel: The expansion process reduces the overall weight without compromising strength. The open spaces within the mesh structure allow for greater flexibility and easier handling.
– Flat Steel: Being solid, flat steel is generally heavier and less flexible but offers a solid, continuous surface needed for numerous structural and architectural applications.
3. Cost and Efficiency:
– Expanded Steel: The manufacturing process utilizes the full sheet, resulting in minimal waste. The reduced weight and material use translate to lower costs, making it an economical choice for large projects.
– Flat Steel: While potentially more expensive due to the need for more material, flat steel is straightforward to install and finish, which can reduce labor costs.
4. Applications:
– Expanded Steel: Commonly used in applications requiring drainage and airflow, such as fencing, grating, and screens. Its slip-resistant surface is beneficial in industrial settings.
– Flat Steel: Preferred for roofing, automotive parts, and structural supports where smooth surfaces and aesthetic finishes are crucial.
In conclusion, the choice between flat expanded steel and traditional flat steel depends on the specific requirements of the project, including weight, strength, cost, and the intended application. Expanded steel’s open structure and cost-efficiency make it suitable for industrial uses, while flat steel’s uniformity and heavier weight cater to structural and aesthetic demands.
“flat expanded steel” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Flat Expanded Steel
We stand by the quality of our flat expanded steel products and are committed to providing exceptional customer service and support. Each of our flat expanded steel items comes with a standard warranty period of one year from the date of purchase. This warranty covers defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and conditions. Should you encounter any issues within this period, such as structural failures or manufacturing defects, we will either repair or replace the product at no additional cost to you.
To initiate a warranty claim, please contact our customer service team with your proof of purchase and a detailed description of the issue. Our support team will guide you through the process and ensure a swift resolution. It’s important to follow the maintenance guidelines provided in the product manual to ensure the longevity and performance of your flat expanded steel.
In addition to our warranty, we offer comprehensive technical support for our flat expanded steel products. Our team of experienced professionals is available to assist you with any questions related to installation, usage, and maintenance. Whether you need guidance on best practices for installing your flat expanded steel or advice on long-term care, our support staff is here to help.
For added convenience, we provide an extensive library of resources on our website, including installation guides, maintenance tips, and frequently asked questions. Our goal is to ensure that you have all the information you need to maximize the value and performance of your flat expanded steel products.
Your satisfaction is our priority. Should you have any concerns or require assistance, please do not hesitate to reach out to our dedicated support team. We are committed to ensuring that your experience with our flat expanded steel exceeds your expectations.
List “flat expanded steel” FAQ
Flat Expanded Steel FAQs
#### 1. What is Flat Expanded Steel?
Flat expanded steel is a type of metal sheet that has undergone a process of being cut and stretched to form a pattern of diamond-shaped openings. Unlike raised expanded metal, flat expanded steel is leveled to a smooth and even surface.
#### 2. What are the Applications of Flat Expanded Steel?
Flat expanded steel is widely used in various applications including:
– Fencing and security screens
– Walkways and platforms
– Grilles and vents
– Filtration systems
– Architectural designs
#### 3. How is Flat Expanded Steel Made?
Flat expanded steel is created by making multiple small cuts in a steel sheet and then stretching it. The sheet is then passed through a leveler to smooth out any raised areas, resulting in a flat, even surface.
#### 4. What Are the Benefits of Using Flat Expanded Steel?
The key benefits include:
– High strength-to-weight ratio
– Cost-effective
– Non-slip surface
– Excellent ventilation and light passage
– Durability and resistance to wear and corrosion (especially when coated)
#### 5. What are the Common Sizes and Thicknesses?
Flat expanded steel is available in various sheet sizes and thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.1 inches to 0.5 inches in thickness. It can be customized based on specific requirements.
#### 6. Can Flat Expanded Steel be Coated or Painted?
Yes, flat expanded steel can be galvanized, powder-coated, or painted to enhance its durability and corrosion resistance, and to meet aesthetic requirements.
#### 7. How Do You Cut and Handle Flat Expanded Steel?
Cutting flat expanded steel can be done using hand shears, power saws, or cutting torches. Always wear protective gear to avoid injury from sharp edges.
#### 8. Is Flat Expanded Steel Environmentally Friendly?
Flat expanded steel is recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option for various industrial and architectural uses.
#### 9. What are the Safety Considerations?
Ensure to handle with caution as the edges can be sharp, and use protective equipment to avoid injury during handling and installation.
By providing robust performance and versatility, flat expanded steel is a practical choice for many projects.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about flat expanded steel for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about sourcing flat expanded steel from China, answered concisely:
1. What is Flat Expanded Steel?
Flat expanded steel is a type of metal that has been uniformly cut and stretched into a mesh-like material. It’s used in applications like flooring, walkways, and security.
2. Why Source Flat Expanded Steel from China?
China’s manufacturers offer competitive pricing, high production capacity, and broad customization options, which makes it an economically viable option for buyers.
3. What Should I Consider When Sourcing from China?
Evaluate the supplier’s experience, quality control measures, certifications (like ISO), and ability to meet your specifications. Conduct due diligence through reviews and verifying credentials.
4. How Can I Ensure the Quality of the Product?
Request product samples, visit the manufacturing site if possible, and ask for third-party inspection reports. Specify your quality standards clearly in the contract.
5. What Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) Should I Expect?
MOQs vary but typically range from 500 to 1,000 square meters depending on the supplier. Some may offer lower MOQs for initial orders.
6. What Are the Common Payment Terms?
Typical payment terms include a 30% deposit before production and 70% balance before shipment. Letters of Credit (L/C) are also commonly accepted for large orders.
7. How Long Does Production and Shipping Take?
Lead times for production range from 2 to 6 weeks depending on order size and customization. Shipping can take another 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the destination and shipping method.
8. Can Suppliers Provide Custom Sizes and Specifications?
Yes, many Chinese suppliers offer custom sizes, shapes, and specifications to meet specific project requirements. Be clear about your needs from the outset.
9. What Certifications Should I Look For?
Look for ISO 9001 for quality management, SGS or equivalent for materials testing, and CE certification if applicable to your region.
10. What Are the Shipping and Import Costs?
These costs vary based on order size, destination, and current market rates. Consider both sea and air freight options. Collaborate with a reliable freight forwarder to get precise quotes and avoid unexpected costs.
By addressing these key FAQs, buyers can streamline their sourcing process and mitigate potential risks.





