laser metal cutting machine Safety Certifications
Laser metal cutting machines require multiple safety certifications to ensure they meet stringent industry standards and safeguard operators. Key safety certifications and standards include:
1. ISO 11553: This international standard defines the safety requirements for laser machines, focusing on minimizing risks associated with laser radiation exposure.
2. CE Marking: For machines sold in the European Economic Area, the CE Marking ensures compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
3. FDA CDRH: In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) regulates laser products to ensure they meet specific safety standards.
4. ANSI Z136: This American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard specifies the safe use of lasers to protect users from laser radiation hazards.
5. EN 60825-1: This European standard outlines safety measures and classifications for laser products.
6. UL (Underwriters Laboratories): UL certification ensures that the laser metal cutting machine has been tested for electrical safety concerns.
7. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): This ensures that hazardous materials are kept to safe levels.
8. CSA (Canadian Standards Association): Certification ensures compliance with Canadian safety standards.
These certifications guarantee that the laser cutting machine has undergone rigorous testing and meets essential safety parameters. Compliance helps mitigate risks such as laser radiation, electrical hazards, and material handling issues, ensuring a safer operating environment. Always ensure the machine has proper ventilation, protective housings, interlock systems, and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to further enhance safety.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “laser metal cutting machine”
Certainly! Below are the key reference technical parameters for a laser metal cutting machine:
1. Laser Power:
– Range: 500W to 12kW (or higher)
– Significance: Higher power allows cutting thicker and denser materials.
2. Laser Source:
– Types: Fiber Laser, CO2 Laser, Disc Laser
– Significance: Fiber lasers offer high efficiency and precision for cutting metals.
3. Cutting Speed:
– Range: Varies depending on material and thickness, e.g., 1m/min to 60m/min
– Significance: Faster speeds increase productivity but may affect cut quality.
4. Cutting Thickness:
– Range: Up to 30mm for steel, 20mm for stainless steel, and 18mm for aluminum
– Significance: Determines the capability of the machine to cut through various metal types and thicknesses.
5. Working Area:
– Size: Common sizes include 1500mm x 3000mm, 2000mm x 6000mm
– Significance: Larger areas facilitate cutting larger sheets of metal without repositioning.
6. Positioning Accuracy:
– Range: ±0.03mm to ±0.1mm
– Significance: Determines the precision of the cuts.
7. Repeatability:
– Range: ±0.02mm to ±0.05mm
– Significance: Ensures consistent quality in repetitive cutting tasks.
8. Assist Gas Types:
– Types: Oxygen (O₂), Nitrogen (N₂), Air, Argon (Ar)
– Significance: Affect the cutting speed, quality, and edge cleanliness.
9. Control System:
– Features: CNC control, intuitive interface, CAD/CAM software compatibility
– Significance: Enhances ease of operation and customization of cutting tasks.
10. Cooling System:
– Types: Water-cooled or Air-cooled
– Significance: Prevents overheating, ensuring machine longevity and consistent performance.
11. Drive System:
– Types: Servo motors, ball screws, or linear guides
– Significance: Affects machine precision, speed, and durability.
These parameters guide the selection and operation of a laser metal cutting machine, ensuring optimal performance for specific industrial applications.
List Product features of “laser metal cutting machine”
A Laser Metal Cutting Machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment that uses a high-powered laser beam to cut through various types of metal with high precision. These machines are equipped with advanced features designed to enhance performance, accuracy, and efficiency. Here are some key features:
1. High Power Laser Source: Utilizes fiber lasers or CO2 lasers capable of generating high power for cutting through thick and hard metals, such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
2. Precision Cutting: Offers exceptional accuracy with cutting tolerances often within micrometers. Achieves intricate designs and fine details with minimal kerf width.
3. Versatile Material Compatibility: Can handle different types of metals including ferrous and non-ferrous materials, making it suitable for a wide variety of applications.
4. Automated Operations: Equipped with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems that automate the cutting process, ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
5. Speed and Efficiency: High cutting speeds significantly reduce processing time, making it suitable for mass production and industrial applications.
6. High-Quality Edge Finish: Produces clean and smooth edges, minimizing the need for secondary finishing processes.
7. Nested Cutting: Allows for the optimal arrangement of parts on the material to maximize material usage and reduce waste.
8. Touchscreen Interface: User-friendly control panels for easy operation and programming.
9. Material Thickness Sensors: Automatically adjusts settings based on the thickness and type of material being cut.
10. Safety Features: Includes various safety mechanisms such as enclosures, laser beam shields, emergency stop capabilities, and smoke/dust extraction systems.
11. Cooling Systems: Integrated cooling systems to prevent overheating and ensure consistent operation.
12. Low Maintenance: Designed for durability and longevity with minimal maintenance requirements.
13. Software Integration: Compatible with various CAD/CAM software for seamless designing and cutting processes.
14. Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: Some models offer real-time monitoring and diagnostics via internet connectivity, enabling quick troubleshooting and maintenance.
These features collectively make the laser metal cutting machine a powerful tool in industrial fabrication, manufacturing, and prototyping applications.
List Various Types of “laser metal cutting machine”
Certainly! Laser metal cutting machines come in various types, each suited for specific applications and materials. Here are some key types:
1. Fiber Laser Cutting Machines:
– Technology: Use a solid-state laser that generates a beam through optical fibers.
– Advantages: High efficiency, lower maintenance, excellent for cutting reflective metals (e.g., aluminum, copper).
– Applications: Ideal for precision cutting in industries like automotive, aerospace, and sheet metal fabrication.
2. CO2 Laser Cutting Machines:
– Technology: Utilize a gas mixture (mainly CO2) to produce a laser beam.
– Advantages: Well-suited for cutting non-metallic materials (e.g., wood, acrylic) as well as metals.
– Applications: Common in sign making, fabric cutting, and various industrial applications.
3. Nd:YAG Laser Cutting Machines (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet):
– Technology: Employs a crystal as the laser medium.
– Advantages: Good for high-power applications, deep cutting, and engraving.
– Applications: Typically used for drilling, engraving, and precision cutting, including medical and aeronautics.
4. Disk Laser Cutting Machines:
– Technology: Similar to fiber lasers but uses a thin disk as the gain medium.
– Advantages: High beam quality, efficient, and robust.
– Applications: Suitable for demanding cutting tasks in heavy industries.
5. Hybrid Laser Cutting Machines:
– Technology: Combine different laser sources or incorporate other cutting technologies.
– Advantages: Versatile, can handle a broader range of materials and thicknesses.
– Applications: Used in multi-material fabrication, combining cutting and engraving tasks.
Each type of laser cutting machine offers unique benefits tailored to specific materials and industry needs. Choosing the right one depends on factors like material type, thickness, production volume, and desired precision.
List Application of “laser metal cutting machine”
Laser metal cutting machines have revolutionized various industries due to their precision, efficiency, and versatility. Below are some primary applications:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Component Fabrication: Cutting intricate parts like gears, body panels, and exhaust systems.
– Prototyping: Rapid prototyping of new designs and components.
2. Aerospace Industry:
– Aircraft Manufacturing: Precision cutting of materials for fuselage, wing components, and turbine engines.
– Maintenance and Repair: Cutting and reshaping damaged parts for refurbishment.
3. Metal Fabrication:
– Structural Components: Creating beams, columns, and other structural elements.
– Custom Metalwork: Tailoring designs for decorative and functional components.
4. Medical Device Manufacturing:
– Surgical Instruments: High-precision cutting for instruments such as scalpels, forceps, and implants.
– Prosthetics: Precision cutting for custom-designed prosthetic components.
5. Electronics Industry:
– Circuit Boards: Cutting and engraving PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards).
– Enclosures: Fabrication of metal enclosures for electronic devices.
6. Jewelry Design:
– Intricate Designs: Cutting and engraving intricate patterns on metal jewelry pieces.
– Custom Orders: Tailoring unique pieces based on specific designs.
7. Signage and Advertising:
– Custom Signs: Creating intricate metal signs for businesses and advertisements.
– Metal Lettering: Precision cutting of metal letters for various applications.
8. Construction Industry:
– Metal Roofing and Facades: Cutting metal sheets for roofing and building facades.
– HVAC Components: Fabrication of ducts and ventilation components.
9. Shipbuilding:
– Hull Components: Cutting large sheets of metal for ship hulls.
– Pipeline Systems: Precision cutting for complex piping systems.
10. Tool and Die Making:
– Mold Fabrication: Creating detailed molds for plastic and metal casting.
– Tool Components: Precision cutting of specialized tools and components.
These applications underscore the versatility of laser metal cutting machines in producing high-precision, high-quality metal components across various industries.
List Buyer Types of “laser metal cutting machine”
Certainly! Here are some common buyer types for laser metal cutting machines:
1. Manufacturing Companies: These buyers utilize laser metal cutting machines for producing parts and components used in various products, from automotive to electronics.
2. Automotive Industry: This sector requires precise and efficient cutting machines to produce car parts. Both large manufacturers and smaller automotive parts suppliers fall into this category.
3. Aerospace and Defense Firms: These companies need high-precision cutting for materials used in aircraft, spacecraft, and defense equipment. Quality and accuracy are paramount.
4. Sheet Metal Fabricators: These businesses specialize in cutting, bending, and assembling sheet metal. A laser metal cutting machine enhances their capability to produce custom parts.
5. Jewelry and Ornament Makers: Though smaller in scale, these buyers use laser cutting for intricate designs and precision detailing in metal jewelry and ornamental objects.
6. Construction Firms: Companies involved in construction projects may use laser cutting for structural components or custom metal fittings, making these machines valuable for their operations.
7. Medical Device Manufacturers: These buyers require precise cutting for parts used in medical instruments and devices. Laser metal cutting machines offer the precision and cleanliness necessary for these applications.
8. Educational Institutions and Research Labs: Universities and research facilities may invest in laser cutting technology for experimental purposes and to train students in advanced manufacturing techniques.
9. Sign and Display Makers: Businesses in this category create custom signs, displays, and architectural features that often require precise metal cutting.
10. Job Shops: These general-purpose machine shops take on a variety of custom metalworking projects from different industries, requiring the versatility and efficiency of a laser metal cutting machine.
11. Renewable Energy Sector: Companies manufacturing solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy equipment may use laser metal cutting machines to produce precise and durable components.
Each of these buyer types values different features of laser metal cutting machines, such as speed, precision, adaptability, and cost-efficiency, to meet their specific operational demands.
List “laser metal cutting machine” Project Types for Different Industries
Certainly! Laser metal cutting machines find extensive application across various industries, catering to diverse project types. Here are some key examples:
1. Automotive Industry
– Prototype Development: Cutting metal parts with precision for new model prototypes.
– Component Manufacturing: Producing vehicle parts such as exhaust systems, brackets, and chassis components.
– Customization: Tailoring custom parts for aftermarket modifications.
2. Aerospace Industry
– Aircraft Construction: Producing intricate components for engines, fuselage, and wings.
– Maintenance and Repair: Precision cutting for replacement parts and repair operations.
– Research and Development: Creating small-scale models and experimental designs.
3. Construction Industry
– Structural Components: Cutting steel beams and girders for building frameworks.
– Architectural Elements: Crafting decorative metal panels and façade elements.
– Infrastructure Projects: Producing parts for bridges, tunnels, and railways.
4. Electrical and Electronics Industry
– Enclosures and Casings: Producing cases for electronic devices and machinery.
– Circuit Board Fabrication: Cutting thin metal sheets for PCB manufacturing.
– Heat Sinks: Precision cutting of metal for efficient heat dissipation.
5. Medical Industry
– Surgical Instruments: Precision cutting for scalpels, scissors, and other surgical tools.
– Implants and Prosthetics: Tailoring metal components for medical implants.
– Diagnostic Equipment: Producing metal parts for MRI machines, X-ray equipment, etc.
6. Jewelry and Fashion Industry
– Custom Designs: Cutting intricate patterns for bespoke jewelry pieces.
– Mass Production: Manufacturing uniform pieces for retail collections.
– Accessory Components: Producing metal parts for belts, bags, and other accessories.
7. Marine Industry
– Shipbuilding: Cutting plates and sections for hulls, decks, and superstructures.
– Maintenance: Repair and replacement of metal parts in marine vessels.
– Offshore Structures: Producing components for oil rigs and underwater pipelines.
8. General Manufacturing
– Tool and Die Making: Producing precision dies and molds for various applications.
– Consumer Products: Cutting parts for appliances, furniture, and hardware.
– Industrial Equipment: Manufacturing components for machinery and production lines.
Laser metal cutting machines offer unmatched precision, efficiency, and versatility, making them invaluable across these varied industries.
laser metal cutting machine Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Upgrading and customizing a laser metal cutting machine can significantly enhance its performance, efficiency, and versatility. Here are some popular accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options:
1. High-Power Laser Sources: Upgrading the laser source to a higher wattage can increase cutting speed and enable the machine to cut thicker materials.
2. Advanced CNC Controllers: Integrating more sophisticated CNC controllers can result in more precise and complex cuts, improved automation, and better user interfaces.
3. Assist Gas Systems: Enhanced assist gas systems, like automatic gas selection and mixing, can improve cutting quality and reduce operating costs. Options include nitrogen, oxygen, and air.
4. High-Precision Linear Guides and Motors: Upgrading to high-precision linear guides and motors ensures smoother and more accurate movement, essential for intricate designs.
5. Cooling Systems: Advanced cooling systems, such as water chillers, are critical for maintaining the laser source at optimal temperatures, prolonging its lifespan, and ensuring consistent performance.
6. Cutting Head Options: Adjustable and specialized cutting heads (e.g., for bevel cutting) can provide more flexibility and improve edge quality.
7. Material Handling Systems: Automated loading and unloading systems, conveyors, and storage solutions can dramatically enhance workflow efficiency and reduce operator intervention.
8. Dust and Fume Extraction Systems: Effective extraction systems are crucial for maintaining a clean working environment and ensuring operator safety by removing hazardous fumes and particulate matter.
9. Custom Software Solutions: Tailored software packages can offer specialized functions like nesting, cost estimation, and production planning, optimizing material usage and workflow management.
10. Vision Systems: Vision systems enhance accuracy by adjusting the cutting path based on real-time imaging, ensuring better alignment and handling of pre-processed materials.
11. Safety Features: Adding safety features such as light curtains, emergency shut-offs, and protective enclosures is crucial for operator safety.
Investing in these upgrades and customizations can transform a standard laser metal cutting machine into a highly specialized and efficient tool tailored to specific manufacturing needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “laser metal cutting machine”
Sure, here’s a concise overview of the quality control and manufacturing process of a laser metal cutting machine:
Quality Control
1. Incoming Material Inspection
– Raw Materials: Ensure metals, optics, and electronic components meet specifications.
– Supplier Qualification: Periodic audits and evaluations of suppliers.
2. Production Monitoring
– In-Process Inspection: Regular checks at different stages, such as assembly and welding.
– Calibration: Frequent calibration of lasers, sensors, and cutting tools for precision.
3. Performance Testing
– Cut Accuracy: Verify the machine’s ability to cut metal at designated parameters.
– Beam Quality: Examine beam consistency and power output.
4. Final Inspection
– Full Functional Testing: Comprehensive tests on all machine functions.
– Safety Checks: Validate safety features like auto-shutoff and shielding.
5. Documentation and Traceability
– Quality Records: Maintain detailed logs of inspections, calibrations, and test results.
– Compliance Verification: Ensure alignment with industry standards and certifications.
Manufacturing Process
1. Design and Prototyping
– CAD Modelling: Create computer-aided designs of all components.
– Rapid Prototyping: Develop prototypes to test the design and functionality.
2. Component Manufacturing
– Machining: Precision machining of metal parts.
– Casting and Molding: Production of specific components using casting.
3. Assembly
– Mechanical Assembly: Assemble mechanical structures, including frames and motion systems.
– Optical Assembly: Install laser sources, mirrors, lenses, and other optical components.
– Electrical Assembly: Wiring and integrating control systems, sensors, and safety interlocks.
4. System Integration
– Software Integration: Install and configure control software.
– Calibration: Calibrate all systems to ensure accurate operation.
5. Testing and Debugging
– Initial Testing: Perform basic functionality tests.
– Error Correction: Address any identified issues or defects.
6. Final Quality Assurance
– Comprehensive Testing: Conduct full-scale tests to verify performance, accuracy, and safety.
– Customer Trials: Sometimes, clients are invited to validate the machine before shipment.
7. Packaging and Shipping
– Protective Packaging: Use specialized materials to protect the machine during transport.
– Logistics Coordination: Arrange and track shipment to ensure safe delivery to the client.
This structured approach ensures the production of high-quality laser metal cutting machines.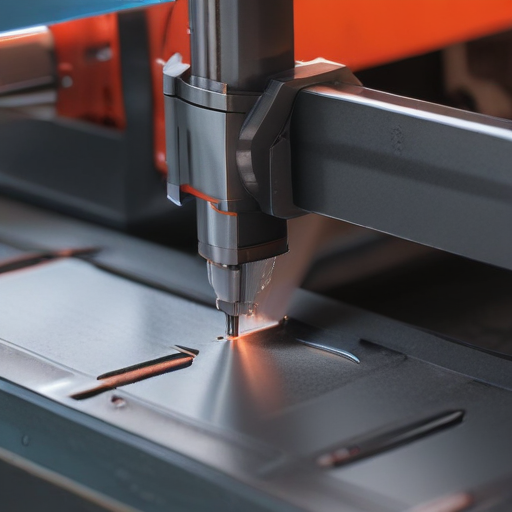
How to use “laser metal cutting machine”
Using a laser metal cutting machine involves several steps to ensure precision and safety. Here’s a concise guide to get you started:
1. Preparation:
– Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the machine’s user manual for specific instructions and safety guidelines.
– Safety Gear: Wear appropriate safety gear like goggles, gloves, and protective clothing.
2. Setup:
– Material Placement: Secure the metal sheet on the cutting bed. Ensure it’s flat and stable to avoid inaccuracies.
– Calibration: Calibrate the machine as per the material’s thickness and type. Input the correct parameters like laser power, speed, and focus.
3. Design and Software:
– Design Creation: Use CAD software to create or import your cutting design.
– Upload Design: Transfer the design file to the laser cutter’s control software, typically via USB or network connection.
4. Machine Configuration:
– Check Settings: Confirm the settings such as material type, thickness, laser power, and cutting speed.
– Test Run: Perform a test run on scrap material to make sure the settings are correct.
5. Cutting Process:
– Initiate Cutting: Start the machine and monitor the cutting process. Ensure the laser is following the design accurately.
– Supervise: Keep an eye on the machine to quickly address any issues that may arise.
6. Post-Cutting:
– Remove Material: Once cutting is complete, turn off the machine and carefully remove the metal piece.
– Clean Up: Clean the cutting area to maintain a safe and organized workspace.
7. Inspection:
– Quality Check: Inspect the cut metal for accuracy and quality. Make any necessary adjustments for future cuts.
By following these steps meticulously, you can efficiently and safely operate a laser metal cutting machine.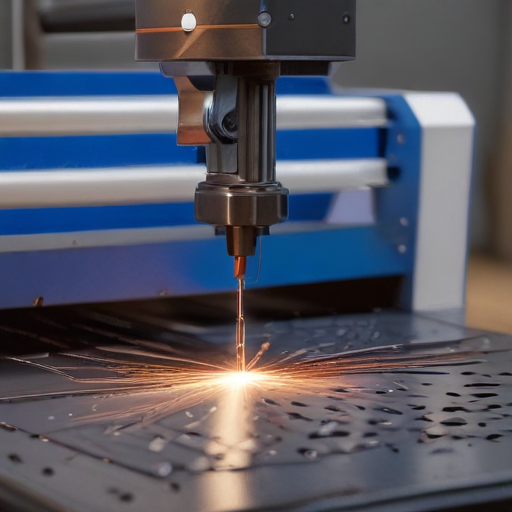
“laser metal cutting machine” Comparative Analysis
A comparative analysis of laser metal cutting machines often revolves around their types, power sources, precision, speed, and overall cost-effectiveness. The three primary types are Fiber Lasers, CO2 Lasers, and Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Lasers.
Fiber Lasers are renowned for their efficiency and high cutting speed, especially with thin metals. They offer excellent precision and low maintenance since they use fiber optics to deliver the laser beam. Fiber lasers also consume less power compared to other types. However, their efficiency diminishes with thicker materials, and they generally come at a higher upfront cost.
CO2 Lasers are versatile and can cut a variety of materials including non-metals. They excel in cutting thicker materials and are typically more economical in terms of initial investment. However, they are less energy-efficient compared to fiber lasers and require more maintenance due to the use of gas and mirrors in their operation.
Nd:YAG Lasers offer high peak power and are particularly effective for applications needing very precise and intricate cuts. They are suitable for thicker and harder metals. However, they come with high operational and maintenance costs due to the complexity of their components.
When it comes to precision, fiber lasers generally lead the pack, followed by Nd:YAG lasers and then CO2 lasers. For cutting speed, fiber lasers again are often the fastest, making them ideal for high-volume production settings.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, CO2 lasers typically offer the lowest purchase price, but their higher operational costs can offset these savings over time. Fiber lasers, while more expensive initially, often prove more economical in the long run due to lower energy consumption and maintenance costs. Nd:YAG lasers, while offering specialized advantages, are usually the most expensive in both initial and ongoing costs.
In summary, the choice of a laser metal cutting machine should be guided by specific use-case requirements: Fiber lasers for speed and low operational cost, CO2 lasers for versatility and lower upfront cost, and Nd:YAG lasers for specialized precision in thicker materials.
“laser metal cutting machine” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Laser Metal Cutting Machines
When investing in a laser metal cutting machine, ensuring adequate warranty and robust support services is crucial for maximizing uptime and protecting your investment.
Warranty:
Typically, laser metal cutting machines come with a warranty period ranging from 1 to 3 years, depending on the manufacturer. This warranty generally covers defects in materials and workmanship. Critical components such as the laser source, CNC system, and mechanical frame are included under this warranty. It’s essential to read the warranty terms carefully to understand what is and isn’t covered. Some manufacturers may also offer extended warranties for additional peace of mind.
Support:
Support services are vital for the smooth operation of your laser metal cutting machine. Reputable manufacturers offer comprehensive support that includes:
1. 24/7 Technical Support: Access to knowledgeable technical experts via phone, email, or chat to resolve issues quickly.
2. On-Site Service: Technicians can be dispatched to your location for more complex issues that can’t be resolved remotely.
3. Training Programs: Detailed training sessions provided for your staff to ensure they can operate the machine efficiently and safely.
4. Software Updates: Regular updates to the machine’s software to improve performance and add new features.
5. Spare Parts Availability: Easy access to genuine spare parts to minimize downtime and maintain machine reliability.
6. Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled maintenance checks to identify and resolve potential issues before they become major problems.
Combining a solid warranty with a robust support system ensures that your laser metal cutting machine operates at peak efficiency, reducing downtime and extending its operational life. Always choose a manufacturer with a strong reputation for both product reliability and top-tier customer support to safeguard your investment.
List “laser metal cutting machine” FAQ
Laser Metal Cutting Machine FAQ
1. What is a laser metal cutting machine?
A laser metal cutting machine uses a high-powered laser beam to cut through metal materials with precision and accuracy. This technology is often used in manufacturing and fabrication industries.
2. How does a laser metal cutting machine work?
Laser cutting machines emit a focused laser beam that melts, burns, or vaporizes the metal. A computer numerical control (CNC) system guides the laser along the desired cutting path, ensuring high precision.
3. What types of metals can be cut with a laser machine?
Laser cutting machines can cut a variety of metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, titanium, and more.
4. What are the advantages of using a laser metal cutting machine?
– Precision: High accuracy and clean cuts.
– Efficiency: Faster cutting speeds compared to traditional methods.
– Versatility: Capable of cutting complex shapes and fine details.
– Minimal Waste: Reduced material wastage due to precision.
5. What are the maintenance requirements?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning optics, checking alignment, replacing worn parts, and ensuring proper cooling and ventilation systems are functioning.
6. What thickness of metal can be cut?
The cutting thickness depends on the machine’s power and type of metal. Generally, machines can cut metals ranging from thin sheets to several inches thick.
7. What safety precautions should be taken?
– Wear appropriate eye protection.
– Ensure proper ventilation to mitigate fumes.
– Follow manufacturer guidelines.
– Keep flammable materials away from the machine.
8. Is there a difference between CO2 and fiber lasers?
Yes. CO2 lasers are typically more suitable for cutting thicker materials and offer good edge quality. Fiber lasers are more efficient, require less maintenance, and are ideal for cutting thin to medium-thickness metals at higher speeds.
9. Can laser cutting be controlled automatically?
Yes, most modern laser cutting machines are CNC-controlled, allowing for automated and highly accurate cutting processes.
10. What are common applications of laser metal cutting?
Applications include automotive parts, medical device components, architectural elements, signage, and aerospace components.
This compilation covers core aspects of laser metal cutting machines in under 300 words and addresses key user queries.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about laser metal cutting machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQ) about sourcing laser metal cutting machines from China, along with their answers, keeping within 300 words:
1. What types of laser metal cutting machines are available in China?
– China offers Fiber Laser Cutting Machines, CO2 Laser Cutting Machines, and YAG Laser Cutting Machines. Fiber lasers are preferred for metal cutting due to their high efficiency and precision.
2. How do I identify a reliable supplier?
– Look for suppliers with certifications like ISO, CE, and FDA. Visit their factory if possible, check customer reviews, and ask for machine demonstration videos.
3. What is the typical lead time for delivery?
– Lead times vary by supplier and machine complexity but generally range between 15 to 60 days.
4. What should I consider regarding machine power?
– Power requirements depend on the material thickness and type. Common power ratings range from 500W to 12,000W for different cutting needs.
5. Do Chinese suppliers offer customization options?
– Yes, many suppliers offer customization in terms of size, power, and additional features to meet specific needs.
6. What is the average cost of a laser metal cutting machine?
– Prices vary based on specifications and brand but generally range from $30,000 to $200,000.
7. What kind of after-sales support is available?
– Reputable suppliers provide technical support, online troubleshooting, and sometimes on-site services. Verify the warranty terms—often 1-2 years.
8. Are spare parts readily available?
– Yes, most suppliers offer spare parts either directly from their inventory or partner with local dealers for quicker access.
9. How is the machine quality ensured?
– Supplier’s adherence to international standards, use of quality components, and quality inspection processes are key indicators.
10. What are the shipping and import duties to consider?
– Shipping costs depend on machine size and destination. Import duties vary by country. Consult local customs for detailed duty rates and paperwork requirements.
By understanding these FAQs, buyers can make informed decisions while sourcing laser metal cutting machines from China.





