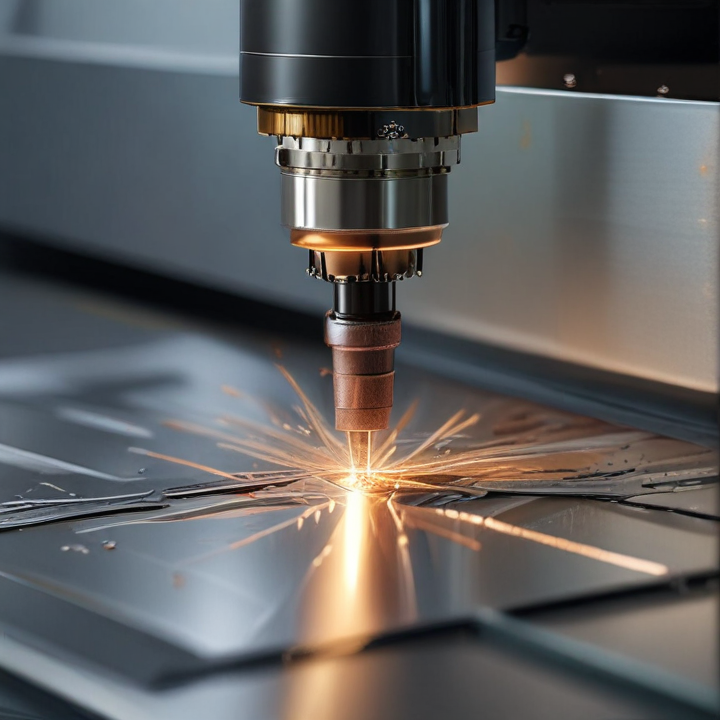
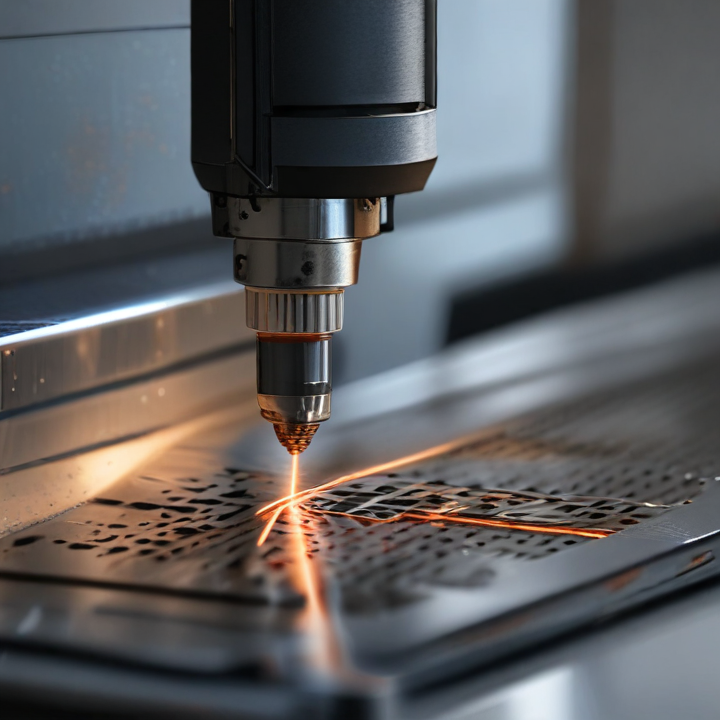
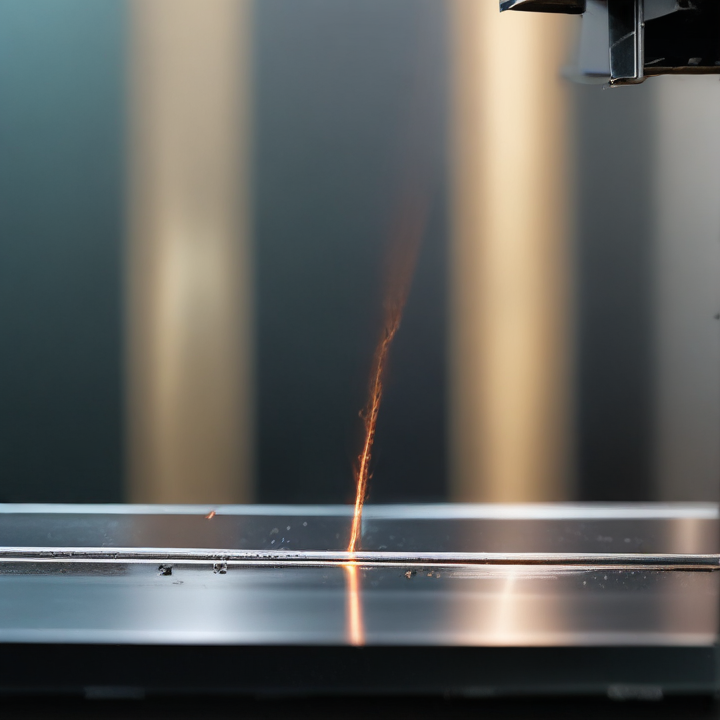
metal sheet laser cutting Safety Certifications
Metal sheet laser cutting is a precise manufacturing process that requires stringent safety protocols to protect operators and ensure compliance with industry standards. Common safety certifications in this field include:
1. ISO 45001: This international standard for occupational health and safety management systems outlines requirements for organizations to improve employee safety, reduce workplace risks, and create better, safer working conditions.
2. CE Marking: For equipment sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Ensuring that laser cutting machines meet these standards is crucial for both compliance and safety.
3. ANSI Z136.1: The American National Standards Institute provides guidelines specific to the safe use of lasers. ANSI Z136.1 outlines control measures, hazard evaluations, and procedural recommendations to minimize risks associated with laser operations.
4. OSHA Standards: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States sets and enforces standards to ensure safe and healthful working conditions. Compliance with OSHA regulations (29 CFR 1910.147 for control of hazardous energy, for example) is mandatory and helps reduce risks when operating laser cutting machinery.
5. NFPA 79: The National Fire Protection Association’s standard for industrial machinery includes safety requirements to prevent electrical hazards, which are significant in laser cutting operations.
6. UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification ensures that laser cutting equipment has been tested for safety, including electrical and fire risks, according to UL’s rigorous standards.
7. Local Building and Safety Codes: Compliance with regional and local safety laws and building codes is essential to ensure that the installation and operation of laser cutting systems meet all legal safety requirements.
Implementing these safety certifications ensures that metal sheet laser cutting operations protect workers, minimize risk, and comply with applicable regulations, contributing to a safer and more efficient workplace.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “metal sheet laser cutting”
Certainly! Here are the key technical parameters for metal sheet laser cutting:
1. Laser Power:
– Definition: The amount of energy the laser beam can deliver.
– Typical Range: 500W to 12kW.
2. Wavelength:
– Definition: The distance between successive peaks of the laser beam.
– Typical Range: 10.6 µm for CO2 lasers, 1.06 µm for fiber lasers.
3. Cutting Speed:
– Definition: The rate at which the laser head moves along the material.
– Typical Range: Up to 75 m/min, depending on material and thickness.
4. Material Thickness:
– Definition: The thickness of the metal sheet to be cut.
– Typical Range: 0.5 mm to 25 mm for steel, up to 50 mm for specialized setups.
5. Focus Position:
– Definition: The distance between the laser focusing lens and the material surface.
– Importance: Proper focus ensures clean cuts and minimizes kerf width.
6. Assist Gases:
– Type: Oxygen, nitrogen, or air.
– Function: Aid in cutting by expelling molten material and providing clean cuts.
– Pressure: Typically ranges from 0.5 to 20 bar, depending on gas type and material.
7. Nozzle Type and Diameter:
– Impact: Influences the gas flow and cut quality.
– Typical Diameter: 1-3 mm.
8. Beam Quality:
– Definition: Measurement of how focused the laser beam is.
– High beam quality (low M² value): Results in finer cuts.
9. Cutting Bed Size:
– Definition: The available area for placing the metal sheets.
– Typical Range: 3m x 1.5m for most industrial machines.
10. Software Parameters:
– CAD/CAM Integration: Enables precise programming of cutting paths.
– Nestling Efficiency: Optimizes material usage and reduces waste.
11. Cooling System:
– Importance: Maintains laser stability and prevents overheating.
12. Machine Precision:
– Tolerance: Typical accuracy ranges within ±0.1 mm.
Understanding and optimizing these parameters allows for efficient and high-quality metal sheet laser cutting, meeting specific production requirements and material properties.
List Product features of “metal sheet laser cutting”
Metal sheet laser cutting is a precise and versatile manufacturing process used widely in various industries. Here are the key product features:
1. High Precision Cutting: Laser cutting offers exceptional accuracy, allowing for tight tolerances and intricate designs. It can achieve precision down to micrometers, ensuring clean and smooth edges.
2. Versatility in Materials: This process can cut a range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, and more. It accommodates various sheet thicknesses, from thin foils to thick plates.
3. Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting is notably faster than traditional cutting methods. The high-speed laser beam cuts through materials swiftly, reducing production time and increasing efficiency.
4. Non-Contact Process: Since the laser beam is non-contact, there’s minimal mechanical stress on the material, reducing the risk of distortion and maintaining the integrity of the metal sheet.
5. Complex Geometries: Laser cutting can easily create complex shapes and intricate patterns that would be challenging with other methods, making it ideal for custom and detailed designs.
6. Minimal Waste: The precision of laser cutting results in less material waste, which is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly. The narrow kerf width minimizes the amount of material removed during the cutting process.
7. Automated Operation: Modern laser cutting machines often come with computer numerical control (CNC), facilitating automated and repeatable cutting. This enhances consistency and quality in high-volume production.
8. No Tool Wear: Unlike mechanical cutting tools that can wear out over time, laser cutting tools do not degrade, maintaining their effectiveness and reducing downtime for maintenance.
9. Clean Cutting Environment: Laser cutting produces minimal dust and contaminants, creating a cleaner work environment and reducing the need for post-processing and cleaning.
10. Energy Efficiency: Advances in laser technology have significantly improved energy efficiency, making the process more sustainable and cost-effective over time.
These features make metal sheet laser cutting an advantageous choice for precision-driven industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, and custom manufacturing.
List Various Types of “metal sheet laser cutting”
Metal sheet laser cutting is a precision fabrication process that uses laser beams to cut and shape metal sheets. Here are various types of metal sheet laser cutting categorized by laser technology and application:
By Laser Technology:
1. CO2 Laser Cutting:
– Uses a gas mixture primarily consisting of CO2.
– Effective for cutting non-metallic and metallic materials.
– Ideal for mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
2. Fiber Laser Cutting:
– Utilizes optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements.
– Higher energy efficiency and cutting speed compared to CO2 lasers.
– Suitable for thin to moderately thick metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
3. Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Laser Cutting:
– Solid-state laser technology.
– Generally used for high-precision cutting of thin metals and more intricate designs.
– Preferred for cutting reflective materials like gold, silver, and copper.
By Application:
1. Industrial Cutting:
– Used in mass production and manufacturing settings.
– Cuts a variety of metals into components for automotive, aerospace, and machinery industries.
2. Prototyping:
– Employed in R&D labs to create prototype parts.
– Allows for iterative designs with quick adjustments and high precision.
3. Custom Fabrication:
– Ideal for customized products, such as bespoke architecture elements, artistic design, and custom vehicles.
– Enables unique and intricate designs that traditional methods can’t achieve.
4. Electrical and Electronics:
– Used for producing precise components like enclosures and connectors.
– Critical for the manufacture of parts requiring complex and intricate patterns.
5. Artistic and Decorative Cutting:
– Applied in producing decorative panels, sculptures, and other art pieces.
– Offers precision and versatility allowing designers to experiment with different shapes and patterns.
By Material Type:
1. Mild Steel Cutting:
– Effective with CO2 and Fiber lasers.
– Common in construction and machinery industries.
2. Stainless Steel Cutting:
– Achieved with Fiber and CO2 lasers.
– Key in kitchenware and medical instruments manufacturing.
3. Aluminum Cutting:
– Best with Fiber lasers due to high reflectivity.
– Used in aerospace, automotive, and packaging.
Laser cutting technology enhances productivity and achieves high precision, catering to a wide range of applications and material types.
List Application of “metal sheet laser cutting”
Metal sheet laser cutting has revolutionized various industries due to its precision, speed, and versatility. Here are some notable applications:
1. Aerospace and Defense: Precision is paramount in aerospace parts and components. Laser cutting ensures exact dimensions for fuselage sections, brackets, and intricate turbine components, enhancing performance and safety.
2. Automotive: From prototypes to production, laser cutting is essential for manufacturing body panels, exhaust systems, and custom parts, facilitating rapid development and improved design flexibility.
3. Construction: Structural elements like beams, columns, and custom architectural designs benefit from laser cutting. It allows for intricate designs in facades, railings, and other decorative elements.
4. Medical Devices: Precision in medical tools and implants is critical. Laser cutting is used to create surgical instruments, orthopedic devices, and heart stents with high accuracy and minimal thermal damage.
5. Electronics and Electrical: Circuit boards, metal enclosures, and heat sinks all utilize laser cutting. It enables the creation of micro-scale parts necessary for modern electronics’ compact and efficient design.
6. Signage and Advertising: It allows the creation of intricate and customized signage, logos, and displays. The ability to cut various metals with precision enables unique and eye-catching designs.
7. Furniture and Interior Design: Custom furniture, screens, and decorative metalwork employ laser cutting for aesthetic and functional pieces. It allows for innovative designs that are otherwise difficult to achieve.
8. Agriculture: Equipment and machinery components such as blades, plows, and harvesters benefit from laser cutting for enhanced durability and precise fitting.
9. Textile and Fashion: Metal accessories, buckles, and fittings for clothing and bags are often laser cut to precise shapes, assisting in high-fashion applications.
10. Energy Sector: Fabrication of parts for solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems use laser cutting for creating efficient, high-quality components.
These diverse applications highlight the substantial impact of metal sheet laser cutting across various fields, ensuring precision, efficiency, and innovation.
List Buyer Types of “metal sheet laser cutting”
1. Manufacturers:
– Automotive: Require precision-cut metal sheets for components like chassis, brackets, and body panels.
– Aerospace: Need high-precision parts for aircraft frames, turbine blades, and other critical components.
– Electronics: Use laser-cut metal sheets for enclosures, brackets, and intricate parts in devices.
2. Construction Companies:
– Utilize metal sheets for building frameworks, facades, and customized architectural elements. Precision cutting is essential for structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
3. Fabrication Shops:
– Offer custom cutting services to a diverse clientele, including businesses needing specialized parts and individuals requiring bespoke designs.
4. Signage and Display Producers:
– Use laser-cut metal for making high-quality, durable signs, logos, and display fixtures.
5. Furniture Designers and Manufacturers:
– Employ laser cutting to create unique, intricate designs in metal furniture pieces, ensuring precise and repeatable cuts for mass production.
6. Medical Device Manufacturers:
– Require precision-cut metal components for surgical instruments, medical devices, and implants, necessitating high levels of accuracy and cleanliness.
7. Renewable Energy Sector:
– Use laser cutting for manufacturing components for solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems, requiring high precision and efficiency.
8. Art and Sculpture Creators:
– Artists and sculptors use laser cutting for detailed and intricate metal artworks, allowing for innovative and complex designs.
9. Education and Research Institutions:
– Use laser cutting in labs and research facilities for prototyping and producing experimental apparatus with high accuracy.
10. Defense and Military:
– Demand precise metal components for weaponry, vehicles, and other military equipment, often with stringent specifications.
Each type of buyer values the precision, speed, and versatility offered by metal sheet laser cutting, which enhances the efficiency and quality of their final products or services.
List “metal sheet laser cutting” Project Types for Different Industries
Metal sheet laser cutting is a versatile technology applied across various industries for precision fabrication. Here are some project types and their respective industries:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Prototyping Parts: Creating prototypes of car components like brackets, mounts, and panels.
– Custom Components: Fabricating bespoke parts for high-performance and luxury vehicles.
– Tooling: Manufacturing tools like dies and molds for production lines.
2. Aerospace Industry:
– Aircraft Components: Cutting precise parts such as airframe sections, brackets, and support structures.
– Maintenance and Repair: Producing replacement parts for aircraft maintenance.
3. Construction Industry:
– Building Facades: Creating intricate designs for metal panels used in building exteriors.
– Structural Components: Cutting beams, columns, and other structural elements.
– Decorative Elements: Producing custom metal artwork and architectural features.
4. Electronics Industry:
– Enclosures and Housings: Manufacturing enclosures for electronic devices and systems.
– Conductive Components: Cutting metal components used in circuit boards and connectors.
5. Medical Industry:
– Surgical Instruments: Producing precision tools and surgical instruments.
– Medical Devices: Fabricating components for devices like MRI machines, CT scanners, etc.
6. Manufacturing Industry:
– Machine Parts: Creating custom machine parts and tooling.
– Consumer Products: Cutting metal components for consumer products like appliances and furniture.
7. Signage and Advertising:
– Custom Signs: Producing detailed and durable signage for businesses.
– Exhibition Displays: Creating metal elements for trade show booths and displays.
8. Marine Industry:
– Shipbuilding Components: Cutting metal parts for ship construction and repair.
– Marine Equipment: Fabricating parts for marine engines, pumps, and navigation systems.
9. Renewable Energy:
– Solar Panels: Producing mounting structures and frames for solar panels.
– Wind Turbines: Cutting components for wind turbine assemblies and maintenance.
These examples illustrate the broad applicability of metal sheet laser cutting across diverse sectors, each benefiting from the precision and efficiency of this advanced manufacturing technique.
metal sheet laser cutting Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Laser cutting is a powerful technique for fabricating metal sheets with precision and efficiency. To optimize its utility, various accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available:
1. Nozzle Types: High-performance nozzles enhance cutting speed and quality. Options include single and double-nozzle configurations for diverse applications.
2. Assist Gas Systems: Utilizing assist gases like oxygen or nitrogen can improve cut quality and reduce oxidation. Advanced gas control systems allow for real-time adjustments.
3. Automatic Nozzle Changers: These systems automate the selection of nozzles, reducing downtime and enhancing efficiency.
4. Focus Lenses: Different lenses can modify the focus and intensity of the laser beam. Options include standard, high-resolution, and multi-focus lenses for varied cutting needs.
5. Beam Shaping: Advanced optics can alter the laser beam’s profile for specialized cutting, such as smoother edges or faster processing.
6. Cooling Systems: Efficient cooling systems are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and prolonging equipment life. Options include water chillers and air-cooled systems.
7. Material Handling: Automated material loaders and unloaders streamline the workflow, reducing manual labor and increasing throughput.
8. Software Upgrades: Modern software packages offer enhanced capabilities like real-time monitoring, advanced nesting algorithms, and predictive maintenance features.
9. Rotary Attachments: These enable the cutting of cylindrical objects, not just flat sheets, broadening the range of manufacturable items.
10. Dust and Fume Extractors: Effective extraction systems improve air quality and reduce maintenance by removing particulates and fumes generated during cutting.
11. Protective Enclosures: Safety enclosures protect operators from laser exposure and contain debris, improving overall safety.
12. Custom Tooling: Custom-designed fixtures and jigs can be created for specific projects, enhancing precision and reducing setup times.
Investing in these accessories and upgrades can significantly improve the efficiency, versatility, and safety of laser cutting operations. Custom solutions tailored to specific industry needs further optimize performance and output quality.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “metal sheet laser cutting”
Quality Control in Metal Sheet Laser Cutting:
1. Material Inspection:
– Check Material Certification: Validate material composition and compliance with specifications.
– Surface Inspection: Ensure sheets are free of defects like rust, scratches, or dents.
2. Machine Calibration:
– Laser Calibration: Regularly calibrate laser settings to ensure precise cutting.
– Focal Alignment: Check the focal point and beam alignment for accuracy.
3. Process Monitoring:
– Cut Quality Check: Inspect cut edges for burrs and dross.
– Dimensional Accuracy: Measure finished parts against design specifications.
– Real-time Monitoring: Utilize sensors and software to monitor and adjust parameters on-the-fly.
4. Post-Process Inspection:
– Dimensional Verification: Use calipers, micrometers, and CMMs (coordinate measuring machines) for accurate measurement.
– Surface Finish: Check surface textures to meet the final application requirements.
– Mechanical Testing: Perform tensile and hardness tests if needed.
5. Documentation and Traceability:
– Record Keeping: Maintain logs for material batches, machine settings, and inspection results.
– Traceability: Ensure each part can be traced back to its material and process records.
Manufacturing Process of Metal Sheet Laser Cutting:
1. Design and Pre-Processing:
– CAD Design: Create detailed CAD models of the required parts.
– Nesting Software: Optimize the layout of parts on the metal sheet to minimize waste.
2. Material Preparation:
– Sheet Loading: Load metal sheets onto the cutting table, ensuring they are clean and properly aligned.
3. Laser Cutting:
– Laser Setup: Configure the laser parameters such as power, speed, and gas pressure based on material type and thickness.
– Cutting Execution: The CNC machine follows the programmed path to cut the metal sheet with the laser.
4. Post-Processing:
– Part Removal: Remove the cut parts from the sheet carefully to avoid damage.
– Deburring: Remove any burrs and clean the edges if necessary.
5. Final Inspection and Shipping:
– Quality Inspection: Conduct thorough inspections to ensure parts meet specifications.
– Packaging: Package parts securely to protect during shipping.
Quality control ensures that the metal sheet laser cutting process consistently delivers high-precision parts, meeting customer specifications and industry standards.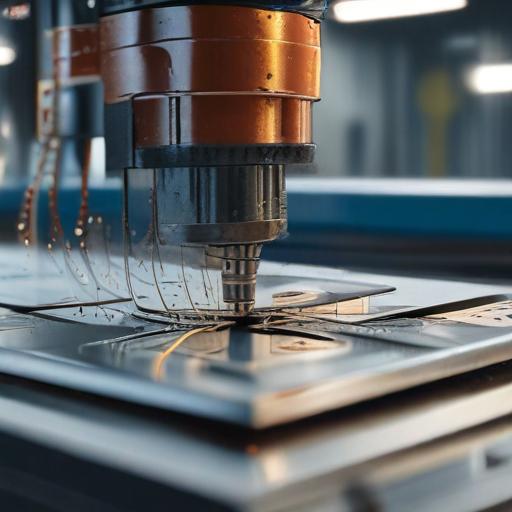
How to use “metal sheet laser cutting”
Metal sheet laser cutting is a precise and efficient method for cutting and shaping metal sheets using a high-powered laser beam. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it:
1. Prepare the Design:
– Use CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create or upload your design. Ensure the design is in the correct format, often DXF or DWG.
2. Material Selection:
– Choose the metal sheet (e.g., steel, aluminum, or stainless steel) based on the project requirements. Ensure the thickness is suitable for the laser cutter’s capacity.
3. Check Laser Cutter Settings:
– Set the appropriate parameters on the laser cutting machine, including power, speed, and focal distance. These settings depend on the material type and thickness.
4. Place the Metal Sheet:
– Secure the metal sheet on the laser cutter’s bed. Ensure it’s properly aligned and held in place to prevent movement during cutting.
5. Adjust Focus and Calibration:
– Adjust the laser focus to match the thickness of the metal sheet. Proper calibration ensures a clean cut.
6. Run a Test Cut:
– Perform a test cut on a small section or a scrap piece to ensure the settings are correct. Adjust if necessary.
7. Start Cutting:
– Initiate the cutting process through the machine’s control software. Monitor the process to ensure accurate cuts and handle any issues immediately.
8. Remove and Inspect:
– Once the cutting is complete, carefully remove the cut pieces. Inspect for precision and quality. Clean any burrs or residues if necessary.
9. Post-Processing:
– Depending on project needs, perform additional finishing processes such as deburring, cleaning, or coating.
Using metal sheet laser cutting ensures high precision, speed, and flexibility in creating complex shapes and patterns, making it ideal for various industrial applications.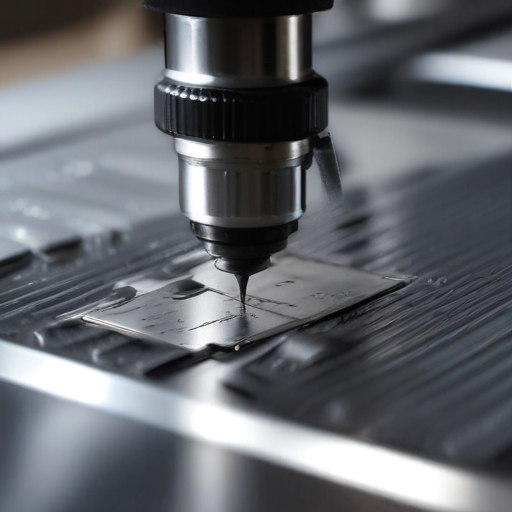
“metal sheet laser cutting” Comparative Analysis
Comparative Analysis: Metal Sheet Laser Cutting
#### Techniques
1. CO2 Laser Cutting:
– Mechanism: Utilizes a gas mixture (typically CO2) to produce a high-energy beam.
– Advantages: Suitable for cutting non-metals and metals; smooth finish; good for thicker materials up to 20mm.
– Drawbacks: High operational costs; complex maintenance; relatively slower for thicker materials compared to modern alternatives.
2. Fiber Laser Cutting:
– Mechanism: Uses optical fibers doped with rare earth elements (like erbium).
– Advantages: Higher efficiency; excellent for cutting thin metals up to 25mm; faster cutting speeds; lower operating costs; reduced maintenance.
– Drawbacks: More expensive initial investment; less effective on non-metals compared to CO2 lasers.
3. Nd:YAG (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Laser Cutting:
– Mechanism: Employs a crystal medium, typically effective in pulsed operation.
– Advantages: Good for high-precision cutting; effective for both metals and ceramics.
– Drawbacks: High initial and operational costs; complex cooling systems needed; less efficient for continuous cutting.
#### Performance Metrics
– Cutting Speed: Fiber lasers generally offer the fastest speeds, especially for thin sheets. CO2 lasers fall behind, particularly for thick metals. Nd:YAG lasers are slower but offer high precision.
– Cut Quality: All three techniques produce high-quality cuts, but the finishing can vary. Fiber lasers and CO2 lasers often produce smoother finishes, with Nd:YAG providing the best results for intricate designs.
– Material Versatility: CO2 lasers excel in non-metallic materials; fiber lasers are better for metals. Nd:YAG is versatile but best suited for specific applications requiring high precision.
#### Economic Considerations
– Initial Costs: Nd:YAG and fiber lasers have higher initial investments. CO2 lasers can be cheaper to purchase but costlier to maintain.
– Operational Costs: Fiber lasers typically have the lowest long-term operational costs. CO2 lasers have higher energy consumption and more frequent maintenance requirements.
Conclusion:
Choosing the optimal laser cutting technique depends on the specific requirements, including material type, precision, operational costs, and production speed. Fiber lasers often represent the best balance of performance and operational efficiency for most metallic sheet applications.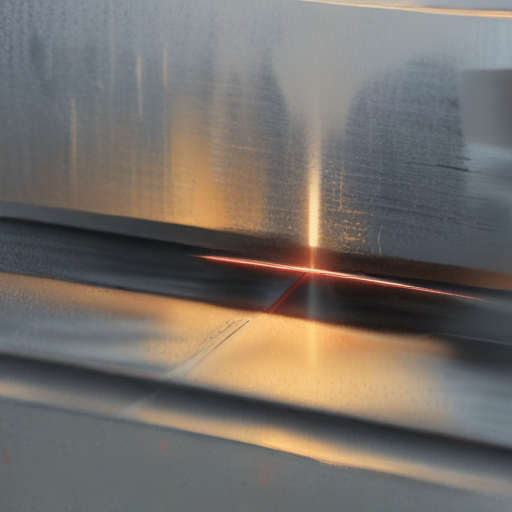
“metal sheet laser cutting” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Metal Sheet Laser Cutting
When investing in a metal sheet laser cutting machine, robust warranty and support services are essential to ensure long-term operational efficiency and peace of mind. Typically, reputable manufacturers offer a comprehensive warranty period, often ranging from one to three years, covering the entire machine. This warranty usually includes parts, labor, and technical support.
Warranty Coverage:
1. Parts and Components: The warranty often covers essential parts, such as the laser source, motors, and control systems. Any defects in materials or craftsmanship are repaired or replaced at no cost to the customer.
2. Labor: Qualified technicians are dispatched to address any issues that arise within the warranty period. This service ensures that your machine is up and running with minimal downtime.
3. Technical Support: Access to a dedicated support team for troubleshooting and operational guidance is usually part of the warranty. This support may include phone consultations, email support, and even remote diagnostics.
Extended Warranty Options:
Manufacturers often offer extended warranty plans that can be purchased to prolong coverage. Extended warranties provide an added layer of security, ensuring continuous protection from unexpected issues after the initial warranty period expires.
Support Services:
1. Installation and Training: Many suppliers offer installation and initial training services to help you get started. This training typically covers machine setup, basic operations, and essential maintenance procedures.
2. Preventive Maintenance: Regular preventive maintenance services are often available to keep the machine in optimum condition. This includes scheduled check-ups, performance assessments, and calibration.
3. Software Updates: Continuous updates to software and firmware ensure that your machine operates with the latest features and security protocols.
4. Spare Parts Availability: Ensuring a steady supply of genuine spare parts is crucial. Many manufacturers guarantee the availability of essential parts for a certain period after purchase.
Opting for comprehensive warranty and support services not only protects your investment but also enhances productivity and operational longevity. Always scrutinize the warranty terms and support offerings before making your purchase decision.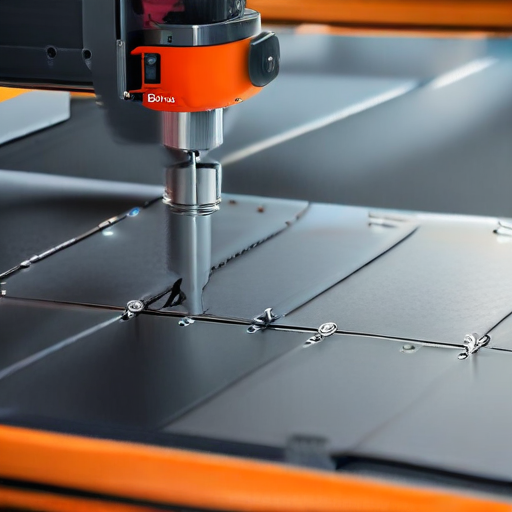
List “metal sheet laser cutting” FAQ
Metal Sheet Laser Cutting FAQ
1. What materials can be cut using a laser?
– Laser cutting is ideal for various metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and carbon steel.
2. What thickness of metal can be cut?
– Typically, metal sheet laser cutting can handle up to several inches depending on the laser’s power and the metal type. For example, CO2 lasers can cut up to 25mm of mild steel, while fiber lasers excel at cutting thinner metals.
3. What are the benefits of laser cutting?
– Laser cutting offers high precision, minimal waste, clean edges, and the ability to create complex shapes. It also minimizes material deformation and does not require physical contact with the material.
4. What is the cutting tolerance of laser cutting?
– The cutting tolerance varies but is generally within ±0.1 to ±0.2 mm, depending on the thickness and type of metal.
5. How fast is the laser cutting process?
– The speed depends on the type of laser and material but can reach several meters per minute. Fiber lasers typically offer faster speeds for thin metals than CO2 lasers.
6. Is laser cutting cost-effective?
– While the initial setup cost can be high, the efficiency, precision, and reduced material wastage make it cost-effective for both prototyping and large production runs.
7. Can laser cutting create detailed engravings?
– Yes, lasers can also engrave patterns, text, and logos onto metal surfaces with high precision.
8. What type of designs can be converted into laser cutting files?
– Most vector-based graphic files (such as DXF, DWG, or SVG) are suitable for laser cutting.
9. Is post-processing required after laser cutting?
– Typically, minimal post-processing is needed due to the clean cuts and smooth edges produced by laser cutting. However, additional treatments like deburring or polishing may be required for specific applications.
10. Is laser cutting safe?
– Yes, when proper safety protocols are followed, including protective eyewear for operators and adequate ventilation for fume extraction.
11. What industries commonly use metal sheet laser cutting?
– Industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, and manufacturing frequently use laser cutting for its precision and efficiency.
By addressing these common questions, businesses and individuals can better understand the capabilities and advantages of metal sheet laser cutting.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about metal sheet laser cutting for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What materials can be cut with a laser?
– Laser cutting can handle a variety of metal sheets such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. The quality of the cut can vary depending on the material and its thickness.
2. What is the typical lead time for metal sheet laser cutting?
– The lead time can vary, but typically it ranges from 7 to 30 days depending on order size, material availability, and the complexity of the design. Some suppliers may offer expedited services for an additional fee.
3. What is the maximum thickness that can be cut?
– This depends on the power of the laser cutter. Most industrial laser cutters can handle up to 20mm of mild steel, 10-15mm of stainless steel, and 10mm of aluminum. Always check with the supplier for their specific capabilities.
4. How does laser cutting compare to other cutting methods?
– Laser cutting provides higher precision, cleaner cuts, and often requires less post-processing compared to other methods like plasma or waterjet cutting. It’s also more versatile in terms of the shapes and designs it can produce.
5. What file formats are acceptable for laser cutting designs?
– Most suppliers accept standard vector file formats like DXF, DWG, or AI. It’s important to check with the vendor for any specific format requirements.
6. Are there any minimum order quantities (MOQ) or sample policies?
– MOQs vary by supplier, but many offer low or no minimums to accommodate prototypes or small runs. Samples may either be free or come at a nominal cost depending on the complexity and material.
7. What quality certifications do suppliers hold?
– Look for suppliers with ISO 9001 certification or other relevant quality management systems. This ensures consistent quality and reliability in their production processes.
8. Can suppliers assist with design and optimization?
– Many suppliers offer design consulting services to help optimize your design for laser cutting, which can help reduce costs and improve efficiency.
9. What are the common payment terms?
– Payment terms typically include a deposit (30-50%) with the balance payable upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net terms based on credit arrangements.
10. How is shipping handled for international orders?
– Most suppliers offer various shipping options including air, sea, and express courier services. Shipping costs will depend on the order size, weight, and the chosen shipping method. Delphi make sure to check for any additional customs or import duties that may apply.
These frequently asked questions should help in navigating the process of sourcing metal sheet laser cutting services from China efficiently.