sealing gaskets Safety Certifications
Sealing gaskets play a crucial role in maintaining the safety, integrity, and efficiency of various industrial systems. Ensuring that these gaskets meet stringent safety standards and certifications is essential for their effective performance and reliability. Here are some common sealing gasket safety certifications:
1. API (American Petroleum Institute) Certification: Complies with standards for gaskets used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring durability and suitability for high-pressure environments.
2. ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) B16.20 & B16.21: Pertains to metallic and non-metallic gaskets, respectively. These standards outline the design, material, and tolerances to ensure gasket integrity under pressure and temperature variations.
3. FDA (Food and Drug Administration) Approval: Essential for gaskets used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. These gaskets must be made from non-toxic materials and comply with rigorous sanitary standards.
4. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) Standards: Specifies testing methods for materials and performance characteristics to ensure safety under various operational conditions.
5. EN (European Norms): Various EN standards apply to gaskets, ensuring they meet specific safety and performance criteria relevant to European markets.
6. UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Certification: Ensures that gaskets used in electrical and mechanical applications meet safety standards for fire resistance and material properties.
7. WRAS (Water Regulations Advisory Scheme) Approval: Relevant for gaskets used within potable water systems, ensuring materials do not contaminate the water supply.
8. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensures that gasket materials comply with regulations restricting the use of hazardous substances, crucial for environmental and user safety.
By adhering to these certifications, manufacturers and end-users can be assured that sealing gaskets will perform safely and effectively in their intended applications, mitigating risks of leaks, contamination, and system failures.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “sealing gaskets”
When evaluating sealing gaskets for industrial or technical applications, it’s crucial to consider various reference technical parameters to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Below is a succinct list of the most critical parameters:
1. Material Composition:
– Elastomers: Nitrile, EPDM, Silicone
– Metals: Stainless Steel, Copper
– Composites: Graphite, PTFE
2. Temperature Range:
– Minimum and maximum operational temperatures, typically specified between -50°C to +300°C for common materials.
3. Pressure Rating:
– Ability to withstand specific pressures, often categorized in PSI (pounds per square inch) or bar.
4. Chemical Compatibility:
– Resistance to various chemicals, solvents, and gases to prevent degradation.
5. Hardness (Shore A):
– Represents flexibility and compression capacity, typically rated on the Shore A scale.
6. Tensile Strength:
– Measurement of the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces, expressed in MPa (megapascals).
7. Compression Set:
– The percentage of deformation the gasket undergoes when subjected to a compressive force over a specified time frame.
8. Permeability:
– The ability to prevent gas or liquid permeation through the gasket material, important for applications requiring airtight or watertight seals.
9. Size and Shape:
– Standard dimensions and custom shapes required to fit specific flanges or interfaces.
10. Environmental Resistance:
– Suitability for various environmental conditions like UV exposure, ozone, and weathering.
11. Permissible Flange Load:
– The maximum load the gasket can support without undergoing permanent deformation or failure.
12. Surface Finish Compatibility:
– Ability to seal effectively against surfaces with specific roughness parameters.
13. Regulatory Compliance:
– Adherence to industry standards such as ASTM, ISO, FDA, or other relevant certifications.
Evaluation of these parameters ensures the selection of a sealing gasket that meets the operational, mechanical, and environmental demands of the application.
List Product features of “sealing gaskets”
Sealing gaskets are essential components used to prevent leakage between two joined surfaces under compression. Here’s a concise list of their key features:
1. Material Versatility:
– Rubber: Offers flexibility, resilience, and resistance to various chemicals.
– Metal: Provides durability, strength, and high temperature resistance.
– Composite: Combines materials for specific performance requirements.
2. Temperature Resistance:
– Capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, both high and low, depending on the material composition.
3. Chemical Resistance:
– Designed to resist exposure to various chemicals, oils, and solvents, ensuring longevity in harsh environments.
4. Pressure Tolerance:
– Crafted to handle a wide range of pressures, making them suitable for high-pressure and vacuum applications.
5. Seal Integrity:
– Ensures a tight seal to prevent leaks, maintaining the integrity of the system.
6. Flexibility and Conformity:
– Capable of conforming to surface irregularities to ensure a better seal, especially useful for uneven or rough surfaces.
7. Variety of Shapes and Sizes:
– Available in numerous standard and custom shapes (O-rings, flat gaskets, etc.) to fit different applications.
8. Ease of Installation:
– Designed for straightforward installation, often requiring minimal tools or expertise.
9. Durability and Longevity:
– Built to provide long-lasting performance, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
10. Waterproof and Weatherproof:
– Effective at sealing out moisture and capable of withstanding various weather conditions.
11. Cost-Effective:
– Durable materials and long lifespan make them a cost-effective sealing solution over time.
12. Compliance with Standards:
– Manufactured in accordance with industry standards to ensure reliability and safety.
These features make sealing gaskets indispensable in a wide range of industries—including automotive, aerospace, plumbing, and industrial machinery—ensuring efficient and leak-free operations.
List Various Types of “sealing gaskets”
Sealing gaskets are crucial components designed to prevent leakage between two surfaces under compression. They come in various types suited for different applications, environments, and pressures. Here are several common types:
1. O-Rings: Circular gaskets widely employed in sealing static and dynamic applications due to their versatility and ease of installation.
2. Sheet Gaskets: Cut from flat sheet materials available in various substances such as rubber, fiber, and graphite, used mainly for flange sealing.
3. Spiral Wound Gaskets: Comprised of alternating metal and filler material layers, suitable for applications requiring high-temperature and high-pressure resistance.
4. Ring Type Joint (RTJ) Gaskets: Metallic gaskets designed for high-pressure and high-temperature settings commonly found in oil and gas industries.
5. Non-Metallic Gaskets: Made from materials like elastomers and PTFE, these are typically used in lower pressure and temperature applications.
6. Metallic Gaskets: Fabricated from a single or combination of metals, offering excellent strength and durability for high-pressure applications.
7. Semi-Metallic Gaskets: A hybrid of metallic and non-metallic materials, offering a balance of durability and flexibility for various conditions.
8. Kammprofile Gaskets: Feature a serrated metal core with a soft facing material, designed to create a strong seal with less bolt load.
9. Jacketed Gaskets: A soft filler material encased in a metallic cover, providing better resilience and sealing capabilities in extreme conditions.
10. Compressed Fiber Gaskets: Made from fibers like aramid mixed with rubber, suitable for a variety of medium pressure and temperature applications.
These gaskets are selected based on factors like operating temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and specific environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
List Application of “sealing gaskets”
Sealing gaskets are versatile components used in various applications to prevent leakage of fluids, gases, and contaminants. Here’s a brief overview of their key applications:
1. Automotive:
– Engine Components: Sealing gaskets are used in cylinder heads, intake and exhaust manifolds, and oil pans to prevent leakage of oils, coolants, and gases.
– Transmission Systems: Gaskets ensure that transmission fluid stays within the system and external contaminants do not enter.
– Fuel Systems: They seal connections in fuel injectors and fuel pumps to prevent fuel leaks.
2. Aerospace:
– Engines: Gaskets provide sealing in aircraft engines, ensuring no loss of coolant or hydraulic fluids.
– Cabin Sealing: They are used around doors and windows to maintain cabin pressure and temperature control.
3. Industrial Machinery:
– Pumps and Compressors: Gaskets are essential for sealing joints and flanges to avoid leakage of fluids and gases.
– Hydraulic Systems: They seal hydraulic connections to prevent fluid loss and maintain pressure.
4. HVAC Systems:
– Ductwork: Gaskets are employed in HVAC systems to seal duct joints, preventing air leaks and improving system efficiency.
– Refrigeration: They seal components in refrigeration units to keep refrigerant contained.
5. Plumbing:
– Pipelines: Gaskets are used at joints and flanges to prevent leaks in water, gas, and sewage lines.
– Valves and Faucets: Ensure a watertight seal to prevent leaks.
6. Electronics:
– Enclosures: Gaskets provide an environmental seal for electronic enclosures, protecting against dust, moisture, and contaminants.
– Heat Sinks: They aid in thermal management by providing a seal between heat sinks and processors.
7. Food and Beverage Industry:
– Processing Equipment: Gaskets ensure sanitary seals in equipment used for food and beverage production, preventing contamination and maintaining hygiene standards.
8. Energy Sector:
– Oil and Gas: Gaskets are crucial in sealing pipelines, tanks, and other equipment to prevent leaks.
– Renewable Energy: Used in wind turbines, solar panels, and other renewable energy equipment to ensure airtight seals.
Sealing gaskets play a critical role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of various systems, preventing costly leaks, and ensuring safe and reliable operation.
List Buyer Types of “sealing gaskets”
Sealing gaskets are indispensable components used in various applications to prevent leakage and ensure the integrity of systems. The buyer types for sealing gaskets are diverse, spanning multiple industries:
1. Automotive Industry: Manufacturers of cars, trucks, and motorcycles require sealing gaskets for engines, transmissions, exhaust systems, and air conditioning systems.
2. Aerospace: Aircraft manufacturers and maintenance companies utilize gaskets to ensure the proper functioning of fuel systems, hydraulics, and airframes.
3. Oil and Gas: This industry demands high-performance gaskets for pipelines, refineries, and drilling equipment to handle extreme pressures and temperatures.
4. Chemical Processing: Companies in this sector need specialized gaskets that resist chemical corrosion and maintain seals in reactors, valves, and pipelines.
5. Food and Beverage: Equipment used in food processing, packaging, and brewing require sanitary gaskets compliant with health and safety standards.
6. Pharmaceuticals: Gaskets used in pharmaceutical manufacturing must meet stringent cleanliness and chemical resistance standards for reactors, pumps, and filtration systems.
7. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): HVAC systems incorporate gaskets to prevent air and fluid leaks in ductwork, pumps, and heat exchangers.
8. Marine: Ships and submarines require gaskets for engines, fuel systems, and watertight compartments to ensure safety and functionality.
9. Water Treatment and Utilities: These sectors need gaskets for pipelines, valves, and filtration systems in water and wastewater treatment plants.
10. Electronics: Manufacturers of electronic devices and appliances use gaskets for sealing components to prevent moisture ingress and provide electromagnetic shielding.
11. General Manufacturing: A wide range of machinery and equipment used in manufacturing processes depend on gaskets for sealing hydraulic, pneumatic systems, and various equipment housings.
In summary, almost every industry that involves the transfer of fluids, gases, or requires containment, relies on sealing gaskets to maintain efficiency and safety in their operations.
List “sealing gaskets” Project Types for Different Industries
Sealing gaskets are critical components in various industries, providing effective sealing solutions to prevent leaks, ensure safety, and maintain system integrity. Here are some project types across different industries where sealing gaskets play a pivotal role:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Engine Gaskets: Cylinder head gaskets, valve cover gaskets, and exhaust manifold gaskets.
– Transmission Gaskets: Used in automatic and manual transmission systems.
– Sealing Solutions for HVAC Systems: Gaskets for air conditioning and heating systems.
2. Aerospace Industry:
– Fuel System Gaskets: Used in fuel tanks, pumps, and lines to prevent leaks.
– Cabin Pressure Seals: Ensuring cabin pressure integrity in aircraft.
– Engine Seals: High-temperature gaskets for jet engines and other aerospace components.
3. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Pipeline Flange Gaskets: Critical in sealing joints within pipelines.
– Wellhead Seals: Used in oil and gas exploration and production.
– Compressors and Pump Seals: Vital for sealing various components in refineries and processing plants.
4. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry:
– Chemical Reactor Gaskets: Sealing solutions for high-pressure and high-temperature reactions.
– Storage Tank Seals: Preventing leaks in tanks holding corrosive substances.
– Pump and Valve Seals: Ensuring leak-proof operations in handling hazardous chemicals.
5. Food and Beverage Industry:
– Sanitary Seals: Used in food processing equipment to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination.
– Beverage Machinery Gaskets: Seals in bottling and packaging equipment to ensure leak-free operations.
– Pressure Cooker and Autoclave Gaskets: Maintaining pressure and integrity during cooking and sterilization processes.
6. Pharmaceutical Industry:
– Sterile Environment Seals: Gaskets for equipment in sterile manufacturing environments.
– Packaging Seals: Ensuring medication packaging integrity.
– Process Equipment Gaskets: For mixers, reactors, and other pharma manufacturing equipment.
7. Marine Industry:
– Hatch and Port Hole Gaskets: Sealing solutions for shipbuilding to prevent water ingress.
– Engine and Propulsion System Seals: Important for marine engine efficiency.
– Pump and Pipe Seals: Used in various marine and offshore applications.
Sealing gaskets are indispensable across diverse projects, ensuring reliability and safety in critical operations.
sealing gaskets Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Sealing gaskets are critical components used in various industries to ensure a secure seal between two surfaces, preventing leaks and maintaining system integrity. To meet diverse requirements, numerous accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options are available.
Accessories for sealing gaskets include installation tools, protective covers, and various types of seals (O-rings, washers). These accessories simplify installation, enhance protection, and improve gasket longevity.
Upgrades can significantly boost performance. Anti-corrosion coatings can extend gasket life in corrosive environments, while high-temperature resistance materials such as Viton or PTFE enable reliable performance under extreme conditions. Reinforced gaskets, featuring embedded metallic or fabric layers, offer enhanced strength and durability.
Custom manufacturing options ensure the gasket perfectly fits the application. Precision cutting techniques like water jet, die, and laser cutting allow for bespoke shapes and sizes. Material customization lets you select from a range of elastomers, rubbers, and composites, tailored to specific chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements. Additionally, advanced simulation software can model gasket performance, ensuring accurate and functional designs.
Overall, these accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options enable sealing gaskets to meet the most demanding industry standards, ensuring reliable performance across applications.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “sealing gaskets”
Quality Control in Sealing Gasket Manufacturing
Quality control (QC) is crucial in ensuring that sealing gaskets meet performance standards and comply with specifications. The QC process typically encompasses several stages:
1. Material Inspection: Raw materials like rubber, silicone, or metal undergo rigorous testing for properties such as tensile strength, hardness, and chemical resistance.
2. Process Monitoring: During manufacturing, parameters like temperature, pressure, and time are constantly monitored to ensure consistency.
3. In-Process Testing: Gaskets are checked during production for dimensions, thickness, and surface finish using calipers, micrometers, and other precision instruments.
4. Final Inspection: After production, gaskets undergo final testing, including leak and pressure tests, to verify their sealing performance.
5. Documentation: All QC activities are documented for traceability and to meet regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing Process of Sealing Gaskets
1. Material Preparation:
– Mixing: Raw materials are precisely mixed to create a uniform compound, often using specialized mixers.
– Milling: The mix is flattened into sheets using milling machines.
2. Forming:
– Cutting: Sheets are cut into rough shapes using die-cutters or water-jet cutters.
– Molding: For more complex shapes, materials are placed into molds and subjected to heat and pressure in a process known as compression molding or injection molding.
3. Vulcanization: The semi-finished gaskets are vulcanized (cured) to enhance their physical properties, such as elasticity and strength.
4. Trimming and Finishing:
– Deflashing: Any excess material (flash) is removed.
– Surface Treatment: Gaskets may undergo additional treatments like polishing or coating to meet specific requirements.
5. Quality Control and Testing: Post-manufacturing, gaskets are subjected to the aforementioned QC processes to ensure they meet all specifications.
Summary
Combining meticulous QC steps with a structured manufacturing process yields high-quality sealing gaskets suitable for various applications. Maintaining stringent standards at each stage ensures reliability and performance in the final product.
How to use “sealing gaskets”
Sealing gaskets are crucial components used to create an airtight or watertight seal between two surfaces, preventing fluid or gas leaks. Here’s a concise guide on how to use them effectively:
1. Choose the Right Gasket: Select a gasket made from a material compatible with the fluids and temperatures it will encounter (e.g., rubber, silicone, metal).
2. Surface Preparation: Ensure both mating surfaces are clean, dry, and free of debris, oil, or old gasket material. Use a solvent or cleaner if necessary to achieve this.
3. Check Surface Flatness: Inspect the surfaces for flatness and smoothness. Irregular or damaged surfaces can prevent proper sealing.
4. Placement:
– Align Properly: Place the gasket correctly aligned with bolt holes or designated areas. Misalignment can lead to leaks or improper sealing.
– Adhesives/Silicone (if required): Some gaskets may require the application of a thin layer of adhesive or silicone sealant to hold them in place during assembly. Apply sparingly to avoid excess squeezing out.
5. Assembly:
– Sequential Torquing: When tightening bolts or screws, do it in a crisscross pattern to distribute pressure evenly. This helps in creating a uniform seal.
– Follow Torque Specifications: Adhere to manufacturer-recommended torque values to avoid over-tightening, which can deform the gasket, or under-tightening, which can cause leaks.
6. Inspection: Once assembled, inspect the seal for any signs of misalignment, bulging, or gaps.
7. Testing: If possible, test the assembly under operating conditions (e.g., pressure testing) to ensure the gasket is sealing correctly.
By carefully selecting, preparing, and securing sealing gaskets, you ensure a reliable and effective seal, enhancing the performance and longevity of your machinery or apparatus.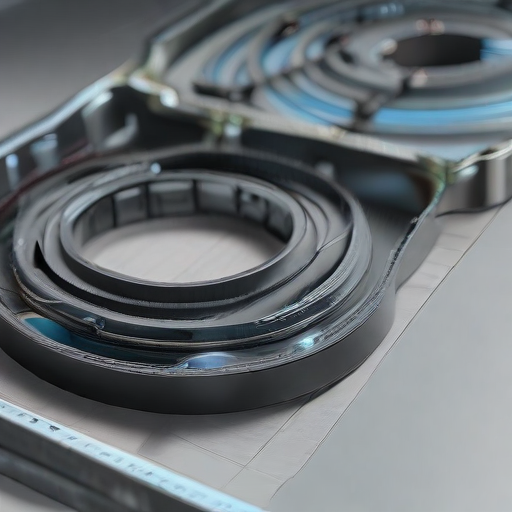
“sealing gaskets” Comparative Analysis
Sealing gaskets are essential components in various industrial applications, ensuring a tight seal between two surfaces to prevent leaks. The effectiveness, durability, and suitability of gaskets depend on the material used and the specific application requirements.
Rubber gaskets, typically made of materials like nitrile, EPDM, or silicone, are widely used due to their flexibility, resistance to compression, and ability to withstand a range of temperatures. Nitrile gaskets are excellent for oil and fuel resistance, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace industries. EPDM gaskets perform well in weather-resistant applications, such as outdoor equipment seals. Silicone gaskets are prized for their high-temperature tolerance and chemical resistance, often found in pharmaceutical and food-processing industries.
PTFE gaskets, made from polytetrafluoroethylene, are known for their exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties. They are ideal for sealing applications involving aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and in food and medical industries where purity and cleanliness are paramount.
Metal gaskets, such as those made from stainless steel or copper, are employed in situations demanding high strength and resistance to extreme pressure and temperature. Spiral wound gaskets, which combine metal and filler materials, offer a robust and resilient seal suitable for high-pressure steam, oil, and gas applications.
Graphite gaskets offer excellent temperature resistance, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability. They are commonly used in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, including power plants and petrochemical industries.
In summary, the choice of sealing gasket depends on factors such as operating temperature, pressure, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Rubber gaskets are versatile and cost-effective for a wide range of applications, while PTFE gaskets provide superior chemical resistance for specialized uses. Metal and graphite gaskets are reserved for demanding environments where durability and high performance are critical. Selecting the appropriate gasket type ensures optimal performance and longevity in various industrial applications.
“sealing gaskets” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Sealing Gaskets
At [Your Company Name], we stand behind the quality and durability of our sealing gaskets. Our products are meticulously crafted to meet the highest standards of performance and reliability. To ensure your complete satisfaction, we offer a comprehensive warranty and support program detailed below.
#### Warranty Coverage
Our sealing gaskets come with a one-year limited warranty from the date of purchase. This warranty covers any defects in material or workmanship under normal use and service. If a defect is identified within the warranty period, we will repair or replace the gasket free of charge. This warranty does not cover damages caused by improper installation, misuse, exposure to extreme conditions, or natural wear and tear.
#### Claim Process
In the unlikely event that you need to make a warranty claim, please follow these steps:
1. Contact Us: Reach out to our customer support team via email or phone with your purchase details, a description of the defect, and any relevant photographs.
2. Evaluation: Our technical team will evaluate the issue and determine whether it falls under our warranty coverage.
3. Resolution: If the claim is approved, we will guide you through the process of returning the defective gasket and receiving a replacement or repair.
#### Support Services
We are committed to providing exceptional support for our products. Our knowledgeable support team is available to assist you with the following:
– Installation Guidance: Step-by-step instructions to ensure proper installation of your sealing gasket.
– Technical Inquiries: Expert advice on usage, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
– Replacement Parts: Assistance in identifying and ordering the correct gasket for your application.
To reach our support team, please visit our website or call our toll-free number. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we strive to respond to all inquiries within 24 hours.
Conclusion
With [Your Company Name], you can have confidence in the reliability and longevity of our sealing gaskets. Our comprehensive warranty and dedicated support ensure you’ll receive the assistance you need, whenever you need it.
List “sealing gaskets” FAQ
Sealing Gaskets FAQ
1. What is a sealing gasket?
A sealing gasket is a mechanical component used to prevent leakage between two mating surfaces, such as in pipes, flanges, and machinery enclosures.
2. What materials are used to make gaskets?
Gaskets can be made from a variety of materials including rubber, silicone, metal, cork, and composite materials. The choice depends on the application’s requirements like temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure.
3. How do I choose the right gasket material?
Consider factors like operating temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and the nature of the fluids being sealed. Each material has specific properties suited for different environments.
4. How do I ensure a proper seal?
Proper installation is crucial. Ensure the gasket and mating surfaces are clean, align the gasket properly, and torque fasteners evenly to avoid uneven compression.
5. What are common gasket types?
– Flange gaskets for piping systems
– Ring gaskets for circular sealing applications
– Sheet gaskets cut to any shape and size
– Spiral wound gaskets for high-pressure and high-temperature applications
– O-rings and seals for dynamic and static applications
6. Can gaskets be reused?
Generally, it is not recommended to reuse gaskets as they can become deformed and lose their sealing integrity after installation and removal.
7. How do you store gaskets?
Store gaskets in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and chemicals. Proper storage helps maintain their integrity and lifespan.
8. What causes gasket failure?
Common causes include improper installation, incompatible materials, over-compression, and aging. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prevent failures.
9. Are there standards for gaskets?
Yes, there are various standards like ASTM, ANSI, and ASME that govern the specifications for gaskets, ensuring quality and compatibility.
10. How often should gaskets be replaced?
This depends on the application and operating conditions. Regular inspections can help determine when a gasket shows signs of wear and needs replacing.
These FAQs provide a concise overview to assist in understanding and selecting sealing gaskets for various applications.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about sealing gaskets for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 FAQs with succinct answers about sealing gaskets for buyer sourcing from China:
1. What Materials Are Commonly Used for Sealing Gaskets?
– Common materials include rubber (EPDM, NBR, silicone), metal (copper, steel), and composite materials. The choice depends on the specific application, temperature, and chemical exposure.
2. How Do I Ensure Quality Control When Sourcing from China?
– Implement strict quality control measures including third-party inspections, factory audits, and sample testing. Utilize ISO-certified manufacturers for added assurance.
3. What Certifications Should I Look for in a Manufacturer?
– Look for ISO 9001, ISO/TS 16949 for automotive applications, and material-specific certifications like FDA for food-grade gaskets.
4. Can I Get Custom-Made Gaskets?
– Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer custom gaskets based on your specific drawings and requirements. Be clear about your specifications and expectations.
5. What’s the Typical Lead Time for Production and Delivery?
– Lead times vary but generally range from 2-6 weeks for production, plus additional time for shipping. This depends on the complexity and quantity of the order.
6. How Can I Validate the Reliability of a Chinese Supplier?
– Check references and reviews, request a business license, and verify their history of exporting. Platforms like Alibaba offer supplier vetting services.
7. Are There Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)?
– Yes, MOQs vary by manufacturer but generally start at 100-1000 units. Negotiate based on your needs and the manufacturer’s capabilities.
8. What Payment Terms Are Commonly Accepted?
– Common terms include T/T (bank transfer), L/C (letter of credit), and sometimes PayPal for smaller orders. Negotiate terms to mitigate risk.
9. Can I Get Samples Before Placing a Bulk Order?
– Most manufacturers provide samples, often at a cost that’s refundable upon placing a bulk order. Specify your requirements clearly.
10. What Shipping Methods Are Available?
– Shipping can be arranged via air, sea, or express courier (DHL, FedEx). Sea freight is cost-effective for large volumes but slower, while air freight is faster but more expensive.
These answers should help you navigate the process of sourcing sealing gaskets from China efficiently and effectively.





