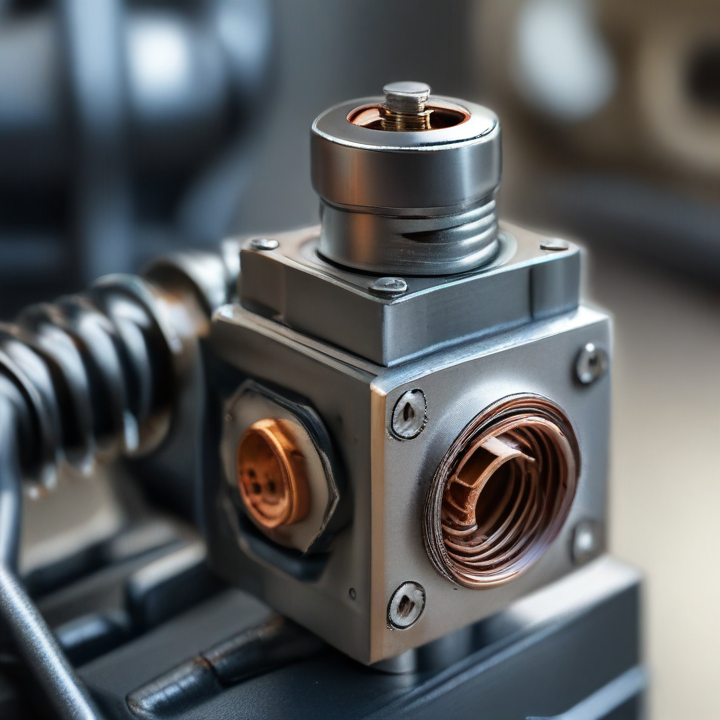
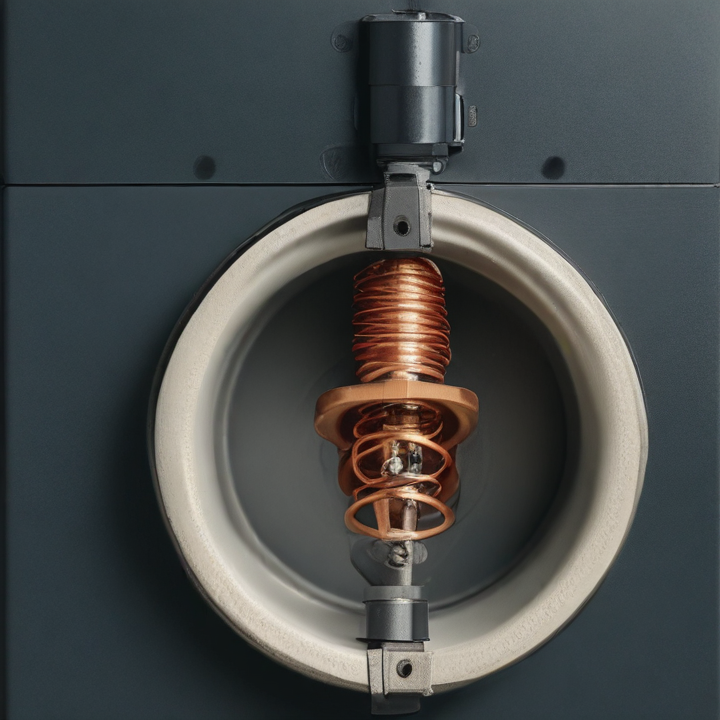
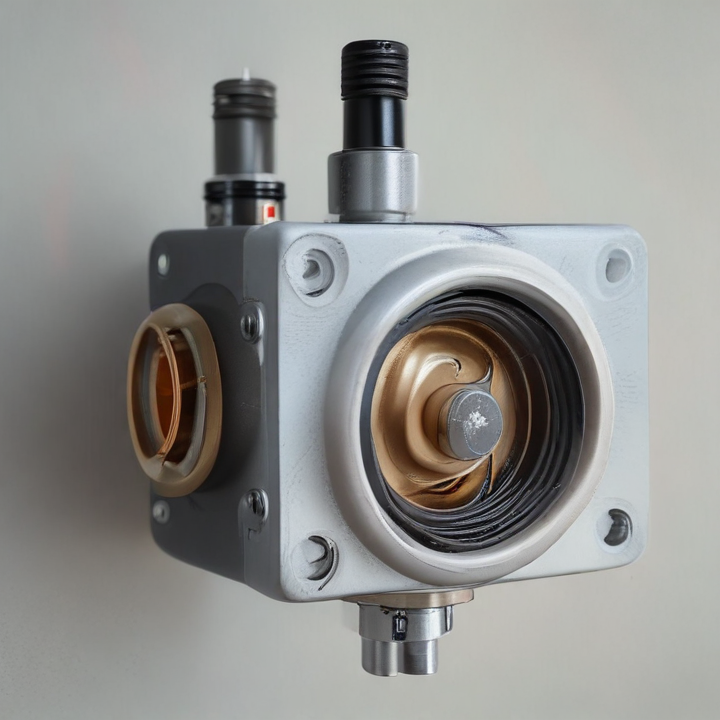
solenoid valve coil Safety Certifications
Solenoid valve coils are essential in a variety of industrial applications, and their safety certifications are critical for ensuring operational reliability and safety. Here are some key safety certifications for solenoid valve coils:
1. CE Marking: This certification indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). It shows that the product meets the essential requirements of relevant European Directives.
2. UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is a globally recognized safety certification, particularly in North America. UL certification ensures that the product complies with stringent safety standards and is safe for use in specified environments.
3. CSA Certification: The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) certification is necessary for products in Canada. It ensures that the solenoid valve coil meets national safety and performance standards.
4. ATEX Certification: Required for equipment used in explosive atmospheres within the European Union, ATEX certification ensures that the product is safe to use in environments with potentially explosive gases, vapors, or dust.
5. IECEx Certification: Similar to ATEX, IECEx certification is an international standard for equipment used in explosive atmospheres. It provides assurance of compliance with international safety standards.
6. IP Rating: The Ingress Protection (IP) rating measures the protection level against solid objects and liquids. High IP ratings indicate that the solenoid valve coil is well-protected against dust and moisture, critical for harsh environments.
7. RoHS Compliance: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) certification ensures that the product does not contain hazardous substances beyond specified limits. It is essential for environmental and health safety, particularly in the European Union.
8. FM Approval: From FM Global, this certification is widely accepted in North America and some other regions. It signifies that the solenoid valve coil has undergone rigorous testing to ensure safety and reliability.
These certifications are essential for verifying the safety, reliability, and compliance of solenoid valve coils with international and regional standards. Always check for these certifications when selecting solenoid valve coils for your applications to ensure optimal safety and performance.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “solenoid valve coil”
Certainly! A solenoid valve coil is a crucial component in the operation of a solenoid valve. Here are the key technical parameters to consider:
1. Voltage: The operating voltage for the coil, typically specified in AC or DC (e.g., 12V DC, 110V AC).
2. Power Consumption: The amount of power the coil uses, generally measured in watts (W). Commonly ranges from 1W to 30W depending on application.
3. Current: Operating current measured in amperes (A), derived from the power and voltage.
4. Resistance: Electrical resistance of the coil, measured in ohms (Ω). Important for calculating current and power.
5. Insulation Class: Specifies the coil winding insulation’s thermal tolerance (e.g., Class F – 155°C).
6. Duty Cycle: Indicates the time percentage a coil can operate before requiring cooling; often 100% for continuous duty but can be lower for intermittent use.
7. Temperature Range: Operating and storage temperature limits, often specified in degrees Celsius (-20°C to 85°C).
8. Protection Rating: IP code indicating protection against dust and water ingress (e.g., IP65).
9. Connector Type and Orientation: Defines the type of electrical connection (e.g., DIN 43650, flying leads).
10. Material: Typically consists of copper or aluminum windings and encapsulating materials such as epoxy for durability and thermal management.
11. Frequency: Applicable primarily for AC coils; typical frequencies are 50Hz or 60Hz.
12. Size and Dimensions: Physical dimensions, including coil thickness, diameter, and overall length.
13. Mounting Position: Some coils require a specific orientation for optimal performance.
14. Max Pressure Rating: The maximum pressure the coil can handle indirectly by controlling the valve.
Understanding these parameters ensures suitable coil selection for specific applications, ensuring efficiency and longevity in the solenoid valve’s operation.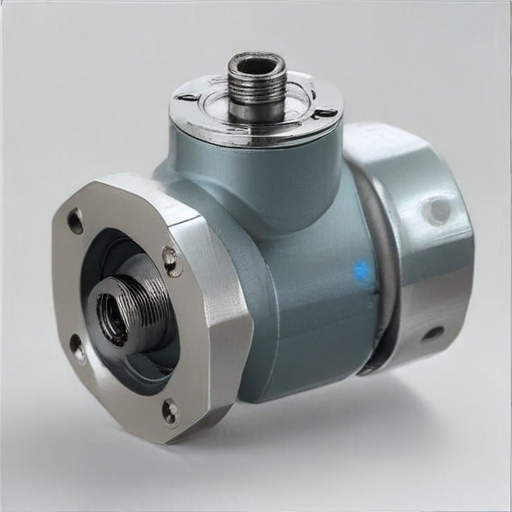
List Product features of “solenoid valve coil”
Sure! Here are the key features of a solenoid valve coil:
1. Material Composition: Typically made from durable materials such as copper or aluminum wire for the winding, and high-strength plastic or metal for the housing, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
2. Voltage Options: Available in a range of voltages, from low-voltage DC (e.g., 12V, 24V) to higher-voltage AC (e.g., 110V, 220V), accommodating various industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
3. Power Ratings: Different power (wattage) ratings are offered to match application needs, balancing performance with energy efficiency.
4. Environmental Resistance: Often designed to resist environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and temperature variations. Some coils come with IP ratings indicating their level of protection against water and dust ingress.
5. Heat Tolerance: Engineered to withstand high temperatures generated through continuous operation, often tested according to international standards to ensure safety and durability.
6. Mounting Flexibility: Offers varied mounting options to suit specific installation requirements, such as vertical or horizontal mounting configurations.
7. Connection Types: Multiple electrical connection types are available, such as flying leads, DIN connectors, or screw terminals, to facilitate easy and secure electrical hookups.
8. Compatibility: Designed to be compatible with a wide range of solenoid valves, offering users flexibility in choosing the appropriate valve-coil combination for their specific application.
9. High Efficiency: Optimized for efficient electromagnetic performance to provide robust actuation while minimizing energy consumption.
10. Quick Response: Engineered for rapid activation and deactivation, providing precise flow control in various fluid handling systems.
11. Certification Standards: Many solenoid valve coils adhere to local and international certification standards (e.g., CE, UL), ensuring compliance with safety and quality regulations.
12. Size Variants: Available in different sizes to accommodate various valve types and installation spaces.
In conclusion, solenoid valve coils are designed to offer reliable, efficient, and versatile performance, making them integral components in fluid control systems across numerous industries.
List Various Types of “solenoid valve coil”
Solenoid valve coils are integral components used to actuate solenoid valves, facilitating the control of fluid or gas flow in various systems. The types of solenoid valve coils vary based on factors such as voltage, power type, material, and environmental suitability. Here is a summary of various types:
1. AC Solenoid Coils:
– These coils are designed to operate on alternating current (AC) voltages. Common voltage ratings include 24V AC, 110V AC, and 220V AC. AC solenoids are often utilized in industrial control applications.
2. DC Solenoid Coils:
– Operate on direct current (DC) voltages, such as 12V DC, 24V DC, and 48V DC. DC solenoids are frequently used in automotive, mobile equipment, and low-voltage applications due to their steady and strong magnetic force.
3. Explosion-Proof Coils:
– Made specifically for environments where explosive gases or dust may be present. These coils are encapsulated to prevent sparks from igniting hazardous materials, making them suitable for chemical plants, mines, and oil refineries.
4. Encapsulated Coils:
– These coils are encased in a protective material (often epoxy) to handle harsh environmental conditions like moisture, dust, and chemicals. They are widely used in outdoor and industrial applications.
5. Waterproof Coils:
– Specifically designed to operate reliably in wet environments. These coils are used in applications such as irrigation systems and wastewater management.
6. High-Temperature Coils:
– Manufactured to withstand elevated temperatures, often found in industrial processes, combustion systems, and automotive applications.
7. Low-Power Coils:
– Designed for energy efficiency, these coils are used in applications where power consumption needs to be minimized. They are common in battery-operated or portable devices.
8. Plastic-Molded Coils:
– Feature a plastic exterior, making them lightweight and resistant to corrosion. Suitable for general-purpose applications where cost is a consideration.
Selecting the appropriate solenoid valve coil depends on the specific application requirements, such as voltage, environmental conditions, and power consumption needs.
List Application of “solenoid valve coil”
A solenoid valve coil is an essential component in a solenoid valve, where it converts electrical energy into mechanical motion to control the flow of liquids or gases. Here are several applications of solenoid valve coils:
1. Industrial Automation: Used in automated machinery for controlling the flow of air, water, oil, and other fluids. They are integral in factories for tasks like cutting, welding, painting, and packaging.
2. HVAC Systems: Essential for regulating the flow of refrigerants in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, ensuring precise temperature control and energy efficiency.
3. Automotive Industry: Utilized in various vehicle systems, including fuel injection systems, transmission systems, and emission control systems for efficient operation and compliance with environmental standards.
4. Medical Equipment: Found in devices like ventilators, dialysis machines, and infusion pumps, where precise control of fluids and gases is critical for patient care.
5. Water Treatment Plants: Employed to manage the flow of water and chemicals in filtration and purification processes, ensuring the safety and quality of drinking water.
6. Irrigation Systems: Used in automated irrigation controllers to regulate water flow, optimizing the distribution of water in agriculture and landscaping.
7. Fire Suppression Systems: Critical in controlling the release of fire suppressants in response to fire detection systems, ensuring rapid and efficient fire suppression.
8. Food and Beverage Industry: Utilized in bottling, filling, and packaging processes where hygiene and precise control of ingredients are essential.
9. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Important in processes that require precise dosing and mixing of chemicals for the production of medications.
10. Marine Applications: Employed in ballast systems, fuel systems, and bilge systems to control fluid flow in ships and submarines.
Solenoid valve coils are versatile and vital in numerous industries, providing reliable operation and precision in controlling fluid and gas flow in various applications.
List Buyer Types of “solenoid valve coil”
When it comes to purchasing solenoid valve coils, the buyer types can generally be categorized into several groups depending on their specific needs and applications. Below are key buyer types for solenoid valve coils:
1. Industrial Manufacturers:
– Automotive Industry: Utilize solenoid valve coils in fuel injection systems, automatic transmission systems, and emission control systems.
– Pharmaceutical & Chemical Plants: Use these coils in systems for precise fluid control, dosing, and mixing processes.
– Food and Beverage Industry: Employ solenoid valves to control the flow of ingredients and fluids in processing pipelines.
2. Maintenance and Repair Operations (MRO):
– Facility Maintenance Teams: These buyers need replacement solenoid valve coils to keep existing machinery and systems running smoothly.
– Third-Party Repair Services: Companies specializing in equipment maintenance for various industries also buy replacement parts to ensure timely repairs.
3. OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers):
– Develop and produce machinery or systems incorporating solenoid valve coils as integral components. These include HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, automated manufacturing equipment, and medical devices.
4. Utilities and Public Services:
– Water Treatment Plants: Use solenoid valve coils in automated systems for water purification, waste-water treatment, and distribution.
– Energy Sector: Purchase solenoids for control systems within power plants, gas distribution networks, and renewable energy setups.
5. Engineering and Design Firms:
– These firms specify solenoid valve coils in custom machinery or specialized systems, often requiring highly specific or custom-designed coils.
6. Retail and Distributors:
– Companies that stock and sell solenoid valve coils to end-users and smaller businesses. They serve as a bridge between manufacturers and other buyer types.
Understanding these diverse buyer types helps in tailoring solutions and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs of each group, thereby enhancing sales and customer satisfaction.
List “solenoid valve coil” Project Types for Different Industries
Certainly! Solenoid valve coils are fundamental components used to control the flow of liquids or gases through a valve. They find applications in various industries, each having distinct project requirements.
1. Oil & Gas Industry
– Wellhead Control Systems: Coils are used in hydraulic control units for precise management of wellhead valves.
– Pipeline Automation: In pipeline systems to control the flow of oil or gas.
2. Chemical & Petrochemical Industry
– Process Automation: Coils are crucial in automated systems for controlling chemical reactions and material flow.
– Safety Systems: Used in emergency shutdown systems to ensure safe operation of chemical plants.
3. Water Treatment
– Filtration Systems: Valves control the flow of water through various filtration stages.
– Wastewater Treatment: Manage the flow of sewage and treated water in municipal and industrial plants.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
– Manufacturing Processes: Precision control of liquid and gas during drug development and production.
– Sterilization Systems: Utilize solenoid valve coils in autoclaves and sterilization equipment.
5. Automotive Industry
– Fuel Injection Systems: Control the delivery of fuel in modern internal combustion engines.
– Automatic Transmissions: Regulate hydraulic fluid flow in automotive transmission systems.
6. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
– Climate Control Systems: Manage refrigerant flow in heating and cooling systems.
– Ventilation Systems: Control airflow in ductwork and other ventilation components.
7. Food & Beverage Industry
– Bottling and Packaging: Precision control of liquids in filling and packaging lines.
– Process Control: Manage the flow of raw materials and ingredients in food processing.
8. Power Generation
– Steam Control Systems: Regulate steam flow in turbines and boilers.
– Cooling Systems: Control the flow of coolant in power plants.
Each industry harnesses solenoid valve coils to meet specific operational needs, ensuring efficient, safe, and automated processes.
solenoid valve coil Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Solenoid valve coils are critical components in fluid control systems, and upgrading or customizing these can optimize performance and extend lifespan. Here are some key accessories and custom manufacturing options:
Accessories
1. Mounting Brackets: Customizable brackets ensure proper alignment and secure installation, reducing wear and tear.
2. Connector Types: Options include DIN connectors, flying leads, and specialty connectors to match various system requirements.
3. Manual Override: Enables manual operation during maintenance or power failure.
4. Surge Protectors: Protect coils from voltage spikes, enhancing durability.
5. Sealed Enclosures: For hazardous or wet environments, sealed enclosures provide added protection.
Upgrades
1. Coil Insulation Classes: Upgrading to higher insulation classes, like Class H, enhances thermal resistance.
2. Material Enhancements: Using better-quality wire materials, such as copper or silver, can reduce resistive losses and improve efficiency.
3. Encapsulation: Fully encapsulated coils offer improved resistance to vibration, moisture, and corrosive environments.
4. Voltage Options: Wide voltage range coils are available for applications requiring different power levels.
5. Energy-Efficient Coils: Low-power consumption coils can significantly reduce operational costs.
Custom Manufacturing
1. Tailored Dimensions: Custom-sized coils to fit unique solenoid valve designs.
2. Special Coatings: Anti-corrosion and weather-resistant coatings extend the coil’s lifespan in harsh conditions.
3. Windings Customization: Specific winding configurations can be designed to meet precise electrical and magnetic requirements.
4. Enhanced IP Ratings: Design coils with high Ingress Protection (IP) ratings for dust and water resistance.
5. Integrated Sensors: Built-in sensors for real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
By leveraging these accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options, you can maximize the functionality, reliability, and efficiency of solenoid valve coils, tailored to meet specific application demands.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “solenoid valve coil”
Quality Control of Solenoid Valve Coils
1. Incoming Material Inspection: Raw materials such as copper wire, insulation materials, and metal housings are scrutinized for compliance with specifications.
2. Winding Inspection: Automated winding machines are monitored to ensure the wire is evenly wound with no overlaps or gaps.
3. Electrical Testing: Coils are tested for resistance, inductance, and continuity to confirm they meet electrical requirements.
4. Dimension Verification: Physical dimensions of the coils are checked via calipers and micrometers to ensure they align with design specifications.
5. Insulation Testing: High-voltage tests ensure the coil’s insulation can withstand operating conditions without breakdown.
6. Functional Testing: Coils are installed in test setups to evaluate their magnetic performance and interaction with solenoid valves.
7. Environmental Testing: Coils undergo thermal cycling, humidity tests, and vibration tests to ensure reliability under varying conditions.
8. Final Inspection: A comprehensive check of all parameters before packaging to ensure defective units are screened out.
Manufacturing Process of Solenoid Valve Coils
1. Design and Prototyping:
– CAD software is used to design the coil specifications.
– Prototypes are produced and tested for initial validation.
2. Material Preparation:
– Copper wire is selected and insulated, typically with enamel coating.
– Metal components are machined and prepped.
3. Winding:
– Automated winding machines wrap the copper wire around a bobbin or core, ensuring precise turns and tension.
4. Insulation and Encapsulation:
– Coils are insulated with varnish or resin to prevent short circuits.
– Some coils undergo encapsulation in epoxy for added protection.
5. Core Insertion:
– Magnetic cores are inserted into the wound coil to form a complete solenoid assembly.
6. Termination:
– Electrical connections for power supply are added, be it leads, terminals, or connectors.
7. Assembly:
– The coil is housed in its metal casing, ensuring robustness and protection from physical damage.
8. Testing:
– Various electrical, dimensional, and functional tests are conducted as per the quality control process.
9. Packaging:
– Final products are labeled and packaged with attention to preventing damage during transportation.
Effective quality control and a streamlined manufacturing process ensure solenoid valve coils meet stringent performance and reliability standards.
How to use “solenoid valve coil”
A solenoid valve coil is an essential component that converts electrical energy into mechanical action to open or close a valve. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it:
1. Identify Components
– Solenoid Valve Body: Contains the orifice that allows fluid to pass.
– Solenoid Coil: The electromagnetic coil.
– Plunger: The moving part that opens or closes the valve.
2. Determine Specifications
– Voltage and Current: Verify that the coil voltage matches your power supply (e.g., 12V, 24V, 110V).
– Connection Type: Ensure the coil’s electrical connections suit your setup (e.g., terminal type or lead wires).
3. Installation
1. Positioning:
– Ensure the solenoid valve is installed in the direction of fluid flow.
– Mount the valve where it’s easily accessible for maintenance.
2. Electrical Wiring:
– Disconnect the power supply before starting.
– Connect the coil to the power source as per the wiring diagram provided by the manufacturer.
– Secure connections to avoid shorts and use proper insulation.
4. Operation
– Activating the Coil:
– Apply the specified voltage to the coil leads.
– The electromagnetic field generated pulls the plunger, causing the valve to open or close.
– Deactivating:
– Disconnect the electrical supply; the plunger returns to its default position (via spring or gravity), reversing the valve action.
5. Maintenance
– Regularly inspect coil and valve for signs of wear, overheating, or damage.
– Clean the components to ensure debris doesn’t obstruct the plunger movement.
Safety Tips
– Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
– Ensure the power is off during installation and maintenance.
– Wear appropriate protective gear.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a solenoid valve coil to control the flow of gases or liquids in various applications.
“solenoid valve coil” Comparative Analysis
A solenoid valve coil is a crucial component in solenoid valves used for controlling the flow of fluids in various industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Here’s a comparative analysis based on different parameters:
Material:
– Copper Coils: Known for excellent electrical conductivity and efficiency but can be more expensive.
– Aluminum Coils: More cost-effective and lightweight, but with slightly lower electrical efficiency compared to copper.
Voltage Ratings:
– AC Coils: Typically used in larger systems where the power supply is AC. They are less prone to overheating.
– DC Coils: More common in smaller, battery-operated systems. They offer precise control but can overheat if not designed properly.
Temperature Range:
– Standard Coils: Operate within moderate temperature ranges and are suited for general applications.
– High-Temperature Coils: Specifically designed for extreme conditions, these coils use materials and insulation that can withstand higher temperatures.
Insulation Class:
– Class A (105°C): Suitable for general-purpose applications with moderate temperatures.
– Class F (155°C) & Class H (180°C): Used in applications where higher thermal endurance is necessary.
Enclosure:
– IP Rating: Indicates protection level against dust and water. Higher IP ratings (e.g., IP65, IP67) are needed for harsher environments.
– NEMA Rating: USA-specific standards that help determine the suitable environment. NEMA 4 is for outdoor use, while NEMA 7 is for hazardous locations.
Operational Lifespan:
– General-Purpose Coils: These offer a balanced performance but have a standard operational lifespan.
– Heavy-Duty Coils: Designed for frequent operations and demanding environments, providing longer operational lifespans.
Applications:
– Industrial Applications: Generally use heavy-duty, high-voltage, high-temperature coils.
– Residential Applications: These often deploy simpler, cost-effective coils since the demand on the valve is less intense.
In summary, the choice of a solenoid valve coil largely depends on application-specific requirements such as power supply type, temperature range, environment, and cost constraints. Understanding these parameters ensures that the appropriate coil is selected, optimizing performance and longevity of the solenoid valve system.
“solenoid valve coil” Warranty and Support
Solenoid Valve Coil Warranty and Support
Warranty:
Our solenoid valve coils come with a comprehensive 12-month warranty from the date of purchase, reflecting our confidence in the quality and durability of our products. This warranty covers any defects in material or workmanship under normal use during the warranty period. Should a defect arise, we will either repair the defective coil, replace it with a new or refurbished one, or offer a full refund, at our discretion.
Support:
For support, our dedicated customer service team is available to assist you with any issues or questions you may have regarding your solenoid valve coil. We offer the following support options:
1. Technical Assistance: Reach out to our technical support team for help with installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance tips. Our experts are available via phone, email, and live chat to provide prompt and thorough assistance.
2. Documentation and Resources: Access a comprehensive library of user manuals, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides on our website. These resources are designed to help you understand, install, and maintain your solenoid valve coils effectively.
3. Replacement Parts: In the event of a malfunction, we offer a range of replacement parts to ensure minimal downtime and uninterrupted operation. Contact our support team for assistance in selecting the correct parts and ensuring compatibility.
4. Extended Warranty Options: For added peace of mind, we offer extended warranty plans that cover your solenoid valve coils beyond the initial 12-month period. These plans are available for an additional fee and provide continued protection against potential defects.
Customer satisfaction is our top priority, and we are committed to ensuring that your experience with our solenoid valve coils exceeds your expectations. For more detailed information about our warranty policy or to request support, please visit our website or contact our customer service team.
Website: www.example.com/support
Customer Service: 1-800-123-4567 
List “solenoid valve coil” FAQ
Solenoid Valve Coil FAQ
Q1: What is a solenoid valve coil?
A solenoid valve coil is an electromagnetic component that controls the operation of a solenoid valve. When energized, the coil generates a magnetic field that actuates the valve, allowing or blocking the flow of fluids or gases.
Q2: How does a solenoid valve coil work?
When electrical current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger or armature within the valve. This movement opens or closes the valve, regulating the flow of the medium.
Q3: What are common voltages for solenoid valve coils?
Common voltage ratings include 12V, 24V, and 48V DC, as well as 24V, 110V, and 220V AC. Always check the coil specifications to ensure compatibility with your system.
Q4: How do I choose the right solenoid valve coil?
Consider the voltage, frequency, power consumption, operating environment, and the type of fluid or gas being controlled. Also, ensure it matches the valve specifications.
Q5: Can solenoid valve coils be replaced?
Yes, solenoid valve coils can often be replaced. Ensure the new coil matches the voltage, power rating, and mounting specifications of the old one.
Q6: What can cause a solenoid valve coil to fail?
Common causes include overvoltage, overheating, frequent cycling, and environmental factors such as moisture or dust. Mechanical wear and tear can also cause failure.
Q7: How can I diagnose a faulty solenoid valve coil?
Check for signs of burning or damage, measure the coil’s resistance with a multimeter, and ensure it’s receiving the correct voltage. A significant deviation from the specified resistance usually indicates a problem.
Q8: Are solenoid valve coils interchangeable between different brands?
While some coils may be interchangeable, it’s generally best to use the manufacturer-recommended coils to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Q9: What maintenance is required for solenoid valve coils?
Regular inspections for signs of wear, ensuring a clean and dry operating environment, and verifying electrical connections can help maintain coil functionality.
Q10: Can solenoid valve coils be used in hazardous environments?
Specialized coils designed for hazardous environments are available. These coils meet specific safety standards and certifications, such as explosion-proof ratings. Always choose coils rated for your specific application needs.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about solenoid valve coil for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is a solenoid valve coil?
– A solenoid valve coil is an electromagnetic component that converts electrical energy into mechanical action, opening or closing a valve. It is an integral part of solenoid valves used for controlling fluid or gas flow.
2. Why should I source solenoid valve coils from China?
– China offers a wide variety of solenoid valve coils at competitive prices, with manufacturers providing high-quality products that meet international standards. Additionally, many Chinese suppliers offer customizable options and fast delivery times.
3. What certifications should I look for?
– Ensure the solenoid valve coils have ISO, CE, ROHS, and UL certifications. These standards indicate compliance with international safety and quality regulations.
4. What materials are commonly used in solenoid valve coils?
– Common materials include copper, aluminum for windings, and high-grade plastics or stainless steel for the housing. These materials ensure durability and efficiency.
5. Can I get customized solenoid valve coils?
– Yes, many Chinese suppliers offer customization services. You can specify parameters such as voltage, current, size, and connection types to fit your specific requirements.
6. What is the average lead time for manufacturing and shipping?
– The lead time varies but typically ranges from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the order size and customization level. Shipping can add an additional 1 to 3 weeks.
7. How do I ensure the quality of the solenoid valve coils?
– Request samples before bulk ordering, ask for detailed product specifications, and seek supplier references. Consider conducting factory audits or hiring third-party inspection services.
8. What are the typical voltage and current ratings?
– Solenoid valve coils are commonly available in voltage ratings of 12V, 24V, 110V, 220V, and can operate on AC or DC currents. The specific rating will depend on your application requirements.
9. What are the payment terms typically offered?
– Payment terms vary by supplier but often include options such as a 30% deposit with the balance paid before shipping, or different arrangements like Letter of Credit. Negotiate to find terms that suit both parties.
10. How to handle after-sales service and warranty issues?
– Verify the warranty period (commonly 1-2 years) and understand the supplier’s after-sales service policies. Establish a clear communication channel for addressing faults or defects promptly.
By addressing these FAQs, buyers can make an informed decision when sourcing solenoid valve coils from China.





