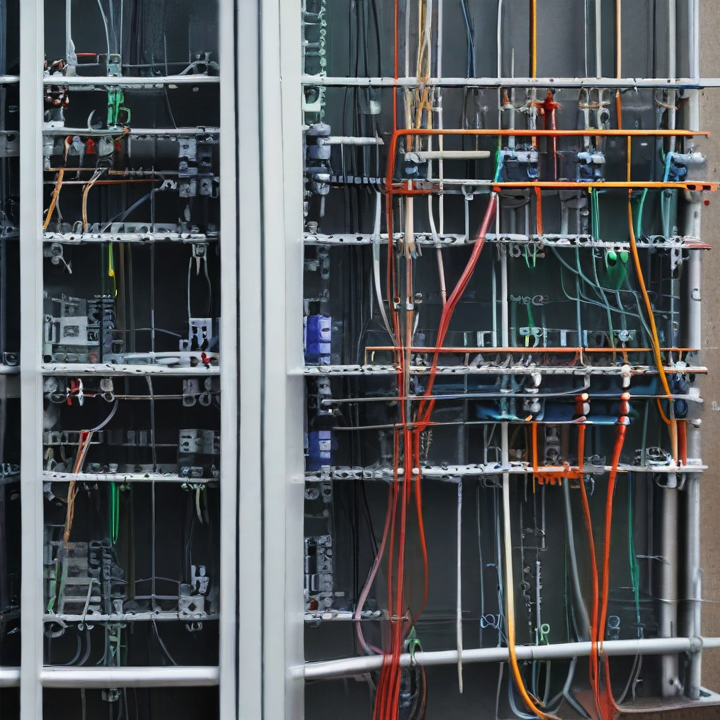
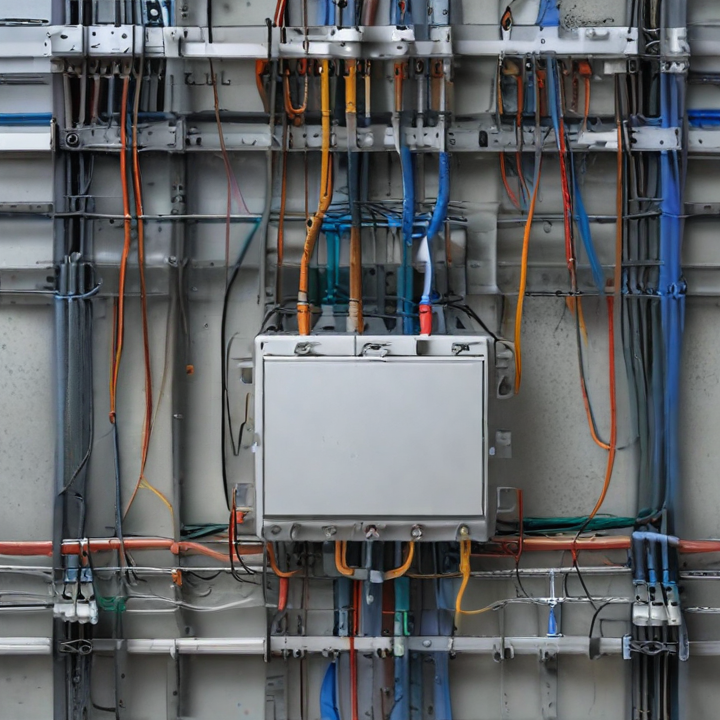
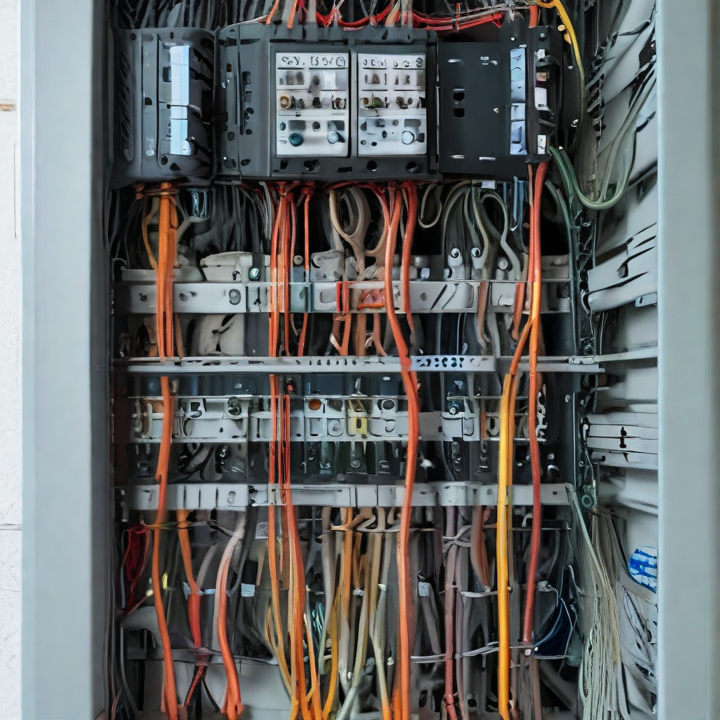
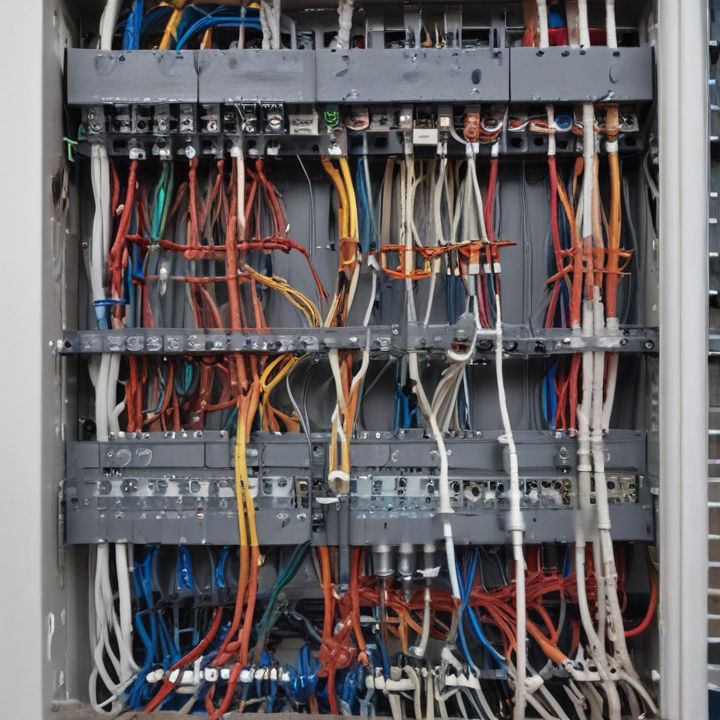
structured wiring Safety Certifications
Structured wiring refers to the comprehensive system of cabling and hardware that provides an organized infrastructure for telecommunication, data, and multimedia in buildings. Safety certifications are crucial to ensure these systems are safe, reliable, and compliant with industry standards. Here are key safety certifications relevant to structured wiring:
1. UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certifies structured wiring components like cables, connectors, and panels. UL certification indicates that these products meet stringent safety standards and are suitable for installation in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
2. ETL Listed Mark: Intertek’s ETL Listed Mark signifies that products have been tested to meet safety standards set by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and other regulatory bodies. ETL listing is comparable to UL certification and often recognized interchangeably.
3. CE Marking: The Conformité Européene (CE) marking is required for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). It indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. Structured wiring products with CE marking have passed rigorous assessments to ensure they are safe for use.
4. RoHS Compliance: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive limits the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic products. RoHS compliance ensures that structured wiring components do not contain harmful substances like lead, mercury, or cadmium, promoting safer, more environmentally friendly installations.
5. FCC Compliance: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates electromagnetic interference (EMI) from electronic devices. Structured wiring products must comply with FCC standards to prevent interference with other electronic devices, ensuring reliable and safe operation.
6. TIA/EIA Standards: The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) set standards for structured cabling systems, including safety and performance criteria. Compliance with TIA/EIA standards ensures that structured wiring installations are safe, reliable, and capable of supporting modern communication technologies.
These certifications and standards are essential for ensuring the safety, performance, and regulatory compliance of structured wiring systems in various applications.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “structured wiring”
Structured wiring refers to a standardized approach to wiring that integrates various types of cables and components into a single, unified system within a building. It typically includes the wiring for telephone, Internet, television, security, and home automation systems. Here are the key technical parameters:
1. Cable Types:
– Category 5e (Cat5e): Supports up to 1 Gbps Ethernet at 100 MHz.
– Category 6 (Cat6): Supports up to 10 Gbps Ethernet at 250 MHz.
– Category 6a (Cat6a): Supports up to 10 Gbps Ethernet at 500 MHz.
– Coaxial Cable (RG-6): Used for television and satellite signals.
– Fiber Optic Cable: Supports high-speed data transmission over long distances.
2. Cable Management:
– Patch Panels: Centralized points for connecting and organizing cables.
– Cable Trays and Conduits: Pathways for running cables throughout the building.
– Labeling: Each cable should be clearly labeled for easy identification.
3. Termination and Connectivity:
– RJ-45 Connectors: Used for Ethernet connections.
– F-Type Connectors: Used for coaxial cables.
– Keystone Jacks: Modular jacks that snap into wall plates.
4. Distribution Panels:
– Structured Media Enclosures: Central locations where all wiring converges.
– Patch Panels: Used to connect and manage cable terminations.
5. Network Performance:
– Bandwidth: The maximum rate of data transfer across the network.
– Latency: The delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction.
– Signal Attenuation: Reduction in signal strength over distance.
6. Compliance and Standards:
– TIA/EIA-568: Standards for commercial building telecommunications cabling.
– NEC (National Electrical Code): Safety standards for electrical wiring.
7. Environmental Considerations:
– Plenum-rated Cables: Used in air handling spaces to reduce fire risk.
– Shielded vs. Unshielded: Shielded cables reduce electromagnetic interference.
8. Future-Proofing:
– Upgradability: Installing higher category cables (e.g., Cat6a) to accommodate future technology upgrades.
– Flexibility: Design allowing for easy changes or additions to the network.
These parameters ensure that a structured wiring system is efficient, scalable, and capable of supporting modern and future technology needs.
List Product features of “structured wiring”
Structured Wiring Product Features:
1. Centralized Hub:
– Houses all connections in one location for ease of management.
– Facilitates the integration of various technologies and systems.
2. Modular Design:
– Allows for flexibility and scalability.
– Simplifies upgrades and additions to the network without significant rework.
3. High-Quality Cables:
– Uses Cat5e, Cat6, or fiber optic cables for high-speed data transmission.
– Ensures reliable and consistent performance across all connected devices.
4. Multiple Connection Points:
– Provides numerous outlets for different rooms and devices.
– Enables seamless connectivity for phones, internet, and entertainment systems.
5. Signal Distribution:
– Efficiently distributes signals for data, video, and voice throughout the property.
– Maintains signal strength and quality over long distances.
6. Interference Shielding:
– Uses shielding techniques to reduce electromagnetic interference.
– Enhances the clarity and reliability of transmitted signals.
7. Future-Proofing:
– Designed to support current and emerging technologies.
– Ensures long-term usability and relevance.
8. Ease of Maintenance:
– Simplifies troubleshooting with clearly labeled connections.
– Reduces downtime with accessible and organized wiring.
9. Aesthetic Integration:
– Concealed wiring for a clean and tidy look.
– Maintains the aesthetic integrity of the property.
10. Security and Control:
– Enables centralized control over the entire network.
– Enhances security with dedicated lines for specific services.
11. Enhanced Home Automation:
– Integrates seamlessly with smart home devices and systems.
– Facilitates automation and remote control of lighting, security, and climate.
12. Professional Installation:
– Typically installed by certified professionals.
– Ensures compliance with industry standards and optimal performance.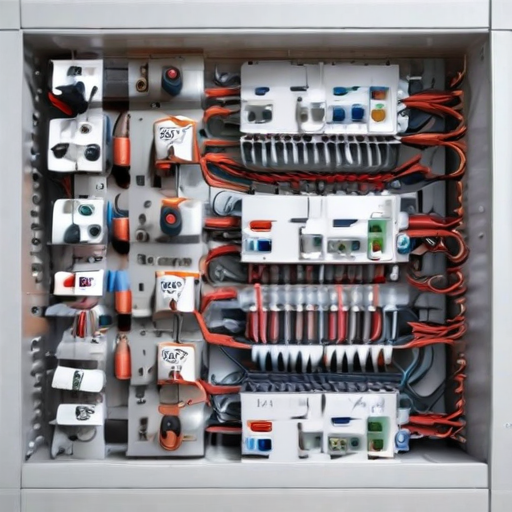
List Various Types of “structured wiring”
Structured wiring refers to a network of cables and hardware designed to provide comprehensive connectivity within a building. Here are various types of structured wiring commonly used:
1. Cat5e (Category 5 Enhanced): A standard twisted pair cable for Ethernet and other network physical layers, providing up to 1 Gbps speeds over a maximum length of 100 meters.
2. Cat6 (Category 6): An upgraded version of Cat5e, supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances (up to 55 meters) and up to 1 Gbps over 100 meters, with better resistance to interference.
3. Cat6a (Category 6 Augmented): Offers improved performance over Cat6, supporting 10 Gbps speeds up to 100 meters, and enhanced shielding to reduce crosstalk and interference.
4. Cat7 (Category 7): Provides high-speed data transmission up to 10 Gbps over 100 meters, with extensive shielding to minimize interference, suitable for high-demand applications.
5. Cat8 (Category 8): The latest standard, supporting speeds up to 40 Gbps over short distances (up to 30 meters), primarily used in data centers.
6. Coaxial Cable: Used for cable television, internet, and other RF signal transmission, offering high bandwidth and resistance to signal loss.
7. Fiber Optic Cable: Utilizes light to transmit data, offering extremely high speeds and bandwidth over long distances with minimal signal degradation, ideal for backbone cabling and high-speed internet connections.
8. HDBaseT: A connectivity standard for transmitting uncompressed high-definition video, audio, power, Ethernet, and control signals over Cat5e/6 cables.
9. Twisted Pair Cable (Shielded/Unshielded): Twisted pair cables like Cat5e and Cat6 can be either shielded (STP) or unshielded (UTP), with STP offering better protection against electromagnetic interference.
10. Speaker Wire: Used for audio systems, typically low-voltage, carrying audio signals from amplifiers to speakers, available in various gauges depending on the distance and power requirements.
11. Security and Alarm Cable: Specialized wiring for security systems, including sensors, alarms, and surveillance cameras, designed for reliable performance and easy installation.
These structured wiring types cater to various needs, from simple home networking to advanced commercial applications, ensuring robust and efficient connectivity.
List Application of “structured wiring”
Applications of Structured Wiring
1. Home Networking: Structured wiring supports home networks by connecting computers, printers, and smart devices, allowing for seamless data transfer and internet connectivity throughout the home.
2. Home Automation: It integrates various home automation systems, such as lighting controls, security systems, and climate control, providing centralized management and enhancing convenience.
3. Home Entertainment: Enables distribution of audio and video signals from a central location to multiple rooms, facilitating whole-home audio systems and centralized control of media devices.
4. Telecommunications: Structured wiring supports telephone systems by connecting multiple phone lines and devices, ensuring clear and reliable voice communication across different rooms.
5. Security Systems: It connects security cameras, sensors, and alarms, allowing for centralized monitoring and control, improving home security and response times.
6. Internet of Things (IoT): Facilitates the integration of IoT devices, including smart appliances and sensors, enabling them to communicate and operate effectively within the home’s network.
7. Business Applications: In commercial settings, structured wiring supports data networks, VoIP systems, and video conferencing, improving communication and productivity.
8. Energy Management: It integrates energy management systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and control of energy usage, contributing to energy efficiency and cost savings.
9. Future-Proofing: Provides a scalable infrastructure that can accommodate future technological advancements and increased demand for bandwidth, ensuring the home or business remains adaptable to new technologies.
10. Aesthetic and Maintenance Benefits: Structured wiring systems are typically concealed within walls, reducing clutter and making it easier to manage and troubleshoot network issues compared to traditional wiring methods.
These applications highlight the versatility and importance of structured wiring in both residential and commercial environments.
List Buyer Types of “structured wiring”
Buyer Types of Structured Wiring
1. Homeowners and Renovators:
– Homeowners looking to upgrade their home network capabilities often invest in structured wiring. This includes those renovating to enhance home automation, entertainment systems, and security features.
2. Builders and Contractors:
– Builders and general contractors who are constructing new homes or commercial buildings need structured wiring to ensure modern connectivity standards. This group includes those developing residential complexes, office buildings, and mixed-use properties.
3. IT and Network Managers:
– IT and network managers in corporate environments require structured wiring to support robust, scalable, and efficient network infrastructure. This is crucial for data centers, office networks, and campus-wide installations.
4. Telecommunications Companies:
– Telecommunication firms need structured wiring for the infrastructure that supports their services. This includes ensuring reliable phone lines, internet connections, and other telecommunications services in residential and commercial areas.
5. Security System Installers:
– Companies specializing in security systems, such as CCTV and alarm systems, require structured wiring to ensure proper installation and functionality of their equipment.
6. Smart Home Technology Providers:
– Providers of smart home technologies, including home automation and IoT devices, rely on structured wiring to ensure seamless integration and operation of their products.
7. Real Estate Developers:
– Real estate developers investing in high-end residential or commercial projects often include structured wiring in their plans to attract buyers who demand modern connectivity and automation features.
8. Healthcare Facilities:
– Hospitals and healthcare facilities require structured wiring to support advanced medical equipment, patient monitoring systems, and efficient hospital management systems.
9. Educational Institutions:
– Schools, colleges, and universities invest in structured wiring to support extensive network requirements for administrative tasks, classroom technology, and campus-wide internet access.
10. Hospitality Industry:
– Hotels and resorts need structured wiring to provide reliable internet access, entertainment systems, and integrated services for their guests.
List “structured wiring” Project Types for Different Industries
Structured Wiring Project Types for Different Industries
1. Residential:
– Home Automation: Installation of wiring for smart home systems, including lighting, security, and HVAC controls.
– Home Entertainment: Wiring for home theaters, multi-room audio systems, and gaming setups.
– Home Networking: Ethernet and Wi-Fi network wiring for high-speed internet throughout the home.
2. Commercial:
– Office Networks: Structured cabling for data and voice networks, enabling efficient communication and internet access.
– Security Systems: Wiring for surveillance cameras, access control, and alarm systems.
– Conference Rooms: Integration of AV systems, including projectors, screens, and video conferencing equipment.
3. Industrial:
– Factory Automation: Cabling for programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and machine interfaces.
– Industrial Networking: Robust wiring for industrial Ethernet networks, supporting communication between machinery.
– Energy Management: Wiring for monitoring and controlling energy consumption and distribution.
4. Healthcare:
– Medical Equipment Integration: Wiring for connectivity between medical devices, such as imaging systems and patient monitoring tools.
– Data Management: Structured cabling for electronic health record (EHR) systems and telemedicine services.
– Facility Security: Wiring for comprehensive security systems, including patient and staff safety measures.
5. Education:
– Classroom Technology: Wiring for interactive whiteboards, projectors, and smart learning devices.
– Campus Networking: Structured cabling to provide reliable internet and intranet access across school buildings.
– Security Systems: Installation of wiring for surveillance cameras and emergency communication systems.
6. Hospitality:
– Guest Services: Wiring for in-room entertainment systems, high-speed internet access, and smart room controls.
– Building Management: Cabling for HVAC systems, lighting controls, and energy management.
– Security and Surveillance: Structured wiring for comprehensive security systems, including CCTV and access control.
7. Retail:
– Point of Sale (POS) Systems: Cabling for POS terminals, inventory management, and customer service systems.
– Digital Signage: Wiring for electronic displays and advertising screens.
– Security Systems: Installation of surveillance cameras, alarm systems, and access control.
These structured wiring projects enable efficient communication, enhanced security, and advanced technological integration across various industries.
structured wiring Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Structured Wiring Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Structured wiring is essential for modern smart homes and businesses, ensuring efficient data, video, and voice communication. Upgrading and customizing accessories can enhance performance and tailor systems to specific needs.
#### Upgrades
1. High-Speed Ethernet Cables: Upgrade to Cat6 or Cat7 cables for faster data transfer rates, reducing latency in networked devices.
2. Patch Panels: Utilize modular patch panels to simplify network management and allow for easier upgrades or repairs.
3. Wireless Access Points (WAPs): Install advanced WAPs to extend and improve wireless coverage, ensuring robust connectivity throughout the space.
4. Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Switches: PoE switches can power devices like IP cameras and WAPs through Ethernet cables, reducing the need for separate power supplies and streamlining installation.
5. Surge Protectors: Integrate surge protectors to safeguard wiring systems from power surges, extending the lifespan of network components.
#### Custom Manufacturing Options
1. Custom Cable Lengths and Configurations: Manufacture cables to exact lengths and specifications to reduce clutter and improve signal integrity.
2. Specialty Connectors and Adapters: Create connectors and adapters tailored to specific requirements, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
3. Enclosures and Racks: Design custom enclosures and racks that fit unique space constraints or aesthetic preferences, providing secure and organized housing for networking equipment.
4. Branded Faceplates and Panels: Custom faceplates and panels can match interior designs and include branding for professional installations.
5. Environmental Considerations: Develop cables and accessories with enhanced shielding or rugged designs for environments exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, or interference.
Upgrading and customizing structured wiring accessories not only optimizes network performance but also ensures the system meets the precise needs of its users, providing a reliable and scalable solution for both residential and commercial applications.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “structured wiring”
Quality Control in Structured Wiring
1. Raw Material Inspection: The quality control process begins with inspecting raw materials like copper, insulation, and other components. Ensuring the materials meet industry standards is crucial for the final product’s performance.
2. In-Process Testing: During manufacturing, continuous in-process testing is conducted. This includes checking for correct wire gauge, insulation thickness, and proper assembly to ensure that the product adheres to specifications.
3. Electrical Testing: Each wire is tested for electrical conductivity, resistance, and signal integrity. This step ensures that the wires will function correctly in their intended applications.
4. Visual Inspection: Wires are visually inspected for defects such as kinks, cuts, or improper labeling. This step is essential for identifying physical imperfections that might affect performance or safety.
5. Final Quality Check: Before packaging, a final quality check is performed. This includes re-testing for electrical properties and ensuring all components meet the required standards.
Manufacturing Process of Structured Wiring
1. Drawing: The manufacturing process begins with drawing copper rods through a series of dies to reduce their diameter to the desired wire gauge. This step is critical for ensuring consistent wire thickness.
2. Annealing: The drawn copper wires are annealed to soften them, making them more flexible and easier to handle during further processing.
3. Stranding: Multiple copper wires are stranded together to form a cable. This process enhances the strength and flexibility of the final product.
4. Insulation: The stranded wires are then coated with an insulating material, typically PVC or polyethylene. This insulation provides electrical isolation and protects the wires from physical damage.
5. Twisting: For structured cabling, pairs of insulated wires are twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, ensuring better signal quality.
6. Sheathing: The twisted pairs are bundled and covered with an outer sheath for additional protection and organization.
7. Testing and Quality Control: The finished cables undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure they meet industry standards and customer specifications.
8. Packaging: After passing all quality checks, the cables are wound onto reels or cut to length, then packaged for shipping.
These steps ensure that structured wiring is reliable, efficient, and meets the necessary performance standards.
How to use “structured wiring”
Structured wiring is a system designed to centralize and organize your home or office network. It integrates various types of wiring, including data, voice, video, and audio cables, into a single infrastructure. Here’s how to use it effectively:
1. Plan the Network:
– Identify all the devices and services you want to connect, such as computers, TVs, telephones, security cameras, and home automation systems.
– Determine the locations of these devices and create a detailed layout.
2. Choose the Right Cables:
– Use Cat5e or Cat6 cables for data and telephone connections. Cat6 is preferable for higher data speeds.
– Use coaxial cables for video and TV connections.
– Opt for fiber optic cables if you need high-speed internet or long-distance data transmission.
3. Install a Central Hub:
– Set up a central distribution panel or structured wiring enclosure in a utility room or closet. This hub will house all the connections and network devices like routers, switches, and splitters.
4. Run the Cables:
– Run cables from the central hub to each room or device location following your layout plan.
– Use conduit or cable trays to protect the cables and ensure easy future access.
5. Terminate and Label Cables:
– Terminate the cables with appropriate connectors, such as RJ45 jacks for Ethernet cables.
– Label each cable clearly to identify its destination or function, making troubleshooting and future modifications easier.
6. Connect to Devices:
– Connect the cables to their respective devices and test each connection to ensure it is working properly.
– Use patch panels in the central hub to organize and manage connections neatly.
7. Maintenance and Upgrades:
– Regularly check connections and replace any damaged cables.
– Upgrade the system as needed to accommodate new technologies or increased bandwidth requirements.
By following these steps, you can efficiently use structured wiring to create a reliable, scalable, and organized network in your home or office.
“structured wiring” Comparative Analysis
Structured wiring and conventional cabling are two distinct approaches to setting up network infrastructures, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Structured Wiring:
1. Design and Organization: Structured wiring involves a pre-planned, centralized system designed to handle future upgrades and modifications efficiently. This system includes a mix of coaxial, Ethernet (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6A), and fiber optic cables organized to provide optimal performance and flexibility. Each device is connected to a centralized patch panel, making the network neat and easily manageable.
2. Scalability and Upgrades: Structured wiring supports easy scalability and upgrades. New devices can be added without disrupting the existing network, thanks to the centralized management system. This is particularly beneficial as technology evolves and the demand for bandwidth increases.
3. Performance and Reliability: The use of higher-grade cables like Cat6 and Cat6A ensures high-speed connectivity (up to 10Gbps), which is crucial for modern applications such as 4K streaming, online gaming, and remote work. The system’s design reduces interference and improves signal quality, leading to more reliable network performance.
4. Installation and Maintenance: While the initial installation of structured wiring can be more complex and costly, it reduces long-term maintenance costs. The organized setup simplifies troubleshooting and minimizes downtime during repairs or upgrades.
Conventional Cabling:
1. Simplicity and Cost: Conventional cabling connects devices directly from one point to another without a centralized system, making it cheaper and simpler to install initially. This method is often used in smaller or less complex networks where budget constraints are a priority.
2. Limitations in Scalability: Conventional systems are less flexible for future upgrades. Adding new devices often requires additional cables and can lead to a tangled, congested setup. This lack of organization can complicate maintenance and troubleshooting.
3. Performance: While conventional cabling can support high-speed networking, it is less efficient in managing large volumes of data traffic. This can lead to slower performance and increased risk of signal interference as more devices are added to the network.
In summary, structured wiring offers significant advantages in terms of scalability, performance, and long-term maintenance, making it the preferred choice for modern, high-demand network environments. However, for smaller or less demanding setups, conventional cabling remains a viable, cost-effective option.
“structured wiring” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support for Structured Wiring
Our structured wiring solutions come with a comprehensive warranty and support package designed to ensure reliability and customer satisfaction.
Warranty Coverage
1. Product Warranty: We offer a 25-year warranty on all our structured wiring products. This covers defects in materials and workmanship, ensuring that our cables, connectors, and related hardware are free from flaws and function correctly when used as intended.
2. Performance Guarantee: Our structured wiring systems are guaranteed to meet or exceed industry standards for performance. If the system fails to deliver the specified data transmission rates or signal integrity, we will address the issue promptly.
3. Installation Warranty: Installations performed by our certified technicians are covered under a 10-year workmanship warranty. This ensures that all components are installed correctly and efficiently.
Support Services
1. Technical Support: Our technical support team is available 24/7 to assist with any issues or questions related to our structured wiring systems. This includes troubleshooting, system optimization, and answering any technical inquiries.
2. Remote Assistance: For quick resolution of issues, we offer remote support services. Our technicians can diagnose and resolve many problems without the need for an on-site visit, minimizing downtime and disruption.
3. On-Site Support: For more complex issues, our certified technicians are available for on-site support. We aim to have a technician at your location within 48 hours of a reported issue, ensuring minimal impact on your operations.
4. Training and Resources: We provide comprehensive training for your IT staff, including detailed manuals and online resources to help them manage and maintain the structured wiring system effectively.
By choosing our structured wiring solutions, you are investing in a robust, reliable infrastructure backed by an extensive warranty and dedicated support services, ensuring long-term performance and peace of mind.
List “structured wiring” FAQ
Structured Wiring FAQ
1. What is structured wiring?
Structured wiring is an organized network of cables and hardware that provides a comprehensive telecommunications infrastructure. This system supports various home automation and communication needs, including internet, phone, TV, and security systems.
2. Why is structured wiring important?
Structured wiring ensures efficient and reliable connectivity for multiple devices. It future-proofs a home by providing the infrastructure needed for new technologies and increases the property’s value.
3. What are the components of a structured wiring system?
A structured wiring system typically includes a central distribution hub, category 5e/6 cables for data, coaxial cables for TV, telephone wires, and sometimes fiber optic cables. It also includes wall plates, connectors, and patch panels.
4. Can structured wiring be installed in an existing home?
Yes, although it is easier to install during new construction, structured wiring can be retrofitted into existing homes. This process may require some modifications to walls and ceilings.
5. What devices can be connected through structured wiring?
Structured wiring supports various devices, including computers, smart TVs, security cameras, home automation systems, gaming consoles, and home theaters.
6. How does structured wiring improve internet performance?
By using high-quality cables and a centralized distribution hub, structured wiring reduces signal interference and enhances internet speed and reliability, providing better performance for wired and wireless devices.
7. Is professional installation required for structured wiring?
Professional installation is recommended to ensure that the system is properly designed, installed, and tested. This guarantees optimal performance and compliance with industry standards.
8. What maintenance does structured wiring require?
Structured wiring systems require minimal maintenance. However, it’s important to periodically check connections and cables for any signs of wear or damage and ensure that the distribution hub remains organized and dust-free.
9. What are the costs associated with structured wiring?
The cost of structured wiring varies based on the size of the home, the complexity of the system, and the quality of materials used. It can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars.
10. Can structured wiring integrate with wireless systems?
Yes, structured wiring complements wireless systems by providing robust wired backbones that enhance the overall performance and reliability of wireless networks.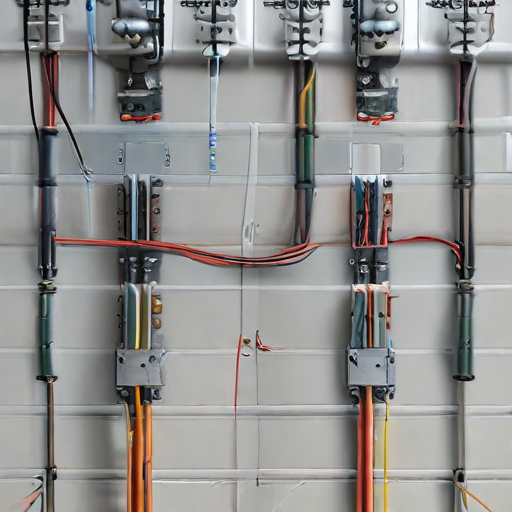
Top 10 FAQ with answer about structured wiring for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQ on Structured Wiring for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is structured wiring?
– Structured wiring is a system of cabling that integrates and connects multiple types of communication services within a building, such as internet, telephone, and television.
2. Why source structured wiring from China?
– China offers competitive pricing, a vast selection of manufacturers, and advanced production capabilities, ensuring high-quality products and cost efficiency.
3. What certifications should I look for?
– Look for certifications like ISO 9001, CE, UL, and RoHS to ensure product quality and compliance with international standards.
4. How do I verify the reliability of a Chinese supplier?
– Verify through third-party audits, requesting product samples, checking references, and using platforms like Alibaba with verified suppliers.
5. What types of cables are included in structured wiring?
– Common types include Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, fiber optic cables, coaxial cables, and audio/video cables.
6. What are the typical lead times for orders?
– Lead times vary but generally range from 2 to 6 weeks depending on order size and customization requirements.
7. Can I get customized structured wiring solutions?
– Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization options for length, color, shielding, and specific technical requirements.
8. How does shipping and logistics work?
– Suppliers typically handle shipping through air, sea, or express courier. Ensure to discuss Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) and confirm responsibilities for customs clearance.
9. What are the payment terms?
– Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and occasionally escrow services. Initial orders might require a deposit.
10. What should I consider for quality control?
– Implement quality control measures like pre-shipment inspections, in-house testing reports, and third-party laboratory tests to ensure product standards are met.
By considering these factors, buyers can effectively source structured wiring from China, ensuring quality, cost-efficiency, and reliable supply chains.