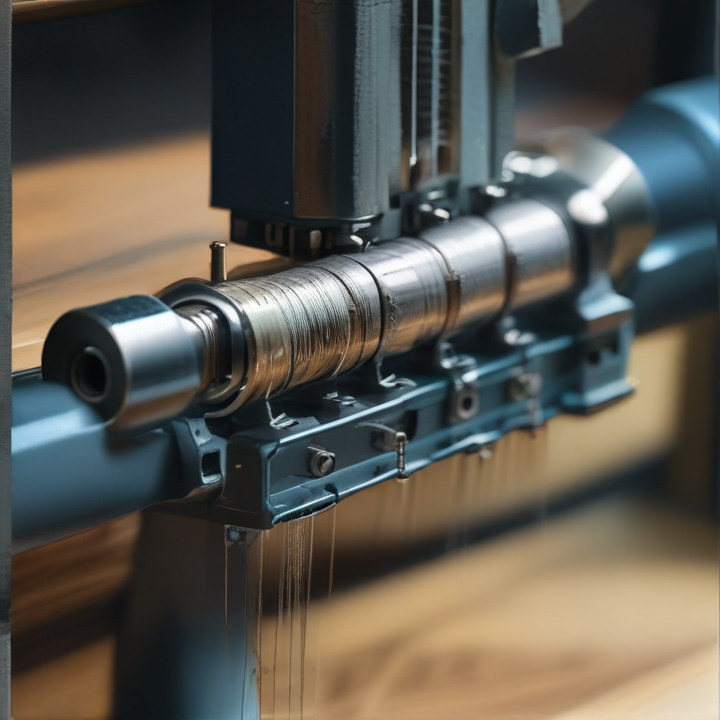
thread rolling machine Safety Certifications
Thread rolling machines are widely used in manufacturing for producing threaded parts through a cold-forming process. Due to the nature of their operation, safety certifications are crucial for ensuring the well-being of operators and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
1. ISO 12100:2010 – This international standard provides guidelines on risk assessment and risk reduction. It is essential for identifying hazards and implementing safety measures in the design and use of thread rolling machines.
2. CE Marking – In Europe, thread rolling machines must be CE marked, indicating compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements. This involves meeting directives like the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, which outlines essential safety requirements.
3. ANSI B11.9-2010 – In the United States, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provides specific safety requirements for the design, construction, care, and use of thread rolling machines. This standard helps mitigate risks related to machine operation.
4. OSHA Regulations – The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) enforces regulations for workplace safety. For thread rolling machines, compliance with OSHA standards (such as Lockout/Tagout 29 CFR 1910.147) is mandatory to protect workers from mechanical hazards.
5. UL Certification – Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification may be required for electrical components of thread rolling machines, ensuring they meet safety standards to prevent electrical hazards.
6. CSA Standards – In Canada, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) provides standards for machinery safety. Being CSA compliant demonstrates that the machine meets national safety benchmarks.
Manufacturers and operators must prioritize these certifications to enhance operational safety, protect workers, and avoid legal liabilities. Regular training and maintenance aligned with these standards ensure ongoing compliance and safe machine operation.
List Reference Technical Parameters of “thread rolling machine”
Sure, here’s a concise list of reference technical parameters for a thread rolling machine:
1. Rolling Pressure: Typically measured in tons or kilonewtons (kN), this indicates the maximum force the machine can exert to form threads.
2. Rolling Speed: Denoted in revolutions per minute (RPM) or meters per minute (m/min), it defines the machine’s operational speed.
3. Thread Rolling Capacity: Specifies the range of thread diameters and pitches the machine can handle, usually in millimeters (mm) or inches.
4. Spindle Diameter: The maximum diameter of the spindle that supports the rolling dies, normally in millimeters.
5. Max Workpiece Diameter: Indicates the largest diameter of the workpiece that can be processed, typically in millimeters.
6. Workpiece Length: Defines the longest workpiece the machine can accommodate, measured in millimeters.
7. Number of Spindles: Single, twin, or multi-spindle configurations determine how many threads can be formed simultaneously.
8. Motor Power: The power rating of the machine’s main motor, usually given in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (HP).
9. Die Type and Size: Information on compatible dies, including flat dies, cylindrical dies, and their dimensions.
10. Control System: Type of control used, such as manual, CNC (Computer Numerical Control), or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller).
11. Feed Rate: Speed at which material is fed into the machine, often in millimeters per second (mm/s).
12. Machine Dimensions: Physical dimensions of the machine, including length, width, and height, typically in millimeters.
13. Weight: Total weight of the thread rolling machine, generally in kilograms (kg) or tons.
14. Cooling System: Specifications of the cooling system used to maintain die and workpiece temperature, including type (air or liquid).
15. Lubrication System: Details about the automatic or manual lubrication system for maintaining machine efficiency.
These parameters provide crucial insights for selecting a thread rolling machine suited to specific industrial needs.
List Product features of “thread rolling machine”
A thread rolling machine is an essential tool in manufacturing, providing a range of features designed to efficiently produce high-quality threads on various materials. Here are its key product features:
1. Durable Construction: Built with robust materials like high-strength steel, ensuring longevity and reliability even under high-pressure operations.
2. Precision Threading: Equipped with advanced mechanisms and fine-tuning capabilities to produce accurate and consistent threads, crucial for both standard and custom applications.
3. High-Speed Operation: Capable of high-speed threading to enhance productivity, reducing cycle times and increasing output.
4. Automatic and Manual Modes: Offers both automatic and manual control options, providing flexibility for different operational needs and expertise levels.
5. Versatile Thread Types: Suitable for rolling various thread types, including metric, inch, trapezoidal, and special profiles, providing versatility for diverse applications.
6. Material Compatibility: Can handle a wide range of materials such as steel, aluminum, titanium, and high-strength alloys, making it suitable for multiple industries.
7. Energy Efficiency: Designed to consume less power without compromising performance, promoting cost savings and environmental sustainability.
8. User-Friendly Interface: Features an intuitive control panel with easy-to-navigate menus, allowing operators to set parameters and monitor processes effortlessly.
9. Maintenance Accessibility: Engineered for easy maintenance with accessible parts and clear guidelines, minimizing downtime and extending machine life.
10. Safety Features: Includes protective guards, emergency stop buttons, and other safety mechanisms to ensure operator safety and comply with industry standards.
11. Compact Design: Space-efficient design enables easy integration into existing production lines without requiring significant floor space.
12. Advanced Cooling System: Incorporates an efficient cooling system to handle high operational temperatures, maintaining machine performance and preventing overheating.
13. Customization Options: Offers the possibility of customization to meet specific production requirements, enhancing operational efficiency.
These features make the thread rolling machine an invaluable asset for high-precision, efficient, and versatile thread production in various manufacturing sectors.
List Various Types of “thread rolling machine”
Thread rolling machines are specialized equipment used in manufacturing to create threads on fasteners like bolts and screws. There are several types of thread rolling machines, each designed for specific applications and material properties. Here are some of the main types:
1. Flat Die Thread Rolling Machine
These machines use two flat dies that move in opposite directions. The workpiece is placed between the dies, which then press and roll the material to form threads. They are commonly used for high-volume production and are suitable for small to medium-sized parts.
2. Cylindrical Die Thread Rolling Machine
Also known as rotary or planetary thread rolling machines, these use cylindrical dies that rotate around a stationary workpiece. This type is ideal for larger diameters and longer threads, and it offers high precision and consistency.
3. Three-Die Thread Rolling Machine
This machine employs three radial dies that simultaneously press against a workpiece, providing superior concentricity and thread quality. They are particularly suitable for producing high-precision threads and are often used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
4. Tangential Thread Rolling Machine
In this machine, the workpiece is stationary while the dies move tangentially. This type is excellent for producing threads on long, slender workpieces and is often used for threading wires and rods.
5. Axial Thread Rolling Machine
Axial machines force the thread-forming dies against the axis of the workpiece. They are useful for parts with complex geometries and for adding threads to pre-formed blanks.
6. Hydraulic Thread Rolling Machine
These machines use hydraulic power to exert the necessary force for thread forming. They offer adjustable pressure settings, making them suitable for a wide range of materials, including high-tensile alloys.
7. Mechanical Thread Rolling Machine
Mechanical thread rolling machines rely on mechanical systems, such as cams and levers, to generate force. While less versatile than hydraulic machines, they are efficient and cost-effective for specific applications.
Each type of thread rolling machine has its unique advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the job—whether it’s the size, material, production volume, or thread precision needed.
List Application of “thread rolling machine”
Thread rolling machines are essential in a range of industrial applications due to their efficiency in creating strong, precise threads. Below are some key uses:
1. Automotive Industry: Thread rolling machines are employed to produce fasteners like bolts and screws that are integral to vehicle assembly. The resulting components are durable, capable of withstanding high stress, and are produced with high efficiency.
2. Aerospace Sector: The aerospace industry demands components with superior mechanical properties. Thread rolling produces threads that can bear high loads and resist fatigue, meeting stringent aerospace requirements for both safety and reliability.
3. Construction: Fasteners such as screws and bolts required in construction can be manufactured using thread rolling machines. These machines ensure a high strength and durability of the threads, crucial for structural integrity in buildings and infrastructure projects.
4. Consumer Electronics: Miniature screws used in assembling consumer electronics, such as smartphones and laptops, are often produced using thread rolling machines. The precision and consistency offered by this process are vital for the tight assembly and longevity of electronic devices.
5. Medical Devices: In the medical field, threaded components in surgical instruments and implants are made using thread rolling machines. The process provides high precision and clean finishes, conforming to the strict hygiene and performance standards required in medical applications.
6. Oil and Gas Industry: Components like drill pipes, connectors, and couplings used in oil and gas extraction benefit from thread rolling due to the robust performance of the threads under extreme conditions.
7. Industrial Machinery: Threads needed in various types of machinery, including pumps, compressors, and gear systems, are produced using thread rolling machines. The strong, durable threads improve the longevity and reliability of industrial equipment.
In summary, thread rolling machines are pivotal across various industries for their ability to produce high-strength, durable, and precise threaded components efficiently.
List Buyer Types of “thread rolling machine”
When it comes to thread rolling machines, there are several distinct buyer types that come into play, each with their own unique set of requirements and expectations. Here’s a brief overview:
1. Manufacturing Companies:
– Automotive Industry: These companies use thread rolling machines for producing high-strength, high-precision threaded components for engines, transmissions, and other vehicle assemblies.
– Aerospace Sector: They require machines with very high precision and reliability for the production of threaded components that meet stringent regulatory standards.
– General Engineering: This category includes diverse manufacturing businesses producing hardware, fasteners, or custom parts that require durable and precise threads.
2. Construction and Infrastructure Firms:
– Companies involved in building infrastructure often need robust threaded components like rebar, bolts, and anchors. They seek machines that can produce high volumes and operate in demanding environments.
3. Oil & Gas Industry:
– This sector requires equipment that can produce threads for various pipes, valves, and couplings used in drilling and transporting oil and gas. Durability and precision are critical due to the harsh operating conditions.
4. Small to Medium Enterprises (SMEs):
– These businesses seek versatile and cost-effective thread rolling machines for smaller production runs. Flexibility and ease of operation are often key considerations.
5. Job Shops and Custom Fabricators:
– These firms handle specialized projects and demand machines capable of quick changeovers and handling diverse materials and thread types. Customization and adaptability are crucial.
6. Medical Device Manufacturers:
– They require machines that can produce precision threads for components in medical devices, implants, and equipment, adhering to stringent health and safety standards.
7. Academic and Research Institutions:
– Universities and research labs might purchase thread rolling machines for experimental and educational purposes, needing machines with diverse capability ranges and high precision.
8. Tool and Die Makers:
– These buyers need machines for creating high-quality threading dies and related tools, where accuracy and durability are paramount.
By understanding these various buyer types, manufacturers and suppliers of thread rolling machines can better tailor their products and services to meet specific market needs.
List “thread rolling machine” Project Types for Different Industries
Thread rolling machines are versatile tools used across various industries for the efficient creation of threaded parts. Below are some key project types in different sectors:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Bolts and Fasteners: Manufacturing high-strength bolts and fasteners for vehicle assembly.
– Engine Components: Creating precisely threaded parts for engines, such as camshafts and crankshafts.
2. Aerospace Industry:
– Aircraft Fasteners: Production of lightweight yet robust threaded fasteners essential for aircraft assembly.
– Landing Gear Components: Manufacturing threads for critical components like struts and supports.
3. Construction Industry:
– Rebar Threads: Creating threaded connectors for reinforcing bars in concrete structures.
– Scaffolding Parts: Producing threaded joints and connectors for scaffolding systems.
4. Oil and Gas Industry:
– Pipeline Connectors: Fabricating threaded connectors and couplings for pipelines.
– Drill Bits: Manufacturing threaded ends for drill bits and other downhole tools.
5. Medical Industry:
– Surgical Instruments: Producing precision-threaded surgical instruments and implants.
– Orthopedic Screws: Creating specialized threaded screws used in orthopedic surgery.
6. Electrical Industry:
– Conduit Connectors: Manufacturing threaded connectors and fittings for electrical conduits.
– Transformer Parts: Producing threaded components for electrical transformers and other equipment.
7. Consumer Products Industry:
– Appliance Parts: Creating threaded components for household appliances.
– Electronic Devices: Manufacturing small-scale threaded parts for various electronic gadgets.
8. Heavy Machinery Industry:
– Machine Bolts and Screws: Producing sturdy, large-scale threaded bolts and screws for heavy machinery.
– Hydraulic Components: Creating threaded parts for hydraulic systems in industrial machinery.
Each industry leverages thread rolling machines to optimize performance, durability, and precision in their threaded components.
thread rolling machine Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Upgrading and customizing a thread rolling machine can significantly enhance its performance, versatility, and efficiency. Here are some key accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options to consider:
1. Automated Feeding Systems: Enhancing productivity by integrating automated feeding systems like hoppers, vibratory bowl feeders, or conveyor belts to ensure continuous and precise part delivery.
2. Adjustable Die Holders: Opt for adjustable die holders to accommodate various die sizes, providing greater flexibility for different threading requirements.
3. Cooling and Lubrication Systems: Extend tool life and improve thread quality by installing advanced cooling and lubrication systems. Options include mist spray units or flood lubrication systems.
4. Servo Motors and Drives: Upgrade to servo motors and drives for precise control and higher efficiency. This allows for better synchronization, consistent thread quality, and faster cycle times.
5. Digital Control Panels: Implement digital control panels with touch-screen interfaces, providing operators with easy access to machine settings, diagnostics, and real-time monitoring.
6. Safety Upgrades: Ensure operator safety with the addition of safety guards, emergency stop buttons, and light curtains, complying with industry safety standards.
7. Custom Dies and Rollers: Design and manufacture custom dies and rollers tailored to specific threading profiles, materials, and sizes, maximizing the versatility of your thread rolling machine.
8. Integration with Industry 4.0: Upgrade to Industry 4.0-compatible systems for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data analytics to optimize machine performance and reduce downtime.
9. Enhanced Frame and Structure: Opt for reinforced frames and upgraded structural components to handle higher production loads and improve machine stability.
10. Quick-Change Tooling: Reduce setup times with quick-change tooling systems, allowing for rapid transitions between different threading tasks without compromising accuracy.
By incorporating these accessories and custom manufacturing options, your thread rolling machine can achieve higher performance, better quality output, and increased operational efficiency, making it a valuable asset in any production environment.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “thread rolling machine”
Quality Control of Thread Rolling Machine:
1. Raw Material Inspection:
– Verify the quality of steel and other materials.
– Check for consistency in dimensions and properties.
2. In-Process Inspection:
– Monitor the machining process to ensure precision.
– Use gauges and micrometers to measure parts.
– Regularly check and calibrate equipment.
3. Component Testing:
– Analyze critical components (e.g., rollers, dies) for hardness, durability.
– Perform surface roughness tests to ensure smooth part interactions.
4. Assembly Inspection:
– Confirm all parts are correctly assembled.
– Perform alignment checks to ensure accurate thread rolling.
5. Operational Testing:
– Conduct trial runs to evaluate machine performance.
– Check thread uniformity and accuracy on rolled products.
6. Final Quality Assurance:
– Review all test and inspection data.
– Certify machine ready for dispatch after comprehensive quality checks.
—
Manufacturing Process of Thread Rolling Machine:
1. Design and Engineering:
– Develop precise designs using CAD software.
– Create detailed blueprints and specifications.
2. Material Procurement:
– Source high-quality steel and components.
– Ensure materials comply with design requirements.
3. Machining and Fabrication:
– Cut, shape, and machine raw materials into components.
– Use CNC machines for accurate and consistent parts.
4. Heat Treatment:
– Harden specific parts like rollers and dies.
– Ensure durability and wear resistance.
5. Surface Finishing:
– Apply painting or coating to prevent corrosion.
– Polish parts where necessary for smooth interaction.
6. Assembly:
– Assemble base, frame, rollers, and other components.
– Integrate hydraulic and electrical systems.
7. Testing and Calibration:
– Adjust settings for optimal performance.
– Verify machine functions correctly under various conditions.
8. Packaging and Shipping:
– Secure machine in protective packaging.
– Coordinate logistics for timely delivery to customers.
How to use “thread rolling machine”
Using a thread rolling machine involves several essential steps to ensure that threads are accurately and safely rolled onto workpieces. Here’s a concise guide:
1. Preparation:
– Select Dies: Choose the appropriate thread rolling dies based on the thread size and type required.
– Inspect Machine: Ensure the machine is in good working condition, clean, and properly lubricated.
2. Setup:
– Install Dies: Secure the thread rolling dies onto the machine. Ensure they are aligned correctly.
– Adjust Settings: Set the machine parameters (speed, feed rate, etc.) according to the material and thread specifications.
3. Load Workpiece:
– Feeding: Place the workpiece into the feeding mechanism of the machine.
– Positioning: Align the workpiece properly to ensure accurate thread rolling. Manual or automated systems might be employed.
4. Thread Rolling:
– Engage Machine: Activate the machine to begin the rolling process. The dies will press into the workpiece, forming the threads through rolling action.
– Monitor Process: Watch the operation to ensure threads are forming correctly and to prevent any deviations or misalignments.
5. Quality Check:
– Inspect Threads: After the rolling process, inspect the threads for accuracy, uniformity, and adherence to specified dimensions.
– Measurements: Use thread gauges or micrometers to ensure threads meet required standards.
6. Adjustments and Maintenance:
– Fine-Tuning: Make any necessary adjustments to the machine settings if threads are not forming correctly.
– Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance such as cleaning dies, checking alignment, and lubricating parts to keep the machine running efficiently.
7. Safety:
– Protective Gear: Always wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses.
– Machine Guards: Ensure all machine guards are in place to prevent accidents.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a thread rolling machine to produce high-quality threads on various workpieces.
“thread rolling machine” Comparative Analysis
Thread rolling machines are essential for producing high-quality threads on fasteners and other cylindrical parts. Different types of thread rolling machines cater to varying production needs, materials, and thread forms. Below, I provide a comparative analysis of several popular types:
1. Flat Die Thread Rolling Machines:
– Operation: Two flat dies with thread profile move relative to each other.
– Advantages:
– High production speed.
– Suitable for mass production.
– Efficient for short threads and small diameter workpieces.
– Disadvantages:
– Limited flexibility in terms of thread types and sizes.
– Higher wear and tear on dies.
2. Radial Thread Rolling Machines:
– Operation: Three or more radial dies surround and roll the workpiece.
– Advantages:
– Ideal for high precision and large diameter threads.
– Even distribution of pressure, resulting in better thread quality.
– Disadvantages:
– Slower than flat die machines.
– Complex setup and higher initial cost.
3. Cylindrical (Planetary) Thread Rolling Machines:
– Operation: Multiple dies rotate around the workpiece.
– Advantages:
– Capable of rolling long threads.
– Flexible in handling different thread forms and sizes.
– Disadvantages:
– Lower production rates compared to flat die machines.
– More maintenance required due to complex mechanism.
4. Tangential Thread Rolling Machines:
– Operation: Dies engage the workpiece tangentially.
– Advantages:
– Excellent for precision threads.
– Suitable for high-strength materials.
– Disadvantages:
– Slower operation speed.
– Limited to certain thread lengths and diameters.
Comparison Summary:
– Speed: Flat Die > Radial > Tangential = Cylindrical.
– Precision: Tangential > Radial > Cylindrical > Flat Die.
– Flexibility: Cylindrical > Tangential > Radial > Flat Die.
– Cost: Flat Die < Radial < Tangential < Cylindrical.
Choosing the right thread rolling machine depends on specific production requirements such as thread type, material, volume, and budget. For mass production and speed, flat die machines are preferable, whereas for precision and versatility, cylindrical and tangential machines stand out.
“thread rolling machine” Warranty and Support
Warranty and Support
Our thread rolling machines are backed by a comprehensive warranty and robust support services to ensure seamless operation and customer satisfaction. The standard warranty coverage for our machines spans 12 months from the date of purchase, covering manufacturing defects, material faults, and craftsmanship issues. During the warranty period, any defective parts will be repaired or replaced at no additional cost. This warranty extends to all components of the machine, ensuring full operational integrity.
To request warranty service, customers must provide proof of purchase and a detailed description of the issue. Our warranty does not cover wear and tear, misuse, or damage resulting from improper maintenance or unauthorized modifications. Additionally, consumable parts such as rolling dies and lubricants are not included under the warranty.
Support services are a cornerstone of our commitment to customer satisfaction. Our dedicated technical support team is available 24/7 to assist with troubleshooting, maintenance advice, and operational guidance. Customers can reach out via phone, email, or through our online support portal.
We offer comprehensive training programs and detailed user manuals to ensure customers can maximize the efficiency and performance of their thread rolling machines. For more complex issues, on-site service visits by our qualified technicians can be arranged, subject to availability.
Customers also benefit from our extensive inventory of spare parts, which ensures that any necessary replacements are readily accessible, minimizing downtime. Regular maintenance packages are available to extend the life and performance of the machine beyond the warranty period.
In summary, our thread rolling machines come with a solid 12-month warranty and a suite of support services designed for efficiency and reliability, ensuring our customers achieve optimal productivity with minimal interruptions.
List “thread rolling machine” FAQ
FAQs about Thread Rolling Machines
1. What is a thread rolling machine?
A thread rolling machine is a device used to form threads on fasteners such as screws and bolts. Unlike cutting, thread rolling involves deforming the workpiece to create the threads, resulting in stronger and more precise threads without material loss.
2. How does thread rolling work?
Thread rolling works through a cold-forming process where cylindrical workpieces are pressed between hardened steel dies containing the thread profile. As pressure is applied, the metal flows into the die grooves, forming the thread.
3. What are the advantages of thread rolling compared to thread cutting?
– Strength: Rolled threads have greater tensile strength and resistance to fatigue.
– Surface Finish: Thread rolling provides a smoother finish.
– Material Conservation: The process does not remove material, minimizing waste.
– Speed: Thread rolling is faster than cutting, increasing production rates.
4. What materials are suitable for thread rolling?
Materials that are ductile and can undergo plastic deformation are suitable. Common examples include steels, aluminum, brass, and certain plastics.
5. What types of thread rolling machines are there?
– Flat-die machines: Use two flat dies that move parallel to each other.
– Rotary-die machines: Use a plunge and through-feed technique for continuous production.
– Planetary machines: Utilize multiple dies to form threads in a planetary motion around the workpiece.
6. How do you maintain a thread rolling machine?
Regular maintenance includes lubrication of moving parts, inspection for wear and tear on dies and guides, and ensuring that all adjustments are correct for consistent thread quality.
7. Is operator training necessary?
Yes, proper training ensures the operator understands machine settings, maintenance, safety precautions, and troubleshooting, leading to optimal machine performance and product quality.
8. Can thread rolling be used for custom threads?
Yes, custom dies can be manufactured to meet specific thread profiles and requirements, making the process versatile for specialized applications.
Conclusion
A thread rolling machine is an efficient, cost-effective tool for producing high-quality threads on fasteners, offering benefits such as stronger threads, better surface finish, and material conservation. Proper maintenance and operator training are essential for optimal performance.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about thread rolling machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is thread rolling?
Thread rolling is a cold-forming process where threads are formed onto a workpiece by pressing it between hardened steel dies. It improves thread strength and surface finish.
2. Why source thread rolling machines from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a wide variety of machines, and advanced manufacturing capabilities. Chinese suppliers can provide cost-effective solutions without sacrificing quality.
3. How do I choose the right thread rolling machine supplier in China?
Look for established manufacturers with certifications (e.g., ISO), positive customer reviews, and robust after-sales support. Visiting the factory for a firsthand assessment is advisable.
4. What types of thread rolling machines are available?
There are mainly two types: flat die thread rolling machines for small to medium-sized threads, and cylindrical die thread rolling machines for larger, more complex threads.
5. What should I consider regarding machine specifications?
Consider thread size range, rolling speed, power consumption, machine dimensions, and compatibility with your material types and production volume.
6. Are Chinese thread rolling machines reliable?
Yes, many Chinese manufacturers produce high-quality and durable machines. It’s crucial to verify the supplier’s reputation and inspect sample machines to ensure reliability.
7. What is the average lead time for a thread rolling machine from China?
Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the supplier and machine customization requirements.
8. What about shipping and import duties?
Shipping costs depend on machine size and destination. Import duties vary by country. Consulting a freight forwarder can provide accurate estimations for cost and time.
9. Is technical support available after purchase?
Reputable Chinese suppliers offer technical support, including remote assistance, manuals, spare parts, and sometimes on-site service through local agents.
10. How do I ensure quality control before shipment?
Request pre-shipment inspections, third-party audits, and testing protocols. Quality assurance can be bolstered by clear communication of specifications and standards with the supplier.
By addressing these FAQs, potential buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing thread rolling machines from China.